Loading
Journal of Cancer Biology
ISSN: 2692-7896
Featured Articles
Implications of the USP10-HDAC6 axis in lung cancer - A path to precision medicine
Xiaohong Mary Zhang, Navnath Gavande, Prahlad Parajuli, Gerold Bepler
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death among both men and women in the United States. Because lung cancer is genetically heterogeneous, tailored therapy alone or in combination with chemotherapy would increase patient overall survival as compared with the one-size-fits-all chemotherapy. TP53-mutant lung cancer accounts for more than half of all lung cancer cases and is oftentimes more aggressive and resistant to chemotherapy. Directly targeting mutant p53 has not yet been successful, so identification of novel therapy targets and biomarkers in the TP53-mutant lung cancer is urgently needed to increase the overall survival in this subgroup.
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.015
Cyclin A2 and Ki-67 proliferation markers could be used to identify tumors with poor prognosis in African American women with breast cancer
Desta Beyene, Tammey Naab, Victor Apprey, Luisel Ricks-Santi, Ashwini Esnakula, Mustafa Qasim, Matthew George, Karen G Minoza, Robert L Copeland Jr, Carolyn Broome, Yasmine Kanaan
Eight protein biomarkers (ER, PR, HER2, Cyclin A2, Cytokeratin 5, Vimentin, Bcl2, and Ki-67) were evaluated using tissue microarrays (TMAs) and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The IHC results from TMAs were analyzed by both supervised and unsupervised clustering methods. The predictive clusters for the supervised and unsupervised methods were compared for agreement with the empirical classification. Kappa values were used to determine the overall percent correct clusters and agreement between specific clusters.
J Cancer Biol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 1, p3-16 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.4.048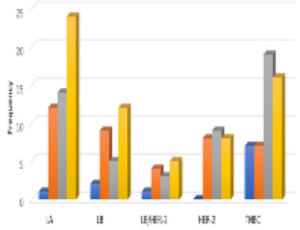
COVID-19 in patients with and without cancer: Examining differences in patient characteristics and outcomes
Nihal E. Mohamed, Emma KT. Benn, Varuna Astha, Qainat N. Shah, Yasmine Gharib, Holden E. Kata, Heather Honore-Goltz, Zachary Dovey, Natasha Kyprianou, Ashutosh K. Tewari
This study examines differences between patients with and without cancer in patient demographic and clinical characteristics and COVID-19 mortality and discusses the implications of these differences in relation to existing cancer disparities and COVID-19 vulnerabilities. Data was collected as a part of a retrospective study on a cohort of COVID-19 positive patients across Mount Sinai Health System from March 28, 2020 to April 26, 2020. Descriptive, comparative, and regression analyses were applied to examine differences between patients with and without cancer in demographic and clinical characteristics and COVID-19 mortality and whether cancer status predicts COVID-19 mortality controlling for these covariates using SAS 9.4. Results showed that, of 4641 patients who tested positive for COVID-19, 5.1% (N=236) had cancer.
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p25-32 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.019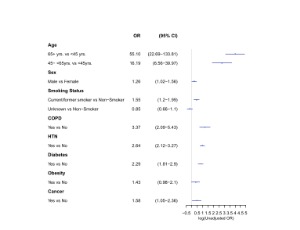
Changing the landscape of non-small cell lung cancer disparities
Joab O. Odera, Muthana Al Abo, Steven R. Patierno, Jeffrey M. Clarke, Jennifer A. Freedman
In the United States, lung and bronchus cancers are the second most common types of cancer and are responsible for the largest number of deaths from cancer, with African Americans suffering disproportionately from lung and bronchus cancers. This disparity likely results from a complex interplay among social, psycho-social, lifestyle, environmental, health system, and biological determinants of health.
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p33-38 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.020
Challenges in the humanized mouse model for cancer: A commentary
Eric Ramirez-Salazar, Meenhard Herlyn, Rajasekharan Somasundaram
The complexity of the tumor microenvironment has been a challenge for understanding the mechanisms of therapy resistance. The development of improved animal models that closely mimic human disease is key for understanding and treating diseases. Recently, a new humanized mouse model has been developed that enables the study of human immune cells in tumor host-cell interactions
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p42-43 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.022
Chromatin dynamics: Nucleosome occupancy and sensitivity as determinants of gene expression and cell fate
Jane Benoit, Mahdi Khadem Sheikhbahaei, Jonathan Dennis
The nucleosome, consisting of ~150bp of DNA wrapped around a core histone octamer, is a regulator of nuclear events that contributes to gene expression and cell fate. Nucleosome organization at promoters and their associated remodeling events are important regulators of access to the genome. Occupancy alone, however, is not the only nucleosomal characteristic that plays a role in genome regulation. Nucleosomes at the transcription start sites (TSSs) of genes show differential sensitivity to micrococcal nuclease (MNase) and this differential sensitivity is linked to transcription and regulatory factor binding events.
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p51-55 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.024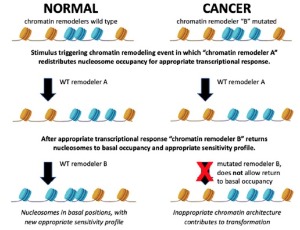
Can electronic-cigarette vaping cause cancer?
Moon-shong Tang, PhD, Yen-Len Tang, MD
The relative safety of E-cigarette (E-cig) has been an emerging topic in the public domain as well as the medical and scientific communities as vaping associated health problems arose. While there were significant amounts of intelligent discussions and opinions on the benefits and deleterious effects of E-cig vaping, there is a lack of solid evidence of the fundamental biochemical and biological effects of E-cig aerosol and nicotine.
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p68-70 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.027
Immuno-oncologic care during COVID-19: Challenges and opportunities for improving clinical care and investigation
Kristen Spencer, Eric A. Singer, Eugenia Girda
Cancer care has been greatly impacted during the COVID-19 pandemic. The number of cases and deaths caused by the COVID-19 pandemic continues to escalate throughout the United States and the world. Worldwide, over 150 million people have been diagnosed with the coronavirus and more than 3 million have died.
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p75-82 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.029
Breaking malignant nuclei as a non-mitotic mechanism of taxol/paclitaxel
Elizabeth R. Smith, Xiang-Xi Xu
Discovered in a large-scale screening of natural plant chemicals, Taxol/paclitaxel and the taxane family of compounds are surprisingly successful anti-cancer drugs, used in treatment of the majority of solid tumors, and especially suitable for metastatic and recurrent cancer. Paclitaxel is often used in combination with platinum agents and is administrated in a dose dense regimen to treat recurrent cancer.
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 4, p86-93 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.031
PAK1 and PAK4 as therapeutic targets for Ewing sarcoma: a commentary
Sydney E. Parks, Jason T. Yustein
Ewing sarcoma (ES) is an aggressive pediatric bone tumor that is prone to metastasis. Due to low five-year survival rates and limited therapeutic options for metastatic disease, there is a dire clinical need for improved ES treatments. Targeting p21-activated kinases (PAKs) may be key. PAK1 and PAK4 are associated with aggressive ES and poor patient outcomes, although their molecular mechanisms remain largely uncharacterized in this disease.
J Cancer Biol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 4, p94-97 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.2.032
