Loading

2025
Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-30
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Integrating mental healthcare into primary healthcare services: Saudi Arabia progress and achievements (1995–2022)
Abdullah Dukhail Al-Khathami , Laifa Saleh Alharbi , Shaker Abdulaziz Alomari , Abdulrahman Abdullah Alqahtani , Deemah Saad Alfadhli
Mental health disorders affect approximately 60% of patients in primary healthcare (PHC) settings, yet conditions like depression and anxiety often remain undiagnosed due to limited provider training. Saudi Arabia has progressively integrated mental health into PHC services, aligning with the WHO’s mhGAP Plan (2013–2030). This study examines these efforts and introduces the Five-Step Model (AlKhathami Approach) as a framework to enhance mental health care delivery.
Curr Res Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.46439/Psychiatry.5.035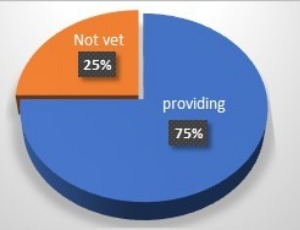
Clinical reasoning, medical error, and treatment failure
H. Paul Putman III
Cognitive error, innate to all human reasoning, commonly interferes with clinical success. Psychiatric education and practice skew toward the lowest levels of clinical reasoning, leaving practitioners unprepared to solve many of the increasingly complex clinical dilemmas we face. Despite our self-confidence, around half of current treatment attempts result in suboptimal outcomes or overt treatment failures, increasingly mislabeled “treatment resistance.
Curr Res Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 5, Issue 1, p9-16 | DOI: 10.46439/Psychiatry.5.036
A commentary on methodological considerations for studying the psychological impact of social media
Tom Grimes, Kristen Sussman
Long-running debates over the psychological effects of media violence have exposed significant methodological problems embedded within 40-plus years of research. Parallel concerns have now emerged within contemporary social media research. This commentary expands on the observations recently published by Grimes and Lasser (2025) to show how social media scholars are in similar danger of relying too much on inconsistent operationalizations of key constructs and insufficient attention to individual differences among people who consume media.
Curr Res Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 5, Issue 1, p17-21 | DOI: 10.46439/Psychiatry.5.037
From complexity to clarity: The Umbrella Collaboration® and the future of tertiary evidence synthesis in psychiatry
Beltran Carrillo
The exponential growth in the publication of systematic reviews and meta-analyses (SRs/MAs) over the past two decades has radically transformed the landscape of scientific evidence.
Curr Res Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 5, Issue 1, p22-25 | DOI: 10.46439/Psychiatry.5.038
The relationships between hopelessness, helplessness, haplessness and their effects on psychological well being
Sevginar Vatan, David Lester
Hopelessness, helplessness and haplessness are concepts that are conceptually related to one another. In empirical studies, it is found that these concepts are associated with psychopathological traits, including suicidal ideation, as etiological or sustaining factors. It is suggested that studying these thoughts in clients is important for both prevention and treatment studies.
Curr Res Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 5, Issue 1, p26-30 | DOI: 10.46439/Psychiatry.5.039
Recommended Articles
Can language use in social media help in the treatment of severe mental illness?
Nationally, patients experience multiple barriers to receiving mental health care. In many parts of the US, access to mental health providers is limited. For many patients, getting an appointment with a psychiatrist is difficult and often takes weeks. When patients are able to schedule appointments with a psychiatrist, the visits are usually short and aimed mostly at prescribing medications. For patients with serious conditions like schizophrenia or major depression, the consequences of unattended emergence or worsening of symptoms during those time intervals can be severe.
Uncertainty and mentalizing in view of COVID19
In the face of the COVID-19 pandemic, the masks we wear, quite paradoxically, are an expression of our shared experience of isolation, as much as they are a signal of our caring for each other. We have not only been fighting this emergency but are struggling with consequences. These days Vienna is additionally shaken by a presumably terrorist shooting in the last hours before lockdown.
The role of psychiatric disorders and gender among patients with severe obesity
This is a comment on the article “Gender-related patterns of psychiatric disorder clustering among bariatric surgery candidates: A latent class analysis”, by Duarte-Guerra et al., J. Affect. Disord. 2018. The study applied multivariate statistical analysis – the latent class analysis – to determine clusters of patients with obesity III (n = 393), based on their psychiatric diagnosis. Key findings indicated that most of patients were symptomatic and presented comorbid patterns of psychiatric disorders before undertaking surgery. The patterns were mixed anxiety-bipolar disorders (47%) and anxiety-depression (up to 25%).
Cancer-related anxiety, COVID-19, and the oncologist: the formation of a ‘Balint’ process group
The management of anxiety and distress in patients with cancer is stressful for the oncology clinicians who treat them. Unfortunately, psychosocial care for patients with cancer is not universally available or standardized. Referrals from oncology services to psychological serves are often not initiated early enough, may not be encouraged from medicine or surgical services, and are subsequently foregone or patients do not follow up beyond a single appointment.
What can reasonably be expected from early intervention for autism?
This commentary addresses three issues raised by a recently published multisite clinical trial designed to test replicability of a comprehensive intervention, the Early Start Denver Model, designed for very young children with ASD.
First, intervention targets and measures may focus on the behavioral symptoms of a condition or on downstream effects of the condition. This study focused on downstream effects on children’s development in those areas most affected by ASD: language and IQ, because of the relationships between standardized scores of language and IQ in childhood on outcomes later in life.
Psychiatric comorbidities of median arcuate ligament syndrome: Indications for intervention across the lifespan
Median Arcuate Ligament Syndrome (MALS) is the terminology that describes the vascular compression of the celiac artery, which at times is associated with numerous gastrointestinal symptoms. Most notably, patients with MALS present with epigastric pain, often worsening post-prandially, and weight loss. Despite the often-striking symptom presentation of patients, significant hesitation in treating MALS is present, partially due to the lack of understanding of the pathophysiological mechanism of pain in this condition.
Commentary on: A comparison of the prevalence of psychiatric disorders in Puerto Rico with the United States and the Puerto Rican population of the United States
The manuscript compares the adjusted rates of psychiatric disorders among three population based representative samples of island and mainland Puerto Ricans, as well as the US population. Results showed similar rates of overall psychiatric disorder between island Puerto Ricans and the US population, but higher rates of substance use disorders (SUD) in Puerto Rico (PR). A prior comparison between island and mainland rates carried almost 30 years ago had shown similar overall rates of psychiatric disorders between the US and the island.
Everything the practicing psychiatrist should know about symptomatic hyponatremia – and then some
Defined as a serum sodium (Na+) concentration below 135 mmol/L, hyponatremia is likely the most prevalent and clinically significant electrolyte abnormality in medical practice, most recently associated with an adverse COVID-19 outcome. A working knowledge of how this disorder presents in mental health practice is advantageous for psychiatrists. Most often arising as an adverse reaction to psychopharmacological agents including antidepressants and mood stabilizers, hyponatremia usually develops slowly, leading to subtle symptoms such as lethargy and confusion.
The epidemiology of mental disorders in very early childhood: What can we learn from recent research?
The significance of the first years of living in determining mental health later in life has been acknowledged since the early psychoanalytic approaches to the understanding of mental illness delivered by Sigmund and Anna Freud, Rene Spitz and John Bowlby. Empirical research since then has documented the early childhood origin of most mental disorders seen in older children and adolescents. Birth cohort studies have provided evidence on the interplay of genes and environment from early stages of prenatal life and the longterm influences of pre-and perinatal risk factors.
Suicide Prevention in Brazil: General concepts and the Experience of a Life Support Program (PRAVIDA)
This paper has several objectives: First, it reviews the concept of suicide; Second, it presents epidemiologic data about suicide and suicidal behavior in the world, in Brazil and in Fortaleza – capital of Ceará - the second ranking city in suicide deaths in Brazil losing only to Sao Paulo which is 5 times bigger; Third, it describes the most common risk factors for suicide; Fourth, it shows interventions to reduce the risk of suicide; Fifth, it proposes useful questions to identify a person with suicide risk; Finally, it presents the PRAVIDA Program.
The tip of the iceberg: Commentary on mental illness and substance use as distal and proximal variables
Given the widespread taboo surrounding suicide, risk of suicide may become even more difficult to face for clinicians, when linked with substance use, another stigmatized behavior. In this commentary, we shall argue that even though suicides are to be taken seriously, we must also be aware of the rarity of completed suicide, and be careful not to exaggerate risks associated with substance use. The primary risk of suicide appears to occur when a range of distal and proximal factors converge.
Technology-based mental health treatment and the impact on the therapeutic alliance update and commentary: How COVID-19 changed how we think about telemental health
Our previous article, Technology-Based Mental Health Treatment and the Impact on the Therapeutic Alliance, explored factors that influence the therapeutic alliance when treatment was delivered via telemental health, such as video conferencing or telephone. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of telemental health became a necessity rather than simply a preference. In this commentary, we explore the use of telemental health in direct response to COVID-19 social distancing orders and offer updated suggestions around best practices for building and maintaining alliance in technology-based mental health treatments.
The tragic rollercoaster of Italian nursing homes during the COVID-19 pandemic
Nursing homes, neglected for too long by government administrations, have paid a very high tribute to the lack of protective measures and social distancing that COVID-19 has imposed. To date, it has been calculated that almost a fifth of all residents in nursing home in northern Italy have died due to COVID-19, with a mortality of Lombardy nursing homes varying between 10% and 50% of all residents. In some cases, 3-4 guests of a single home died in a single day.
Active involvement of patient representatives in research: roles, tasks, and benefits in a pilot intervention study
Patient involvement in research and development has been increasingly applied and studied during the last decades. There is rising consensus that collaboration with patients or their representatives (e.g., parents, family members, partners) in co-developing new treatment interventions and participating in treatment studies is beneficial for patients, researchers, and society at large. In studying the feasibility of Tackle your Tics, an innovative treatment program for children with tic disorders, patient representatives played a unique role throughout the research process, performing multiple important tasks from start (co-designing the study, obtaining a grant, developing and leading workshops and parent meetings) to finish (interpretation of the data, providing feedback to the article, giving congress oral presentations).
Post-trauma brain: A commentary on functional brain alterations after trauma and implications to post-traumatic stress disorder
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a highly debilitating psychiatric condition that develops in a subset of individuals following a traumatic event, such as a threat of death, serious injury or sexual assault. Over the past two decades, substantial body of research has focused on key neural regions and circuits that play a role in pathogenesis and maintenance of PTSD symptoms. More specifically, hyper-activation of amygdala, insula, and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, as well as hypo-activation in ventral medial prefrontal cortex and altered function of hippocampus have been repeatedly reported.
Being inspired: What we have learned about picky eating in childhood from using questionnaires on feeding practices and behaviors in a longitudinal birth cohort
We have made an extensive study of the development of picky eating behavior in childhood, and its effects on diet and growth, using data from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Mothers were recruited during pregnancy in 1991/2 and they and their child have been followed using questionnaires plus measurements at research clinics from infancy onwards. A wealth of information was collected prospectively about feeding the child in their first 1000 days and beyond. Questions were asked at regular intervals about difficulties parents had in feeding their child and how they responded to these difficulties.
Self-evaluation and the personality disorders
In all 502 adults rated their attractiveness, health, IQ and EQ and completed an established measure of the personality disorders (PDs). The self-ratings were highly inter-correlated and a total self-evaluation score was computed. The self-rated score was correlated with the 14 Personality Disorders showing ten significant, mostly negative, correlations. A regression with self-ratings as the criterion variable showed three PDs positively (Histrionic, Narcissistic and Obsessive Compulsive) and two negatively (Depressive and Schizoid) associated with the positive self-evaluation.
Electroconvulsive therapy in the elderly: An update
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) remains one of the most effective treatments for depression, catatonia and other conditions. Additionally, it appears to be particularly efficacious in the elderly population. Furthermore, since ‘Electroconvulsive Therapy in Geriatric Psychiatry: A Selective Review’ was previously published there has been additional evidence of not just ECT efficacy in this subset of the population, but also its safety. This commentary will aim to inform others about advances in this uniquely effective treatment consistent with the latest treatment guidelines and evidence.
Wake up to the benefits of timely management of sleep problems in toddlers with Williams Syndrome
This commentary relates to Gwilliam, Joyce, and Dimitriou and their longitudinal work on sleep problems in toddlers with Williams syndrome (WS). WS is a rare and sporadic genetic disorder caused by a small deletion of genes on chromosome 7. Individuals with WS experience a range of medical and developmental difficulties and sleep disturbances are highly prevalent. The aim, here, is to address why early identification of sleep problems could be beneficial for children with WS and their families.
Negative self-referential emotions and mental health in youth: The importance of self-criticism
There are many measures available that survey positive and negative emotional indicators of wellbeing in children and adolescents. In fact, our work identifies 98 measures, designed to measure negative self-emotions in youth populations. However, only eight of these measures incorporated a negative self-referential emotion item or subscale; that is, an item, or items, where the subject and the reference are directed toward the self in the final measure. This is important because negative self-referential emotions, especially self-criticism, are key antecedents of mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression and eating disorders.
