Loading
2025
Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-24
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Recent discoveries in stem cell therapy: Charting new territories in regenerative medicine
Prerna Mehta
The regenerative medicine landscape is undergoing its fastest change due to the breakthroughs in stem cell therapy. The versatility of stem cells places them at the frontline of medical research with a promise of the possibilities of treating numerous diseases, both degenerative and traumatic.
Arch Stem Cell Ther, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-2 | DOI: 10.46439/stemcell.6.024
Stem cell–based strategies for HIV-1 remission: Emerging frontiers and translational challenges
Aditi Chatterjee, Giovannino Silvestri
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) has transformed HIV-1 from a fatal infection into a manageable chronic condition. Yet ART cannot eradicate latent viral reservoirs, necessitating lifelong adherence and leaving more than 38 million people worldwide without a definitive cure [1].
Arch Stem Cell Ther, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p3-5 | DOI: 10.46439/stemcell.6.025
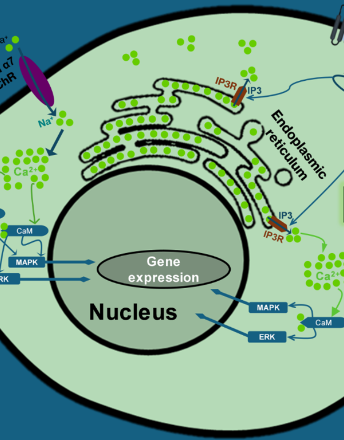
COL2A1 mutations and type II collagenopathies: molecular mechanisms and iPSC-based modeling of cartilage disorders
Latifa Mohammed Aljuid, Dareen Alyousfi, Manal Hosawi, Ayman Z. Elsamanoudy
Type II collagen (COL2A1) is the principal structural protein of cartilage and is crucial for maintaining extracellular matrix integrity during skeletal development. Pathogenic variants in COL2A1 disrupt collagen folding, secretion, and fibrillar assembly, leading to defective cartilage architecture and impaired chondrocyte maturation. These molecular alterations underline a broad group of autosomal dominant skeletal disorders collectively known as type II collagenopathies.
Arch Stem Cell Ther, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p6-24 | DOI: 10.46439/stemcell.6.026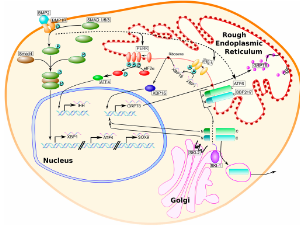
Recommended Articles
Effect of acute low oxygen exposure on the proliferation rate, viability and myogenic regulatory gene expression of C2C12 myoblasts in vitro
Within human tissue, oxygen concentrations are considerably less than the 21% O2 concentrations found in ambient air and is termed physiological hypoxia. Typically, the partial pressure of oxygen
(pO2) of human tissue lies between 1% and 14%, with considerable local and regional variations
How to improve the regenerative potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for the use in regenerative medicine?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are widely used in regenerative medicine. They can be isolated from different adult tissues. However, the regenerative potential of MSCs obtained from various sources and from different age donors may significantly differ.
Role of the rapid delayed rectifier K+ current in human induced pluripotent stem cells derived cardiomyocytes
The action potential (AP) in cardiac tissue is important for initiating and coordinating contractions in the heart. In addition, the long refractory period minimizes the potential for developing extrasystoles and arrhythmias. The AP is generated by coordinate changes in different ionic currents. In human (or canine) adult ventricular cells, the depolarization phase of the AP is mainly through the influx of Na+ and Ca2+ through specific voltage gated channels.
Drosophila male germline stem cells and their transit amplifying daughters depend on G-protein signaling for increasing their mitotic indices in response to mating
In many metazoan tissues, highly specialized cells are constantly lost and need to be replaced by tissue homeostasis from adult stem cells. When adult stem cells divide by mitosis their daughter cells either become new stem cells, or enter a proliferation and differentiation path. Recent studies in Drosophila males showed that germline stem cells (GSCs) can increase their mitotic activity in response to repeated mating.
Lysyl oxidase inhibition in primary myelofibrosis: A renewed strategy
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) that portends a poor prognosis and has limited options for treatment. PMF is often driven by clonal mutations in one of three genes that regulate the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, leading to hyperactivation of this signaling pathway and over-proliferation of megakaryocytes (MKs) and their precursors. PMF presents with debilitating symptoms such as splenomegaly and weight loss.
Molecular signatures of aggressive pediatric liver cancer
Liver masses account for 5 to 6% of pediatric cancer, which includes hepatoblastoma (HBL) along with rare cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The most dangerous form of pediatric liver cancer is aggressive HBL, which can be characterized by chemo-resistance and multiple nodules or metastases at diagnosis, all correlating with worse clinical prognosis. Despite intensive studies and a significant improvement in overall outcomes, very little is known about the key molecular pathways which determine the aggressiveness of pediatric liver cancer.
mTOR: A possible therapeutic target against SARS-CoV-2 infection
The recent pandemic of SARS-CoV-2 has emerged as a health emergency to develop effective therapeutic strategies for restricting deadly disease, COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 infects cells by the endocytosis process via receptor-mediated binding and priming by cellular proteases.
Updated protocols for optimizing sperm recovery after steroid use
The prevalence of hypogonadism is an increasing problem that affects increasingly more men of reproductive age. With the mainstay of hypogonadal treatment involving testosterone therapy (TTh), the fertility potential of many of these men must be investigated and considered accordingly. There exist multiple treatments for the recovery of anabolic steroid-induced hypogonadism, including gonadotropin replacement therapy to induce both spermatogenesis as well as intratesticular testosterone production.
A small peptide possesses great potentials in myocardial infarction intervention
Damaged myocardial tissue is difficult to recover after myocardial infarction (MI), and scars without systolic function formed on the heart put patients at risk of arrhythmia or cardiac failure. Common surgical and medical management mainly function to attenuate the associated symptoms, with fewer effects on promoting regeneration of the damaged myocardium.
Research update on the state of the evidence for stem cell and regenerative medicine in cerebral palsy
Stem cell therapy for the treatment of cerebral palsy is a rapidly expanding area of research that has been identified as a high priority by consumers. There are several types and sources of stem cell therapies under investigation. Stem cell treatments proposed for cerebral palsy are believed to provide benefit via some or all of the following mechanisms including immunomodulation, paracrine signaling and supporting endogenous reparative processes.
Deregulation of Slug/Snail2 and TGF-β crosstalk in airway epithelial stem/progenitor cells: A key link between COPD and lung cancer?
This commentary focuses on two recent publications showing deregulation of the transcription factor Slug/Snail2 and TGF-β function in primary bronchial basal/progenitor cells of patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and the impact on proliferation and the expression of genes involved in stem cell maintenance. We discuss the molecular mechanisms related to the exhaustion of airway basal stem/progenitor cells in tobacco smoke-induced COPD, as well as putative links between COPD and lung cancer at the molecular level.
Nemo-like kinase as a potential target for treatment of Diamond Blackfan Anemia
Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) is a congenital bone marrow failure syndrome characterized by hypoproliferative anemia, in which the major defect is ineffective erythropoiesis. Over 70% of patients with DBA have mutations in ribosomal protein subunits, although the precise molecular mechanisms contributing to the pathogenesis of DBA are not well understood.
The significance of triple-capsid-mutant AAV8 for treatment of Sanfilippo Syndrome Type B
Sanfilippo Syndrome Type-B remains an untreatable childhood neurodegenerative disease with great burden for both patient and caregiver. Very few clinical trials have been undertaken to treat the disease, and none of these have yet yielded clinically obtainable products for patients. Caused by a simple enzyme function deficiency, Sanfilippo Syndrome Type-B has been considered a great prospect for gene-therapy interventions.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and PRP combined therapy promotes gastric leak closure following sleeve gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy is the most common bariatric surgery worldwide. However, such a surgery caries risk of complications associated with morbidity and mortality. Gastric leak can occur and represents one of the most severe complications following sleeve gastrectomy. Since the two last decades, regenerative medicine has emerged, offering new strategies to face to sleeve gastrectomy complications.
Post-allogeneic stem cell transplant FLT3-targeted maintenance therapy: updates and considerations for clinical practice
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is characterized by multiple molecular and cytogenetic abnormalities, with increasing data to support clinical and prognostic implications to guide clinical decision making. One of the most well described mutations involves fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) that results in a constitutively active tyrosine kinase and is generally associated with poor prognosis involving shorter overall survival and higher rates of relapse.
Considering Taguchi method as a feature selection method in agent-based models of cancer disease: A mini-review
Cancer biology involves complex dynamics and interactions between cells and the tissue environment. Mathematical modeling and computer simulation can provide a powerful instrument for considering this complexity. Agent-based modeling is a particular discrete hybrid modeling method.
Can regulatory-driven process innovation open the door for cellular therapies in emerging markets?
Due to their impressive clinical success, CAR-T therapies are becoming a more mainstream treatment for patients with hematologic malignancies. In order to make this promising form of therapy accessible to patients in need worldwide, a robust scale-up of such a complex supply chain, that is also affordable worldwide, is essential. Already a challenging endeavor in most privileged countries, but a chimerical undertaking in the more logistically challenged regions and emerging markets across the globe.
The tumor dose sensitivity matrix and stem cells in head and neck cancer
Radiation therapy (RT) is one of the pillars of locally advanced head and neck cancer (HNSCC) treatment in combination with cisplatin or epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Despite a very high local tumor control rate, approximately 50% of patients with locally advanced disease will develop a recurrence.
Stem cell secretome-mediated alleviation of scalp psoriasis: A case report
Scalp psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, thickened (erythematous), well-demarcated patches or plaques with overlying silvery-white scales, affecting part or all of the scalp, is an autoimmune disease accompanied by itchy skin. The disease is associated with faulty functioning of adaptive and innate components of immune systems. The key pro- inflammatory cytokines mediating immunopathology of psoriasis are IL-17 and IL-23 which promote proliferation of Th 17 cells which in turn induce proliferation of keratinocytes leading to the disease.
Advancing towards HIV-1 remission: Insights and innovations in stem cell therapies
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) continues to pose a significant global health challenge despite advances in combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), which has transformed HIV-1 infection from a fatal disease to a manageable chronic condition. However, cART is not curative, and its long-term use is associated with challenges such as pill burden, drug toxicities, and the emergence of drug-resistant viral strains.
