Loading
Journal of Cancer Biology
ISSN: 2692-7896
Latest Articles
Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with pre-existing autoimmune disease
Wint Yan Aung, MD , Margaret Locke , Adit Singhal, MD , Nagashree Seetharamu, MD
The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) targeting CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 pathways has revolutionized cancer treatment with significantly improved outcomes across a spectrum of cancers [1,2]. Although ICI therapy offers significant clinical benefits, these treatments can also lead to various immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that may negatively impact patient outcomes. Although the precise mechanism of irAE is not fully understood, they demonstrate many clinical features similar to autoimmune diseases. IRAEs are thought to result from bystander effects of activated T-cells, cross-reactivity between tumor and host tissues, and the role of the gut microbiome in immune activation [3].
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.068
Advances in glyconanotechnology based biomedical applications
Divya Kamath , Stefan H. Bossmann
There is an emerging awareness in cancer biology that glycobiology plays a significant, if not decisive role in oncogenesis, tumor survival, and proliferation. The human glycome is even more complex than the human genome, because glycans are synthesized as secondary gene products by sequentially acting glycosidases and glycosyltransferases. Glycans act as a communication system within the organism and between different organisms.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p4-9 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.069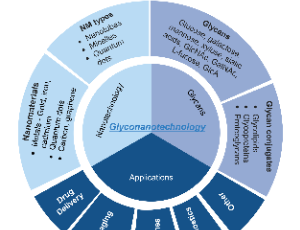
Mechanisms of cancer cell rescue against pancreatic cancer therapeutics: Intrinsic and acquired resistance
Jeevan Ghosalkar , Vinay Sonawane , Kalpana Joshi
Pancreatic Cancer (PC) with dismal prognosis poses a significant challenge to healthcare systems worldwide. PC is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality globally and is projected to surpass lung cancer as the second foremost cause by 2030. The poor prognosis associated with PC is primarily due to the low rate of early detection, rapid progression, and limited treatment options. Chemotherapy remains a cornerstone of treatment for PC in all stages of disease.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p10-22 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.070
Cancer stem cells as a biomarker – A mini review
Urja Joshi , Dhara Jani , Linz-Buoy George , Hyacinth Highland
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) also known as tumor stem cells (TSCs), are pivotal in cancer development and progression. They can be identified through specific markers and surface proteins (e.g., CD44, CD133) that differ from those on non-CSC tumor cells. As well high CSC levels often correlate with poor prognosis, aggressive disease, and resistance to conventional therapies. CSCs are more resistant to standard treatments like chemotherapy and radiation, leading to relapse and metastasis.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p23-33 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.071
Nuclear mTORC2 and its emerging role in gene regulation
Moinuddin , Narayan Kumar , Smrati Bhadauria
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), a critical regulator of cell growth, metabolism, survival, and actin-cytoskeletal organization, is primarily recognized for its cytoplasmic functions. However, emerging evidence suggests that the mTOR and its constituent partners also localize to the nucleus, where it may play distinct roles in gene expression regulation, chromatin remodeling, and transcriptional control. This review highlights the evolving understanding of nmTORC2 (nuclear mTORC2), with a particular focus on its composition, functional implications, and relevance in cancer biology.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p34-46 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.072
Effectiveness of comprehensive nursing intervention on alleviating postoperative fatigue and anxiety in patients with oral cancer
Sukanta Nath , Khemchand Falwaria , Shiromani Debbarma , Matrujyoti Pattnaik , Ankita Debnath
Postoperative functional impairments are common in patients with oral cancer following surgery. Furthermore, these patients frequently experience fatigue and anxiety, which are strongly linked to a lower quality of life (QOL). The goal of our study was to investigate the effectiveness of comprehensive nursing intervention on alleviating postoperative fatigue and anxiety in patients with oral cancer.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p47-54 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.073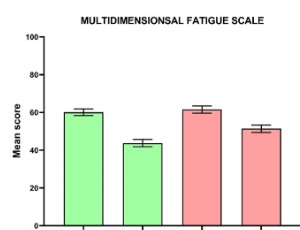
Targeting m6A in cancer – new prospective
Grossmann L.D , Moshitch-Moshkovitz S
The field of mRNA modifications has rapidly developed over the last years, outlining a new realm of gene expression regulation that appears to play a major role in health and disease states including cancer. Considering the information regarding chemical modifications of DNA and proteins, decades of research proved beyond any doubt that chemical modifications affect chromatin structure as well as enzymatic activity.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p55-63 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.074
Oncogenic specificity in nevus and melanoma formation
Konrad Kaminiow , Stephen M Ostrowski , David E Fisher
There is striking clinical, histological, and molecular diversity observed across melanocytic tumors. Activating mutations in BRAF and NRAS are well-established initiators of benign melanocytic nevi and melanoma. However, accumulating evidence reveals that the biological outcome after oncogene activation is dependent on cellular state differences that vary by anatomic site, developmental timing, and cell of origin.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p64-70 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.075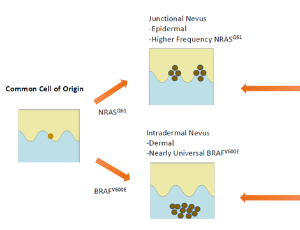
Advances in the understanding of health disparities in the United States Hispanic population
Asma Pinkey , Masuma Anzuman , Mrudang Desai , Anna M. Eiring
Health disparities have become a major concern for global public health, disproportionately affecting minority and underserved populations throughout the United States (U.S.). Hispanics make up the fastest-growing minority group in the U.S., and they often experience significant health disparities when it comes to chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. These disparities are likely driven by a confluence of socioeconomic disadvantages, structural inequities, environmental exposures, and cultural barriers.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p71-75 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.076
Thyroid cancer-tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) spatial transcriptomics reveals novel players
Shafiya Imtiaz Rafiqi, DVM, PhD , Juan Carlos Jaume, MD
Thyroid cancer (TC) encompasses several pathological types, notably papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), follicular thyroid cancer (FTC), medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC). While PTC accounts for the most common type, ATC, despite representing only 1–2% of all TC cases, is recognized as the most lethal and treatment-resistant endocrine malignancy. Despite sharing a common cellular origin, these two subtypes differ markedly in their clinical trajectories, response to therapy, and immune profiles.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p76-81 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.077
Bridging cancer and neurodegenerative disease: Drug repositioning through cheminformatic, bioinformatic, and systems biomedicine approaches
Hui-Heng Lin , Koken Hirose , Yifan Zhu
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as the Alzheimer and the Parkinson's, currently lack effective pharmacotherapies. They are posing a significant global health threat, and it is urgent to discover and develop effective pharmacotherapies for patients. However, due to pathogenic mechanisms are poorly understood, the interventional drug clinical trials for neurodegenerative diseases have high failure rates.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p82-90 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.078
Unleashing Wnts: Wnt ligands fuel cancer spread
Kailey P. Caroland , Jonathan B. Trapani , Ethan Lee , Vivian L. Weiss
Wnt signaling has long been implicated in cancer development, but recent studies have revealed new insights into how Wnt ligands themselves drive metastasis. Currently, research identifies Wnt1, Wnt2, Wnt2b, Wnt3, Wnt3a, Wnt4, Wnt5a, Wnt5b, Wnt6, Wnt8a, Wnt9b, Wnt10a, Wnt10b, and Wnt16 as pro-metastatic Wnt ligands, while Wnt7a, Wnt7b, Wnt8b, Wnt9a, and Wnt11 exhibit conflicting pro- and anti-metastatic roles.
J Cancer Biol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p91-107 | DOI: 10.46439/cancerbiology.6.079
