Loading
New Articles
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Articles in Press
Recommended Articles
Biological effects of low power nonionizing radiation: A narrative review
Background and controlled electromagnetic radiation (EMR) on cells and tissues induces thermal, non-thermal, and dielectric property change. After EMR interaction with cells/tissues the resulting signal is used for imaging, bio-molecular response, and photo-biomodulation studies at infrared regime, and therapeutic use. We attempt to present a review of current literature with a focus to present compilation of published experimental results for each regime viz. microwave (extremely low frequency, ELF to 3 GHz), to cellular communication frequencies (100 kHz to 300 GHz), millimeter wave (300 GHz-1 THz), THz (1 THz-20THz) and the infra-red band extending up to 461 THz.
Radiation induced radicular hypoplasia: A rare case report
Irradiation is considered as one of the causes that may inhibit tooth development. Radiation exposure during the period of tooth development may result in impaired, delayed, or absolute failure to develop/eruption of the tooth. Radiation exposure at high dosage may also impair facial development in the pediatric population who had received radiation therapy for a malignant tumor in the head and neck region. Here we reported a case of Radiation-Induced Radicular Hypoplasia (RIRH) in a 19-year-old patient who received radiotherapy ten years ago for the Embryonal Rhabdo Myo Sarcoma of the soft palate.
Modification of circumsolar radiation for anisotropic diffuse radiation models: Photovoltaic collectors on sloped planes
Photovoltaic fields are deployed in multiple collector rows on horizontal and on sloped planes, therefore the second (and subsequent rows) sees the sky dome with a smaller angle than the first (front) row. A relatively large number of diffuse radiation models have been proposed based on isotropic and anisotropic models. The anisotropic models include circumsolar radiation and horizon brightening, and refer to single rows of collectors. The present article modifies the anisotropic models by two factors: (a) Sky view factor of a second row, depending on the collector and field parameters, (b) Modification to circumsolar brightening.
Comparison of T1 FLAIR BLADE with and without parallel imaging against T1 turbo spin echo in the MR imaging of lumbar spine in the sagittal plane
Spinal cord and nerves are best visualized by MRI, which is able to show structural and functional anomalies of the spine. The primary objective of this study is to identify advantages or disadvantages of the T1-weighted fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequence with BLADE technique (T1W-FLAIR BLADE), with and without parallel imaging when compared with T1 Turbo Spin Echo (T1 TSE) sequence when performing MRI examination of the lumbar spine in a sagittal view. L-spine examinations with T1W-FLAIR BLADE (with and without parallel imaging) and T1 TSE were acquired on 44 patients using a 1.5T scanner. These sequences were assessed by two radiologists a) quantitatively by comparing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) and relative contrast (ReCon) measurements and b) qualitatively based on different features of the images such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) nulling.
Journal of Radiation Research and Imaging: Welcome letter
It is a great honor to be a part of the editorial board of Journal of Radiation Research and Imaging (JRRI) which has been designed with the intention of serving worldwide scientific researchers and healthcare professionals with the latest advances and developments in the field of radiation. I feel privileged to play a role in creating a scientific space online for budding analysts and radiation imaging enthusiasts to not just avail new information but also to comprehensively understand and extensively indulge in this whole new experience.
High-LET targeted microbeam irradiation induces local chromatin reorganization in living cells showing active basal mechanisms at highly complex DNA damage sites
DNA repair eukaryotic cells have additional protective mechanisms that avoid uncontrolled interaction of different parts of the chromatin and damaged regions. Key factors here are the regulation of chromatin density and mobility. The 4D (temporal and spatial) organization of chromatin is controlling this security barrier by regulating the accessibility of genes, flexibility of DNA, and its ability to move inside the nucleus. How this regulation mechanisms are involved in DNA repair upon radiation damage is until now rarely known but an important part to understand the enhanced effectiveness of high linear energy transfer (LET) particles. The damage recognition via PARP1 and the subsequent chromatin decondensation via PARylation is a crucial step in the DNA damage response (DDR). Upon We used the SNAKE microbeam with a beam spot size of <1 µm to induce highly localized DNA damage in living cells using 55 MeV Carbon ions to investigate the chromatin rearrangements in the early stage of DDR.
“Academic success depends upon research and publications!” - PHILIP ZIMBARDO
Journal of Radiation Research and Imaging (JRRI) are excited to introduce the First edition of 2023 to our passionate researchers and upcoming academicians. This issue is dedicated towards publishing break-through research studies in the field of Radiation Research and Imaging. This journal includes authors and readers as clinicians at all levels including trainees, specialists and consultant radiologists and scientists. High quality original research articles and timely reviews on current developments in the field of science and research is our forte.
Artificial intelligence-augmented breast ultrasound: Advancing diagnostic precision and equity in cancer care-Kuwait
Breast cancer remains the most diagnosed malignancy among women worldwide and continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. In Kuwait, the disease accounts for 40.1% of all new female cancer cases according to the World Health Organization’s Global Cancer Observatory (2022) [1], reflecting a pressing national health challenge.
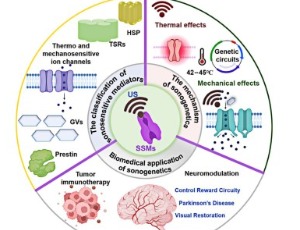
Medical imaging and perspective on sonogenetics
Medical imaging is the process of creating visual pictures of the inside of the human body for diagnostic and treatment purposes. This article provides an overview about different types of medical imaging. Each technique is used in different circumstances