Loading

2025
Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-107
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with pre-existing autoimmune disease
Wint Yan Aung, MD, Margaret Locke, Adit Singhal, MD, Nagashree Seetharamu, MD
The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) targeting CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 pathways has revolutionized cancer treatment with significantly improved outcomes across a spectrum of cancers [1,2]. Although ICI therapy offers significant clinical benefits, these treatments can also lead to various immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that may negatively impact patient outcomes. Although the precise mechanism of irAE is not fully understood, they demonstrate many clinical features similar to autoimmune diseases. IRAEs are thought to result from bystander effects of activated T-cells, cross-reactivity between tumor and host tissues, and the role of the gut microbiome in immune activation [3].
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.068
Advances in glyconanotechnology based biomedical applications
Divya Kamath, Stefan H. Bossmann
There is an emerging awareness in cancer biology that glycobiology plays a significant, if not decisive role in oncogenesis, tumor survival, and proliferation. The human glycome is even more complex than the human genome, because glycans are synthesized as secondary gene products by sequentially acting glycosidases and glycosyltransferases. Glycans act as a communication system within the organism and between different organisms.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p4-9 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.069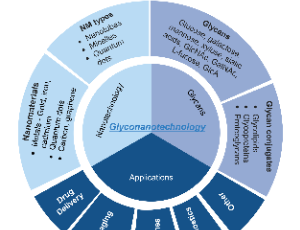
Mechanisms of cancer cell rescue against pancreatic cancer therapeutics: Intrinsic and acquired resistance
Jeevan Ghosalkar, Vinay Sonawane, Kalpana Joshi
Pancreatic Cancer (PC) with dismal prognosis poses a significant challenge to healthcare systems worldwide. PC is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality globally and is projected to surpass lung cancer as the second foremost cause by 2030. The poor prognosis associated with PC is primarily due to the low rate of early detection, rapid progression, and limited treatment options. Chemotherapy remains a cornerstone of treatment for PC in all stages of disease.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p10-22 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.070
Cancer stem cells as a biomarker – A mini review
Urja Joshi, Dhara Jani, Linz-Buoy George, Hyacinth Highland
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) also known as tumor stem cells (TSCs), are pivotal in cancer development and progression. They can be identified through specific markers and surface proteins (e.g., CD44, CD133) that differ from those on non-CSC tumor cells. As well high CSC levels often correlate with poor prognosis, aggressive disease, and resistance to conventional therapies. CSCs are more resistant to standard treatments like chemotherapy and radiation, leading to relapse and metastasis.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p23-33 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.071
Nuclear mTORC2 and its emerging role in gene regulation
Moinuddin, Narayan Kumar, Smrati Bhadauria
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), a critical regulator of cell growth, metabolism, survival, and actin-cytoskeletal organization, is primarily recognized for its cytoplasmic functions. However, emerging evidence suggests that the mTOR and its constituent partners also localize to the nucleus, where it may play distinct roles in gene expression regulation, chromatin remodeling, and transcriptional control. This review highlights the evolving understanding of nmTORC2 (nuclear mTORC2), with a particular focus on its composition, functional implications, and relevance in cancer biology.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p34-46 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.072
Effectiveness of comprehensive nursing intervention on alleviating postoperative fatigue and anxiety in patients with oral cancer
Sukanta Nath, Khemchand Falwaria, Shiromani Debbarma, Matrujyoti Pattnaik, Ankita Debnath
Postoperative functional impairments are common in patients with oral cancer following surgery. Furthermore, these patients frequently experience fatigue and anxiety, which are strongly linked to a lower quality of life (QOL). The goal of our study was to investigate the effectiveness of comprehensive nursing intervention on alleviating postoperative fatigue and anxiety in patients with oral cancer.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p47-54 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.073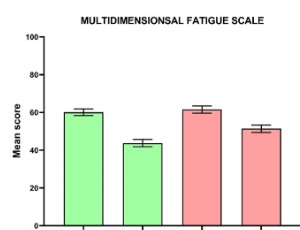
Targeting m6A in cancer – new prospective
Grossmann L.D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S
The field of mRNA modifications has rapidly developed over the last years, outlining a new realm of gene expression regulation that appears to play a major role in health and disease states including cancer. Considering the information regarding chemical modifications of DNA and proteins, decades of research proved beyond any doubt that chemical modifications affect chromatin structure as well as enzymatic activity.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p55-63 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.074
Oncogenic specificity in nevus and melanoma formation
Konrad Kaminiow, Stephen M Ostrowski, David E Fisher
There is striking clinical, histological, and molecular diversity observed across melanocytic tumors. Activating mutations in BRAF and NRAS are well-established initiators of benign melanocytic nevi and melanoma. However, accumulating evidence reveals that the biological outcome after oncogene activation is dependent on cellular state differences that vary by anatomic site, developmental timing, and cell of origin.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p64-70 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.075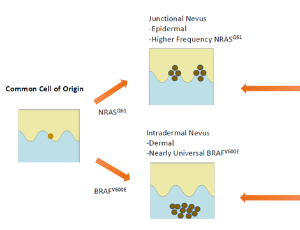
Advances in the understanding of health disparities in the United States Hispanic population
Asma Pinkey, Masuma Anzuman, Mrudang Desai, Anna M. Eiring
Health disparities have become a major concern for global public health, disproportionately affecting minority and underserved populations throughout the United States (U.S.). Hispanics make up the fastest-growing minority group in the U.S., and they often experience significant health disparities when it comes to chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. These disparities are likely driven by a confluence of socioeconomic disadvantages, structural inequities, environmental exposures, and cultural barriers.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p71-75 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.076
Thyroid cancer-tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) spatial transcriptomics reveals novel players
Shafiya Imtiaz Rafiqi, DVM, PhD, Juan Carlos Jaume, MD
Thyroid cancer (TC) encompasses several pathological types, notably papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), follicular thyroid cancer (FTC), medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC). While PTC accounts for the most common type, ATC, despite representing only 1–2% of all TC cases, is recognized as the most lethal and treatment-resistant endocrine malignancy. Despite sharing a common cellular origin, these two subtypes differ markedly in their clinical trajectories, response to therapy, and immune profiles.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p76-81 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.077
Bridging cancer and neurodegenerative disease: Drug repositioning through cheminformatic, bioinformatic, and systems biomedicine approaches
Hui-Heng Lin, Koken Hirose, Yifan Zhu
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as the Alzheimer and the Parkinson's, currently lack effective pharmacotherapies. They are posing a significant global health threat, and it is urgent to discover and develop effective pharmacotherapies for patients. However, due to pathogenic mechanisms are poorly understood, the interventional drug clinical trials for neurodegenerative diseases have high failure rates.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p82-90 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.078
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Unleashing Wnts: Wnt ligands fuel cancer spread
Kailey P. Caroland, Jonathan B. Trapani, Ethan Lee, Vivian L. Weiss
Wnt signaling has long been implicated in cancer development, but recent studies have revealed new insights into how Wnt ligands themselves drive metastasis. Currently, research identifies Wnt1, Wnt2, Wnt2b, Wnt3, Wnt3a, Wnt4, Wnt5a, Wnt5b, Wnt6, Wnt8a, Wnt9b, Wnt10a, Wnt10b, and Wnt16 as pro-metastatic Wnt ligands, while Wnt7a, Wnt7b, Wnt8b, Wnt9a, and Wnt11 exhibit conflicting pro- and anti-metastatic roles.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p91-107 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.079
Recommended Articles
Oncogenic specificity in nevus and melanoma formation
There is striking clinical, histological, and molecular diversity observed across melanocytic tumors. Activating mutations in BRAF and NRAS are well-established initiators of benign melanocytic nevi and melanoma. However, accumulating evidence reveals that the biological outcome after oncogene activation is dependent on cellular state differences that vary by anatomic site, developmental timing, and cell of origin.
Correlation of bone marrow morphologic assessment and genetic aberrations in plasma cell myeloma with clinical outcomes
Plasma cell myeloma is a hematopoietic neoplasm with morphologic and genetic heterogeneity. Genetics have been shown to play an important role in risk stratification of plasma cell myeloma however the correlation between genetic aberrations and morphologic features is not well studied. In performing a systematic study of 266 multiple myeloma bone marrow biopsies from 329 patients, we initially investigated the association between bone marrow morphology, conventional cytogenetics, gene expression profiling and gene mutations
CD133 and centrosomes: How CD133 inhibits autophagy and induces the undifferentiated state of cancer cells at centrosomes
CD133 is a transmembrane protein that mainly localizes to the plasma membrane of normal stem cells as well as cancer stem cells, and is widely known as a cancer stem cell marker. CD133 was recently shown to localize in the cytoplasm; however, its transport pathway and functions currently remain unknown.
Role of H3K9 demethylases in DNA doublestrand break repair
H3K9 demethylases can remove the repressive H3K9 methylation marks on histones to alter chromatin structure, gene transcription and epigenetic state of cells. By counteracting the function of H3K9 methyltransferases, H3K9 demethylases have been shown to play an important role in numerous biological processes, including diseases such as cancer.
The Oncogenic Role of ADAR1-Mediated RNA Editing in Thyroid Cancer
A-to-I RNA modifications performed by the adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADAR) protein family are gaining traction as important mechanisms in cancer biology. A-to-I RNA editing changes adenosine to inosine on double stranded RNA, which co-transcriptionally alters transcript sequence and structure. A number of microRNA (miRNA) precursors are known to be edited by the ADARs, which alters the expression and/or function of the mature miRNA.
Machine learning for precision medicine in cancer: Transforming drug discovery and treatment
Machine learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence that uses an algorithm to process the data, retrieve valuable information, learn from it, find a pattern, and make predictions. Manual data analyses suffer from several disadvantages including it is time-consuming and subject to error.
The rising tide of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A review of risk factors, diagnostic challenges, and treatment updates
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PAC) is an aggressive malignancy that is frequently locally invasive or widely metastatic at the time of diagnosis. As such, morbidity and mortality remain extremely high. Despite growing advances in surgical technique and medical management, the incidence and mortality rate are expected to increase over the next two decades.
Implications of the USP10-HDAC6 axis in lung cancer - A path to precision medicine
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death among both men and women in the United States. Because lung cancer is genetically heterogeneous, tailored therapy alone or in combination with chemotherapy would increase patient overall survival as compared with the one-size-fits-all chemotherapy. TP53-mutant lung cancer accounts for more than half of all lung cancer cases and is oftentimes more aggressive and resistant to chemotherapy. Directly targeting mutant p53 has not yet been successful, so identification of novel therapy targets and biomarkers in the TP53-mutant lung cancer is urgently needed to increase the overall survival in this subgroup.
Granular cell tumor (Abrikossoff's tumor) of the tongue: A case report
Granular cell tumor, also known as Abrikossoff’s tumor, is a benign tumor that is relatively rare and is slightly more common in female patients, with a higher prevalence between the fourth and sixth decades of life although it is possible to appear at any age. It can appear in any part of the body but about 45-65% of all the lesions appear in the head or neck areas. Intraoral lesions represent about 70% of these cases.
Sézary's syndrome: Review of the clinical, histomorphological and diagnostic aspects of a rare cutaneous lymphoma
Sézary's Syndrome consists of a rare type of non-Hodgkin cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), being a very aggressive leukemic variant of CTCL. Given its rarity and its ability to mimic other more common diseases, this neoplasm represents a major diagnostic challenge for both clinicians and pathologists.
Perturbation of cellular integrity by nicotine: A major component of e-cigarette smoke
In recent years, the use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) or “vape” in which nicotine is the major component has been dramatically increasing, particularly among teenagers and young adults. This is due to a general perception that e-cigarettes are harmless to use, in particular for the cessation of tobacco smoking. Thus, a better understanding of whether e-cigarettes pose a risk to human health is urgently needed. Nicotine exposure can accelerate malignant growth of cancer cells.
Cryoablation is a safe alternative to surgery for low-risk breast cancer
Cryoablation of breast cancer offers an alternative to surgery for women who are not ideal surgical candidates. It is a minimally invasive procedure that has already had success in fibroadenoma treatment with good tumor reduction and cosmesis. The findings of cryoablation as treatment for early-stage, low-risk breast cancer has been previously discussed in the recently published article ‘Cryoablation: A promising non-operative therapy for low-risk breast cancer’.
Advances in the investigation of the Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) in Colombia during the last 20 years
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) belongs to the family Herperviridae, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, genus Lymphocriptovirus [1]. It is one of the most common human viruses as most people get infected with EBV at some point in their lives. EBV spreads most commonly through bodily fluids, primarily saliva. Although viral DNA has been detected in breast milk and genital secretions [2], the evidence for sexual transmission is extremely limited [3].
COVID-19 in patients with and without cancer: Examining differences in patient characteristics and outcomes
This study examines differences between patients with and without cancer in patient demographic and clinical characteristics and COVID-19 mortality and discusses the implications of these differences in relation to existing cancer disparities and COVID-19 vulnerabilities. Data was collected as a part of a retrospective study on a cohort of COVID-19 positive patients across Mount Sinai Health System from March 28, 2020 to April 26, 2020. Descriptive, comparative, and regression analyses were applied to examine differences between patients with and without cancer in demographic and clinical characteristics and COVID-19 mortality and whether cancer status predicts COVID-19 mortality controlling for these covariates using SAS 9.4. Results showed that, of 4641 patients who tested positive for COVID-19, 5.1% (N=236) had cancer.
The role of exercise and physical activity in osteosarcoma for patients and survivors
Exercise has been found to improve function, mitigate disability, enhance the anticancer immune system response, and improve quality of life for patients with osteosarcoma and its survivors. Of late, exercise has additionally been implemented as an adjuvant to standard therapies. These products of exercise, along with the benefits of physical activity in pre- and postoperative rehabilitation, were summarized in the recently published book chapter Exercise and Physical Activity in Patients with Osteosarcoma and Survivors.
Plasma oncology - Physical plasma as innovative tumor therapy
In medical diagnostics, complex physical techniques are state of the art and everyday clinical practice would be unthinkable without them. But also, in the field of therapeutic interventions there are several physical procedures. For example, ionizing radiation is used in oncology and non-ionizing radiation in dermatological (UV light) and photodynamic therapies (laser). Similarly, electrosurgical and laser procedures are well established in surgery.
DKK2 mediated immunosuppressive pathway and angiogenesis for colon cancer progression
Available targeted therapies for colorectal cancer (CRC) are limited. Immunotherapy offers new options for cancer treatment, but most of CRC are refractory to current immune checkpoint blockade, which indicates the possible presence of yet uncharacterized immune-suppressive mechanisms. Herein we report that high levels of Dickkopf-related protein 2 (DKK2) are expressed in human CRC tumors, and the DKK2 blockade caused stronger activation of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells in ex vivo culture. A correlation of high DKK2 expression
Changing the landscape of non-small cell lung cancer disparities
In the United States, lung and bronchus cancers are the second most common types of cancer and are responsible for the largest number of deaths from cancer, with African Americans suffering disproportionately from lung and bronchus cancers. This disparity likely results from a complex interplay among social, psycho-social, lifestyle, environmental, health system, and biological determinants of health.
Reflex ordered testing for molecular biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma: An update
Molecular biomarker testing is essential to the work up of metastatic and advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma. Despite molecular testing guidelines proposed by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Association for Molecular Pathology, and many others, multiple reports continue to indicate that lung cancer patients are inadequately tested for key molecular biomarkers. Within our hospital system, reflex ordered testing of a panel of molecular biomarkers in all newly diagnosed lung adenocarcinomas was approved and implemented in 2017.
Telangiectatic osteosarcoma: A bare bones account
Examination of the surface of bones (from which soft tissues have been removed) provides a window complementary to that provided by clinical, standard anatomic, laboratory and radiologic studies. That approach, utilized successfully for analysis of other forms of osteosarcoma is applied to the high grade telangiectatic version of medullary osteosarcoma.
