Loading

2024
Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-37
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
AI-driven designed protein epigenomics
Shiri Levy, Hannele Ruohola-Baker
The biological revolutions of computationally designed proteins, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and the CRISPR-Cas9 system finally enables modifications that can spur deep understanding of spatial requirement of epigenetic information. This commentary describes the utility of a computationally designed protein, EED Binder (EB), when fused to dCas9 (EBdCas9) for identifying critical sites of PRC2 dependent histone H3K27me3 marks in the chromatin. By using EBdCas9 and gRNA, PRC2 function can be inhibited at specific loci, resulting in precise reduction of EZH2 and H3K27me3 marks, and in some (but not all) locations, activation of the gene and functional outcomes (such as regulation of cell cycle or trophoblast transdifferentiation).
Clin Res Oncol, 2024, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/Oncology.1.01
Fight tumor heterogeneity
Meihong Chen
Intratumor heterogeneity has attracted more and more attention in recent years. Heterogeneity is the driving force of tumor clone evolution. Chromosomal instability, somatic mutation, epigenetic modification and extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) contribute to tumor heterogeneity. The degree of such heterogeneity is extremely high.
Clin Res Oncol, 2024, Volume 1, Issue 1, p4-5 | DOI: 10.46439/Oncology.1.002
Modulating the immunotolerant tumor microenvironment to enhance irreversible electroporation ablation therapy
Michelle Yu, Jim Xiang
Over the years, several ablation techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation, and cryoablation, have been developed and implemented in the treatment of different cancers. Of these ablation technologies, RFA is the most widely used. RFA is a form of thermal ablation that relies on radio waves to produce an electrical current at the tip of an inserted electrode, thus allowing for heat production at the site of the tumor.
Clin Res Oncol, 2024, Volume 1, Issue 1, p6-9 | DOI: 10.46439/Oncology.1.003
Harnessing innovation for the future of breast cancer management
Tamer A. Addissouky, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Majeed M. A. Ali, Mahmood Hasen Shuhata Alubiady, Yuliang Wang
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancerrelated mortality in women worldwide. Incidence rates continue to rise globally. Breast cancer encompasses a heterogeneous group of tumors with varying molecular features, clinical behaviors, and responses to therapy. While survival rates have improved, challenges persist such as invasive cancers, recurrent metastatic disease, and mortality among subgroups.
Clin Res Oncol, 2024, Volume 1, Issue 1, p10-17 | DOI: 10.46439/Oncology.1.004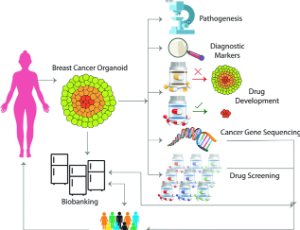
Pediatric and adolescent cancer in a national referral hospital in Peru in 2024: Epidemiological profile and public health challenges
Jesús Domínguez-Rojas, Lily Jannete Saldaña Gallo, Jenny Villalobos Alva
Background: Pediatric cancer remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in low- and middle-income countries. In Peru, structural barriers limit timely diagnosis, comprehensive treatment, and proper epidemiological registration. This study aims to characterize the epidemiological and clinical profile of the pediatric cancer population at INSN-Breña in 2024.
Methods: A retrospective, observational, and descriptive study based on the 2024 institutional cancer registry from the Instituto Nacional de Salud del Niño (INSN) using the national epidemiological surveillance guideline.

The role of the nervous system in the development of brain tumorigenesis: From neurons to the tumor microenvironment
Cheng Xue
Brain tumors, especially malignant gliomas and metastases, continue to pose serious clinical challenges due to their complex biology and limited treatment options. The traditional research paradigm mainly focuses on the tumor cells themselves and their interaction with the immune microenvironment, while the critical role of the nervous system (including neurons, glial cells, neurotransmitters/modulators, and nerve fibers) in the pathological process of tumors has been underestimated for a long time.
Clin Res Oncol, 2024, Volume 1, Issue 1, p24-37 | DOI: 10.46439/Oncology.1.006
Recommended Articles
AI-driven designed protein epigenomics
The biological revolutions of computationally designed proteins, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and the CRISPR-Cas9 system finally enables modifications that can spur deep understanding of spatial requirement of epigenetic information. This commentary describes the utility of a computationally designed protein, EED Binder (EB), when fused to dCas9 (EBdCas9) for identifying critical sites of PRC2 dependent histone H3K27me3 marks in the chromatin. By using EBdCas9 and gRNA, PRC2 function can be inhibited at specific loci, resulting in precise reduction of EZH2 and H3K27me3 marks, and in some (but not all) locations, activation of the gene and functional outcomes (such as regulation of cell cycle or trophoblast transdifferentiation).
Fight tumor heterogeneity
Intratumor heterogeneity has attracted more and more attention in recent years. Heterogeneity is the driving force of tumor clone evolution. Chromosomal instability, somatic mutation, epigenetic modification and extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) contribute to tumor heterogeneity. The degree of such heterogeneity is extremely high.
Modulating the immunotolerant tumor microenvironment to enhance irreversible electroporation ablation therapy
Over the years, several ablation techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation, and cryoablation, have been developed and implemented in the treatment of different cancers. Of these ablation technologies, RFA is the most widely used. RFA is a form of thermal ablation that relies on radio waves to produce an electrical current at the tip of an inserted electrode, thus allowing for heat production at the site of the tumor.
Harnessing innovation for the future of breast cancer management
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancerrelated mortality in women worldwide. Incidence rates continue to rise globally. Breast cancer encompasses a heterogeneous group of tumors with varying molecular features, clinical behaviors, and responses to therapy. While survival rates have improved, challenges persist such as invasive cancers, recurrent metastatic disease, and mortality among subgroups.
Pediatric and adolescent cancer in a national referral hospital in Peru in 2024: Epidemiological profile and public health challenges
Background: Pediatric cancer remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in low- and middle-income countries. In Peru, structural barriers limit timely diagnosis, comprehensive treatment, and proper epidemiological registration. This study aims to characterize the epidemiological and clinical profile of the pediatric cancer population at INSN-Breña in 2024.
Methods: A retrospective, observational, and descriptive study based on the 2024 institutional cancer registry from the Instituto Nacional de Salud del Niño (INSN) using the national epidemiological surveillance guideline.
The role of the nervous system in the development of brain tumorigenesis: From neurons to the tumor microenvironment
Brain tumors, especially malignant gliomas and metastases, continue to pose serious clinical challenges due to their complex biology and limited treatment options. The traditional research paradigm mainly focuses on the tumor cells themselves and their interaction with the immune microenvironment, while the critical role of the nervous system (including neurons, glial cells, neurotransmitters/modulators, and nerve fibers) in the pathological process of tumors has been underestimated for a long time.
EUnetCCC: Rising to the growing challenge of cancer in Europe
According to the most recent estimates of the European Cancer Information System (ECIS) [1] cancer is the second cause of death in Europe [2] and the number one cause of death among Europeans under 65 years of age [3,4]. It is estimated that 1 in 2 Europeans will develop cancer in their lifetime and that 1 in 5 will die because of cancer [3].
Targeting ESR1 mutations: Imlunestrant and the next chapter in ER-positive breast cancer care
Around 80% of breast cancers in women aged 45 years and older are estrogen receptor–positive (ER+). Despite advances in endocrine therapy, resistance driven by ESR1 mutations remains a major clinical challenge. These mutations cause constitutive receptor activation even in estrogen-deprived environments, limiting the efficacy of aromatase inhibitors and fulvestrant.
