Loading
Journal of Experimental Nephrology
ISSN: 2767-3383


John Albert St.Cyr.
Director
Jacqmar, Inc. , USA
Featured Article
The beneficial role of vitamin B12 in injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion: beyond scavenging superoxide?

Featured Article
Beneficial effects of nicotinamide on hypertensive mice with impaired endothelial nitric oxide function
About this Journal
Journal of Experimental Nephrology is an open access peer reviewed journal that publishes scholarly and high quality articles based on the studies of kidney and its associated disorders including glomerulonephritis, tubular diseases, electrolyte disturbances, and hypertension. It talks about restorative procedures like dialysis, haemofiltration, diabetic nephropathy, renal replacement therapy, transplantation.
Articles
Analysis of chronic kidney disease on diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and related risk factors in patients with lymphoma: A mini-review
Currently, the field of tumor nephrology continues to evolve, and the interplay between chronic kidney disease (CKD) and lymphoma merits further investigation. The incidence of CKD among lymphoma patients is substantial, posing a significant long-term risk for CKD progression. CKD should be regarded as an independent prognostic factor for mortality in lymphoma patients. In this mini-review, we aim to extend the research direction outlined in "Diagnosis and Treatment of Secondary Nephrotic Syndrome with Rash as the Initial Symptom: A Case Report", with a focus on elucidating the correlation between CKD and lymphoma.
Clinical and urodynamic findings in children and adolescents with refractory neurogenic bladder undergoing augmentation cystoplasty
Augmentation cystoplasty (AC) is a surgical procedure for patients with refractory neurogenic bladder (NB). This study aimed to evaluate urinary incontinence (UI), vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), and urodynamic parameters in patients’ post-AC and compare these results to preoperative data.
Difficulties of diagnosing hyponatremia disorders. Overcoming limitations with a 3-step approach and web-based diagnostic application
Hyponatremia presents a complex diagnostic challenge due to its broad differential diagnosis and the difficulties of its evaluation. The available diagnostic algorithms often have substantial limitations. Therefore, clinicians frequently struggle to distinguish the underlying causes of hyponatremia, leading to diagnostic and management errors that contribute to considerable morbidity and mortality.
Association of fundus damage, renal function deterioration, and ferroptosis in chronic kidney disease patients
Introduction: This study aimed to explore the changes in ferroptosis markers and their relationship with fundus lesion severity in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Methods: We enrolled 118 CKD patients and collected clinical, renal function, fundus imaging data, and ferroptosis markers. We performed correlation and regression analyses between renal dysfunction and fundus lesions, and assessed the changes and mediating roles of serum iron (Fe), malondialdehyde (MDA), and reduced glutathione (GSH) in CKD deterioration and retinal damage.
The beneficial role of vitamin B12 in injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion: beyond scavenging superoxide?
Vitamin B12 is one of the most complex non-protein compounds as described by Dorothy Hodgkin, a Nobel Prize-winning chemist, who discovered the molecular crystal structure of B12. Cobalamins (vitamin B12 derivatives) contain the rare transition metal, cobalt (Co), positioned in the center of a corrin ring and weakly bound to carbon. While cobalamins are synthesized only in certain bacteria and archaea, not in mice or humans, they are co-enzymes essential for all life except for plants. For example, in higher vertebrates, methyl-cobalamin and 5’-deoxyadenosyl-cobalamin are essential for the function of methionine synthase and methylmalonyl CoA mutase, respectively.
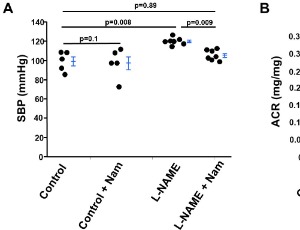
Beneficial effects of nicotinamide on hypertensive mice with impaired endothelial nitric oxide function
Nicotinamide (Nam, amide form of niacin acid or nicotinate), a precursor for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), is important for normal physiological function of organisms. Nam also suppresses mobilization of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum into cytoplasm through inhibiting ADP-ribose cyclase. Previously, we have demonstrated that a pharmacological dose of Nam normalizes maternal blood pressure in mouse models of preeclampsia, a pregnancy related hypertensive disorder.
The beneficial role of vitamin B12 in injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion: beyond scavenging superoxide?
Vitamin B12 is one of the most complex non-protein compounds as described by Dorothy Hodgkin, a Nobel Prize-winning chemist, who discovered the molecular crystal structure of B12. Cobalamins (vitamin B12 derivatives) contain the rare transition metal, cobalt (Co), positioned in the center of a corrin ring and weakly bound to carbon. While cobalamins are synthesized only in certain bacteria and archaea, not in mice or humans, they are co-enzymes essential for all life except for plants. For example, in higher vertebrates, methyl-cobalamin and 5’-deoxyadenosyl-cobalamin are essential for the function of methionine synthase and methylmalonyl CoA mutase, respectively.
Beneficial effects of nicotinamide on hypertensive mice with impaired endothelial nitric oxide function
Nicotinamide (Nam, amide form of niacin acid or nicotinate), a precursor for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), is important for normal physiological function of organisms. Nam also suppresses mobilization of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum into cytoplasm through inhibiting ADP-ribose cyclase. Previously, we have demonstrated that a pharmacological dose of Nam normalizes maternal blood pressure in mouse models of preeclampsia, a pregnancy related hypertensive disorder.
The beneficial role of vitamin B12 in injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion: beyond scavenging superoxide?
Vitamin B12 is one of the most complex non-protein compounds as described by Dorothy Hodgkin, a Nobel Prize-winning chemist, who discovered the molecular crystal structure of B12. Cobalamins (vitamin B12 derivatives) contain the rare transition metal, cobalt (Co), positioned in the center of a corrin ring and weakly bound to carbon. While cobalamins are synthesized only in certain bacteria and archaea, not in mice or humans, they are co-enzymes essential for all life except for plants. For example, in higher vertebrates, methyl-cobalamin and 5’-deoxyadenosyl-cobalamin are essential for the function of methionine synthase and methylmalonyl CoA mutase, respectively.
Beneficial effects of nicotinamide on hypertensive mice with impaired endothelial nitric oxide function
Nicotinamide (Nam, amide form of niacin acid or nicotinate), a precursor for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), is important for normal physiological function of organisms. Nam also suppresses mobilization of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum into cytoplasm through inhibiting ADP-ribose cyclase. Previously, we have demonstrated that a pharmacological dose of Nam normalizes maternal blood pressure in mouse models of preeclampsia, a pregnancy related hypertensive disorder.
