Loading
Archive
2025
2024
2023
2022
Recommended Articles
Fertility-sparing surgery for a young breast cancer patient — A case report and literature review
Here, we report a 26-year-old Chinese woman diagnosed with breast cancer. The patient expressed her concern for possible impact on fertility, as well as the cosmetic outcomes of the surgery. Therefore, the patient was consulted for preserving fertility function by cryopreservation after ovariectomy, with sentinel lymph node biopsy and breast reconstruction surgery simultaneously.
Breast cancer: an up-date review
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in the world and the most common cancer among women. The most common presenting symptoms are a painless subareolar lump, nipple retraction, and bleeding from the nipple.
EZH2 and cancer progression: An intricate relation that continues to grow
Genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors play disposing role in breast cancer initiation and progression. Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes act as molecular players acting as activator, repressor or co-activator. Polycomb repressor protein Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) predominantly act as repressor protein have shown its substantial contribution in genetic, epigenetic as well as environmental factors induced breast tumor development.
Commentary on: The actual benefit of intraoperative radiation therapy using 50 kV x-rays in early breast cancer: A retrospective study of 676 patients
We recently published the results of a retrospective multicenter study of 676 early breast cancer patients with favorable prognostic factors, treated by breast-conservative surgery and intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT). This study confirmed that partial breast irradiation (PBI) using IORT via a 50 kV photon device is safe and well-tolerated in select early breast cancer patients.
Progress and perspectives of organoid cultures of primary human breast cancer
The prospect of precision or personalized medicine has revived the entire field of predictive drug testing originally pursued in clonogenic assays and soft agar colony forming assays some four decades ago. In particular, the human breast and its derived tumors, while relatively trivial in composition, have proven enormously difficult to establish and interpret ex vivo.
Kindlins as modulators of breast cancer progression
Kindlin-1 (K1, FERMT1), Kindlin-2 (K2, FERMT2), and Kindlin-3 (K3, FERMT3) are the three members of the kindlin family of adapter proteins found in mammals. One or more kindlins are found in most cell types, K1 primarily in epithelial cells, K3 in primarily hematopoietic cells and also endothelial cells, and K2 is very broadly distributed.
How to inhibit breast cancer and breast cancer metastasis with Akt inhibitors: Lessons learned from studies in mice
The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is frequently hyperactivated in different types of breast cancer. In the past two decades, major efforts have been made to develop inhibitors of this pathway to treat cancer patients.
Analysis of treatment and outcomes in patients with locally advanced breast cancer
Background: Locally advanced (stage III) breast cancer has high local recurrence and distant metastasis rates and its prognosis is poor. Multimodal local treatment consisting of surgery/radiotherapy after chemotherapy is generally recommended.
Weaknesses with research models and disparities: how PDX models strengthen both
In the manuscript titled Drug resistance profiling of a new triple negative breast cancer patient-derived xenograft model, our research group generated a novel PDX model TU-BcX-2K1 (2K1 for short) by implanting a piece of primary patient tumor derived from a pre-neoadjuvant 59-year-old Black woman with invasive ductal carcinoma, triple negative subtype, into SCID/Beige mice.
Oncologist well-being in the era of COVID-19: A call to action
To date, the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in over 44.8 million cases and 722,000 deaths in the US alone [1]. Breast cancer patients faced many delays in care at the beginning of the pandemic. Patients with cancer, especially those currently receiving chemotherapy, are at significantly higher risk of morbidity and mortality if infected with COVID-19, but delay in cancer treatment is also known to be associated with worse overall survival [2-9].
A new population screening program for BRCA mutations in Israel – Attitudes and barriers among Ashkenazi Jewish women
Israeli Jewish women of Ashkenazi ancestry have a high BRCA mutation carrier rate. Therefore, recently, Israel included free genetic testing among all Jewish women with Ashkenazi ancestry, 25 yrs. and older in its public health system. The aim of this study was to assess the intention of eligible women to be tested for BRCA mutations, and to find factors that may affect their decision.
Loss of breast reconstruction services during the COVID-19 pandemic: Negative impact on patient quality of life and wellbeing
Surgery is still one of the key components of Breast Cancer treatment. Even with the advancement in treatment options and surgical techniques, at least 35% of patients still undergo mastectomy, with a recent trend showing increasing rates of mastectomy [1].
Advances in shared decision-making for breast cancer screening in Spain
One of the most recent goals of health programmes in many countries is developing a person-centred healthcare model; however, strategies to implement it are still scarce, especially in health contexts such as preventive medicine. In the context of screening programmes, Shared Decision Making (SDM) can be a good alternative.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy in early breast cancer: A brief review
In breast cancer, the status of the axillary lymph node decides the prognosis of the disease. Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) was the traditional method to address the lymph node. Final histopathological examination is the confirmatory method to detect metastasis in axillary lymph node. As the tumor stage advances, the rate of metastasis in axillary lymph nodes increases, simultaneously.
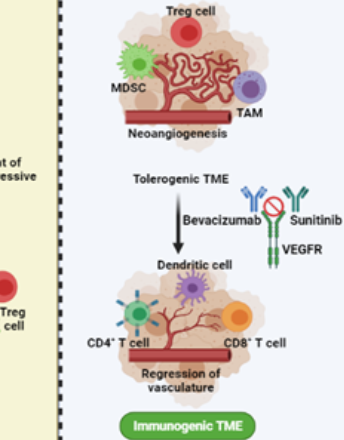
Neoangiogenesis and immune-regulation: Two armour of VEGF in the tumor microenvironment
The formation of new blood vessels, or angiogenesis, is a hallmark of cancer and one of the most important conditions for tumor growth. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of the most important factors in angiogenesis. Increased VEGF expression has been associated to rapid cancer progression and poor prognosis.
NTRK fusions: A novel diagnostic and therapeutic methodology for cancer
In our previous publication, “Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer with NTRK Gene Fusion on Tissue but not on ctDNA Molecular Profile, [1]” we discussed a case of a middle-aged female with metastatic triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) harboring an ETV6-NTRK fusion which was observed only on recent tissue molecular profiling, but not on circulating tumor DNA or years prior tissue molecular profiling.
Tumor grade as a novel predictor of outcomes in medullary thyroid cancer
Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) is a neuroendocrine tumor arising from the parafollicular calcitonin producing cells of the thyroid [1]. Representing about 2-3% of all thyroid cancer diagnoses, the rarity of disease has limited understanding of the disease and hindered advances in developing optimal therapy for patients.
Metastatic breast cancer-derived exosomes and osteoclast-mediated bone metastasis
The progress of bone metastases mainly depends upon the interaction among the cells of the bone microenvironment such as endothelial cells, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), immune cells and bone cells [bone-forming osteoblasts (OBs) and bone-resorbing OCs], strengthening the growth, migration, dormancy and reactivation of metastatic BC cells [7]
A case of sentinel node-negative breast cancer with axillary lymph node recurrence 10 years after surgery
Introduction: Sentinel node biopsy is currently the standard of care for axillary treatment of clinically axillary node-negative breast cancer. In this report, we describe a case of axillary lymph node recurrence 10 years after surgery in a patient with a negative sentinel node biopsy at the time of initial surgery.
Investigating the role of HSP90 in cancer cell phenotypic plasticity
“What are the mechanisms driving tumor evolution under the selective pressure of chemotherapeutics?” The emerging importance of epigenetic gene regulation in cancer progression necessitates not only our understanding of which genes are potential targets but also what mechanisms are employed in targeting those genes.