Loading
Journal of Biomed Research
ISSN: 2693-5910


Giuseppe Lanza
Senior University Researcher
University of Catania, Italy
Featured Article
Non-invasive optical brain pulse monitoring: Experience from the first 195 patients

Featured Article
CRISPR-Cas systems: A revolution in genome editing and its diverse applications
Featured Article
Modeling of psychological time cognition with Human Language based Consciousness model
About this Journal
Journal of Biomed Research is an international scientific peer reviewed journal having a broad scope of incorporating both clinical and basic science topics of medicine in health and diseases. The journal publishes original research articles, reviews, editorials, case reports, short communications, commentary etc. in the field of medicine and its subspecialties.
Articles
Non-invasive optical brain pulse monitoring: Experience from the first 195 patients
Continuous, non-invasive optical brain pulse monitoring (OBPM; Cyban Pty. Ltd., Melbourne, Australia) represents a significant advancement in the field of neurological monitoring. OBP monitoring uses red and infrared light sources to capture cardiac and respiratory waves from brain pulse waveforms, which reflect changes in both brain oxygen levels and brain movement.
Blinding uveitis induced by secukinumab: A case-based review
Secukinumab, a human monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-17A (IL-17A), is widely used for treating immunoinflammatory disorders. While effective, drug-induced uveitis (DIU) is a rare but serious adverse effect associated with biologic medications like TNF-α inhibitors and more recently, IL-17 inhibitors such as secukinumab. We present a case of posterior uveitis in a 42-year-old male with AS who developed ocular symptoms two years after starting secukinumab.
Role of cellular, acellular and matrix-like products (CAMPs) in wound bed preparation in diabetic foot
Diabetic foot ulcers account for 70-80% of all ulcer cases, with this proportion rising to 21–27% in developing countries. The associated mortality rate ranges from 3.75% to 58.8%.
Clinical insights and research needs in atezolizumab induced neurotoxicity
In recent years, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed the scope of cancer treatment. Atezolizumab, is a humanized monoclonal antibody that specifically targets programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) to block its interaction with PD-1 and B7-1 receptors, thereby reinstating T cell response.
Skin necrosis following dobutamine extravasation
Dobutamine is a synthetic catecholamine with activity on both alpha-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptors. It is used intravenously as an inotropic agent for short term treatment of heart failure. Dobutamine side effects involve usually cardiovascular system. Cutaneous side effects such as inflammation in the administration site following accidental extravasation could occur. Skin necrosis from intravenous soft tissue infiltration is a rare but serious complication of intravenous therapy. Herein we report a rare case of a local skin necrosis in dobutamine infusion site.
The pathogenetic roles of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase, xanthine oxidase and hyaluronidase in inflammatory diseases: A review
Inflammation is a complex biological process essential for protecting the body from harmful stimuli. However, dysregulated or chronic inflammation can contribute to the pathogenesis of various diseases, including asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. Pro-inflammatory enzymes, such as arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase (A5-LOX), xanthine oxidase, and hyaluronidase, play key roles in the initiation, progression, and resolution of inflammation.
Half-time hydration and re-warm-up strategies for football players
We have read the commentary by Fernandes H (2024) with interest on a mini-review entitled Hydration Strategies for Elite Soccer Players. Given the popularity of the game globally and the busy tournament schedules without a break for the soccer players, their fitness remains a primary concern for the players and their coaches alike. Hence, elite soccer performance is crucial and depends on physiological readiness, technical skills, and tactical execution.
Interaction effects of FTO polymorphisms on post-surgery weight, and post-BMI after bariatric surgery
Obesity is associated with increased morbidity and mortality and is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Therefore, preventing and treating obesity has become a major public health goal. Bariatric surgery is considered the intervention most effective for patients with severe obesity (BMI ≥40 kg/m2 or ≥35 kg/m2) with comorbidities and to maintain weight loss and glycemic control in the long-term. In addition, improvement or long-term remission of comorbidities such as T2D, hypertension, and dyslipidemia after bariatric surgery has been reported.
Knowledge, attitude and practice of life style modification in the management of hypertension
Hypertension remains as one of the most important public health challenges worldwide because of the associated morbidity, mortality, and the cost to the society. Despite the availability of safe and effective antihypertensive medications and the existence of clear treatment guidelines, hypertension is still inadequately controlled in a large proportion of patients worldwide. Unawareness of lifestyle modifications, and failure to apply these were one of the identified patient-related barriers to blood pressure control.
Prevalence of Equine Strongyloidiasis and associated risk factors in Guder, Ethiopia
Equines, which include horses, donkeys, mules, and zebras, are large hoofed mammals characterized by long legs, strong hooves, and a diet primarily composed of grasses. These animals play an important role in ecosystems and have been closely connected to human societies throughout history.
Risk factors of stroke: A cross cut survey study on the basis of social class
Stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide and the leading cause of long-term disability. A worldwide study based on vital record and data imputation shows that per year 15 million people faces the event ‘stroke’ which causes 5 million deaths and a further 5 million patients living with permanent cognitive and physical disability.
Prevalence of gastrointestinal nematodes and associated risk factors of exotic chicken in selected farm of poultry in and around Ambo, Ethiopia
Poultry is kept in backyards or commercial production systems in most areas of the world. Compared to a number of other livestock species, fewer social and religious taboos are related to the production, marketing, and consumption of poultry products. For these reasons, poultry products have become one of the most important protein sources for humans throughout the world.
Commentary on the use of the Taguchi method for electrocoagulation optimization in dairy effluent treatment
Dairy industry wastewater, characterized by its high load of organic and inorganic pollutants, continues to pose significant challenges to conventional treatment technologies. Electrocoagulation (EC) has emerged as an effective alternative, but its success depends on the careful optimization of multiple interrelated parameters.
Overview of Fasciolosis: Biological, Epidemiological, and Clinical Perspectives
Fasciolosis (fascioliasis) is an important parasitic disease of both animals and humans, caused by Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica. These liver flukes have a complex life cycle involving freshwater snails as intermediate hosts, with infection occurring through ingestion of metacercariae on contaminated vegetation or water.
Prevalence of Brucellosis in Saudi Arabia: A meta-analysis
Brucellosis is a preventable bacterial illness that is common all over the world and a consistent problem in Saudi Arabia. Understanding the true prevalence of the disease in Saudi Arabia could provide information on how to tackle this health concern.
Comparative analysis of initial outcomes: Magnetic sphincter augmentation versus fundoplication in gastroesophageal reflux disease - A systematic review and meta-analysis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a long-term digestive condition marked by the backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus. The worldwide combined prevalence of GERD was found to be 13.98%. GERD remains a significant public health problem due to its high global prevalence and potential for severe complications, including esophagitis, strictures, and progression to Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in the modern therapeutic era: A critical synthesis of epidemiology, diagnostics, and policy implications with regional context from Korea
This review aims to synthesize contemporary evidence on progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), a rare, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system caused by reactivation of the John Cunningham virus (JCV) in immunocompromised individuals. Since its initial description in 1958, PML has evolved from being predominantly associated with hematological malignancies to a multifaceted opportunistic infection seen in HIV/AIDS, autoimmune disorders, transplantation medicine, and in patients receiving monoclonal antibody therapies such as natalizumab.
Non-invasive optical brain pulse monitoring: Experience from the first 195 patients
Continuous, non-invasive optical brain pulse monitoring (OBPM; Cyban Pty. Ltd., Melbourne, Australia) represents a significant advancement in the field of neurological monitoring. OBP monitoring uses red and infrared light sources to capture cardiac and respiratory waves from brain pulse waveforms, which reflect changes in both brain oxygen levels and brain movement.
Digital workflow for high-risk, low-volume procedure simulation
For thousands of years, simulations have been used by doctors for training before performing high-risk procedures on patients. Due to changes in healthcare and academic environments, as well as the introduction of new technologies, we have seen an increase in the use of simulation for education and competency assessment.
Human and Earth evolution through CO2: Perspective for climate crisis
Although human civilization has developed through genomic evolution, including its fingernail-functional cooperation, the daily lives of humans have resulted in a significant amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) being released into the atmosphere since the Industrial Revolution, which started almost 200 years ago. Recently, climate change has been documented to have spread globally.
A longing for flawless awakening from general anesthesia
Anesthetic recovery can be a critical period since neurocognitive problems such as agitation and delirium are often seen during the early recovery phase. We recently demonstrated that an α2-adrenergic agonist dexmedetomidine-induced unconsciousness and accompanying brain dynamics changes were completely and instantly reversed by the α2-adrenergic antagonist in the nonhuman primate model.
Syndrome similar to Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia (FHH) produced in mice deleted of the gene encoding transient receptor potential canonical channel 1 (TRPC1)
We recently found that global deletion of TRPC1 produces phenotypes similar to FHH. These TRPC1 null mice have mildly elevated serum Ca in both fasted and unfasted conditions from 3.5 through 21.5 months of age, and inappropriately elevated parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels. They also have hypocalciuria, similar to FHH patients.
Cell therapies for neonatal encephalopathy: On the question of dose, route of administration, timing, and single versus multiple doses
The optimal range of cell dose, route of administration, and timing for the treatement of neonatal encephalopathy are not known. However, it is not practical to systematically interrogate all combinations of these variables in animal models to define the optimal cell therapy protocol. Despite this limitation, a number of trends are present in the literature that should be considered when designing future clinical and preclinical trials.
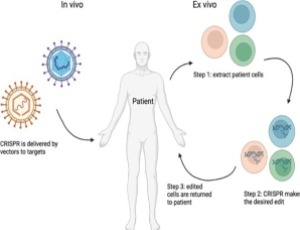
CRISPR-Cas systems: A revolution in genome editing and its diverse applications
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) Cas (CRISPR6 associated protein) system is an advanced adaptive immune system found in prokaryotes. First discovered in1987, CRISPR Cas has revolutionized genetic research in the past two decades. CRISPR-Cas9 the most widespread system enables precise gene editing by creating double strand breaks.
A longing for flawless awakening from general anesthesia
Anesthetic recovery can be a critical period since neurocognitive problems such as agitation and delirium are often seen during the early recovery phase. We recently demonstrated that an α2-adrenergic agonist dexmedetomidine-induced unconsciousness and accompanying brain dynamics changes were completely and instantly reversed by the α2-adrenergic antagonist in the nonhuman primate model.
Syndrome similar to Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia (FHH) produced in mice deleted of the gene encoding transient receptor potential canonical channel 1 (TRPC1)
We recently found that global deletion of TRPC1 produces phenotypes similar to FHH. These TRPC1 null mice have mildly elevated serum Ca in both fasted and unfasted conditions from 3.5 through 21.5 months of age, and inappropriately elevated parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels. They also have hypocalciuria, similar to FHH patients.
Commentary: SARS-CoV-2 new variants: Characteristic features and impact on the efficacy of different vaccines
A recent article published by Abbas et al. in the Journal of Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy systematically revealed about the vaccines developed against the recent pandemic agents SARS-CoV-2 and its variants [1]. The authors insightfully provided an overview on the distinct features of the SARS-CoV-2 new variants, the associated mortality rate, hospitalization, re-infection and finally the efficacy of different vaccines.
Attaining highest honors: A study proposal for the medical student’s honors bar expectancy and values changes within medical education
Expectancy-Value theory was originally proposed by John William Atkinson in the 1950s and 60s as an attempt to understand different behaviors of students including persistence, decision making when given multiple opportunities to choose from, and the effort of striving for success.
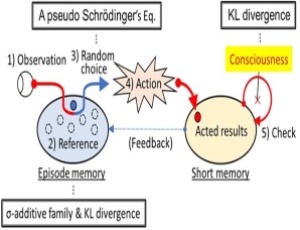
Modeling of psychological time cognition with Human Language based Consciousness model
This paper interprets subjective psychological time in a model of consciousness called the HLbC model proposed by the authors. Time has an objective physical time and a subjective psychological time. Subjective psychological time is thought to vary in its flow depending on the individual and the situation. For this explanation, this paper introduces surreal numbers into the perception of subjective psychological time.
Digital workflow for high-risk, low-volume procedure simulation
For thousands of years, simulations have been used by doctors for training before performing high-risk procedures on patients. Due to changes in healthcare and academic environments, as well as the introduction of new technologies, we have seen an increase in the use of simulation for education and competency assessment.
Human and Earth evolution through CO2: Perspective for climate crisis
Although human civilization has developed through genomic evolution, including its fingernail-functional cooperation, the daily lives of humans have resulted in a significant amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) being released into the atmosphere since the Industrial Revolution, which started almost 200 years ago. Recently, climate change has been documented to have spread globally.
Blending into the crowd: electrophysiological evidence of gestalt perception of a human dyad: extended discussion and theoretical viewpoint
In this commentary, we provide further discussion and interpretation of a recent article entitled “Blending into the Crowd: Electrophysiological Evidence of Gestalt Perception of a Human Dyad”, published one year ago by the first author of the present commentary. Firstly, drawing a parallel between the experiment described in the above article and another closely comparable experimental study, we propose that the neural integration process evidenced when seeing two human shapes close in space is a marker of the categorization of a stimulus as a group of humans (two here) represented as an entity per se.
Cell therapies for neonatal encephalopathy: On the question of dose, route of administration, timing, and single versus multiple doses
The optimal range of cell dose, route of administration, and timing for the treatement of neonatal encephalopathy are not known. However, it is not practical to systematically interrogate all combinations of these variables in animal models to define the optimal cell therapy protocol. Despite this limitation, a number of trends are present in the literature that should be considered when designing future clinical and preclinical trials.
Commentary: SARS-CoV-2 new variants: Characteristic features and impact on the efficacy of different vaccines
A recent article published by Abbas et al. in the Journal of Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy systematically revealed about the vaccines developed against the recent pandemic agents SARS-CoV-2 and its variants [1]. The authors insightfully provided an overview on the distinct features of the SARS-CoV-2 new variants, the associated mortality rate, hospitalization, re-infection and finally the efficacy of different vaccines.

