Loading
Journal of Breast Cancer Research
ISSN: 2769-2418
All Articles
Fertility-sparing surgery for a young breast cancer patient — A case report and literature review
Cunye Yan, Chenyu Sun, Min Ren, Benzhong Wang
Here, we report a 26-year-old Chinese woman diagnosed with breast cancer. The patient expressed her concern for possible impact on fertility, as well as the cosmetic outcomes of the surgery. Therefore, the patient was consulted for preserving fertility function by cryopreservation after ovariectomy, with sentinel lymph node biopsy and breast reconstruction surgery simultaneously.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.001
Oncologist well-being in the era of COVID-19: A call to action
Anna Chichura, Katherine Yao
To date, the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in over 44.8 million cases and 722,000 deaths in the US alone [1]. Breast cancer patients faced many delays in care at the beginning of the pandemic. Patients with cancer, especially those currently receiving chemotherapy, are at significantly higher risk of morbidity and mortality if infected with COVID-19, but delay in cancer treatment is also known to be associated with worse overall survival [2-9].
J Breast Cancer Res, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.2.010
NTRK fusions: A novel diagnostic and therapeutic methodology for cancer
Rishika Singh, Nupur Singh, Gregory Vidal
In our previous publication, “Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer with NTRK Gene Fusion on Tissue but not on ctDNA Molecular Profile, [1]” we discussed a case of a middle-aged female with metastatic triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) harboring an ETV6-NTRK fusion which was observed only on recent tissue molecular profiling, but not on circulating tumor DNA or years prior tissue molecular profiling.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.3.016
A case of sentinel node-negative breast cancer with axillary lymph node recurrence 10 years after surgery
Kimiyasu Yoneyama, Motohito Nakagawa, Asuka Hara
Introduction: Sentinel node biopsy is currently the standard of care for axillary treatment of clinically axillary node-negative breast cancer. In this report, we describe a case of axillary lymph node recurrence 10 years after surgery in a patient with a negative sentinel node biopsy at the time of initial surgery.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.4.020
Harnessing high-concentration (179 mg) capsaicin patches for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Evidence and implications from the QUCIP study
Rainer Sabatowski, Michael Patrick Lux, Tamara Quandel
Chemotherapy remains a cornerstone of modern cancer treatment, yet its neurotoxic side effects can pose significant challenges. Peripheral nerve damage and the resulting pain not only affect patients’ quality of life but also contribute to substantial economic burden.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.025
Tumor grade as a novel predictor of outcomes in medullary thyroid cancer
Ashok R Shaha, Aradhya Nigam
Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) is a neuroendocrine tumor arising from the parafollicular calcitonin producing cells of the thyroid [1]. Representing about 2-3% of all thyroid cancer diagnoses, the rarity of disease has limited understanding of the disease and hindered advances in developing optimal therapy for patients.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p4-7 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.3.017
Breast cancer: an up-date review
Fogante M
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in the world and the most common cancer among women. The most common presenting symptoms are a painless subareolar lump, nipple retraction, and bleeding from the nipple.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p4-8 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.002
A new population screening program for BRCA mutations in Israel – Attitudes and barriers among Ashkenazi Jewish women
Amar S, Lieberman S, Biderman A, Lahad A, Feinsilver T
Israeli Jewish women of Ashkenazi ancestry have a high BRCA mutation carrier rate. Therefore, recently, Israel included free genetic testing among all Jewish women with Ashkenazi ancestry, 25 yrs. and older in its public health system. The aim of this study was to assess the intention of eligible women to be tested for BRCA mutations, and to find factors that may affect their decision.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p4-13 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.2.011
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Investigating the role of HSP90 in cancer cell phenotypic plasticity
Vincent Sollars, Alexandria Chapman, Nicole R. Liang, Seth Myers
“What are the mechanisms driving tumor evolution under the selective pressure of chemotherapeutics?” The emerging importance of epigenetic gene regulation in cancer progression necessitates not only our understanding of which genes are potential targets but also what mechanisms are employed in targeting those genes.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p5-10 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.4.021
Metastatic breast cancer-derived exosomes and osteoclast-mediated bone metastasis
Manh Tien Tran
The progress of bone metastases mainly depends upon the interaction among the cells of the bone microenvironment such as endothelial cells, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), immune cells and bone cells [bone-forming osteoblasts (OBs) and bone-resorbing OCs], strengthening the growth, migration, dormancy and reactivation of metastatic BC cells [7]
J Breast Cancer Res, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p8-10 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.3.019
Histopathological insights and oncological implications in aesthetic breast surgery specimens
Giovanni André Pires Viana, Renata Andréa Pietro Pereira Viana
Mammaplasty and mastopexy are surgical procedures designed to reshape and reposition the breast tissue. Reduction mammaplasty primarily aims to decrease breast volume and alleviate symptoms such as back pain and postural discomfort, while mastopexy focuses on elevating and reshaping the breast to restore a more youthful contour.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p9-12 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.026
EZH2 and cancer progression: An intricate relation that continues to grow
Kanchan Kumari, Sandip K Mishra
Genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors play disposing role in breast cancer initiation and progression. Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes act as molecular players acting as activator, repressor or co-activator. Polycomb repressor protein Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) predominantly act as repressor protein have shown its substantial contribution in genetic, epigenetic as well as environmental factors induced breast tumor development.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p9-13 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.003
Fine needle aspiration in the evaluation of patients with suspected breast cancer in a suburban Nigerian teaching hospital: A five-year review
Esteem Tagar, James Kpolugbo, Afokeoghene G. Tagar, Ehiremhen Ozah, Lucky A. Ehiagwina, Orume Enegbuya
Reduction of deaths from breast cancer is currently a top health care priority and an important path of achieving this goal is early detection of the disease [1]. The triple assessment approach which comprises clinical, radiological, and pathological assessment remains an excellent tool in the evaluation of palpable breast lumps. Its diagnostic accuracy exceeds 99% when all three modalities are concordant [2].
J Breast Cancer Res, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p11-16 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.4.022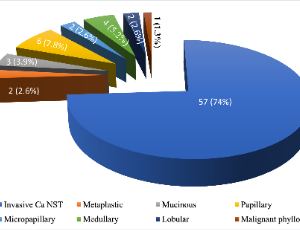
Breast cancer prognostic tests: Taking us one step closer to personalized treatment
Shyamili Goutham, Manjiri M Bakre
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women worldwide, with the highest mortality rates. While breast tumors can have heterogeneous biology, the mutational burden/genomic alterations, etc, are relatively less when compared to other malignancies like pancreatic cancer or glioblastomas, rendering breast tumors comparatively less aggressive.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p13-19 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.027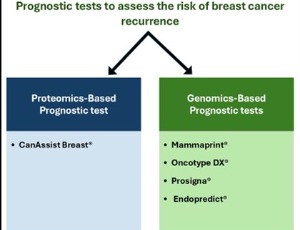
Commentary on: The actual benefit of intraoperative radiation therapy using 50 kV x-rays in early breast cancer: A retrospective study of 676 patients
Félix Felici, Gilles Houvenaeghel, Monique Cohen, Agnès Tallet
We recently published the results of a retrospective multicenter study of 676 early breast cancer patients with favorable prognostic factors, treated by breast-conservative surgery and intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT). This study confirmed that partial breast irradiation (PBI) using IORT via a 50 kV photon device is safe and well-tolerated in select early breast cancer patients.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p14-16 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.004
Loss of breast reconstruction services during the COVID-19 pandemic: Negative impact on patient quality of life and wellbeing
Jenna Shepherd, Mairi Fuller, Sue Rodwell, Rachel Moir, Beatrix Elsberger, Yazan A. Masannat
Surgery is still one of the key components of Breast Cancer treatment. Even with the advancement in treatment options and surgical techniques, at least 35% of patients still undergo mastectomy, with a recent trend showing increasing rates of mastectomy [1].
J Breast Cancer Res, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p14-18 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.2.012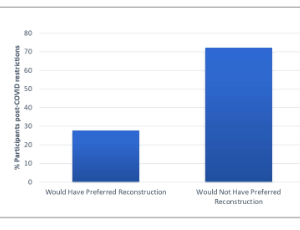
Rab GTPases and breast cancer progression
Manh Tien Tran
BC, a heterogeneous disease, is thought to be the second leading cause of death in women globally. In only 70-80% of the BC patients with early-stage, non-metastatic disease is curable [1]. In advanced BC metastasis, it is incurable [2].
J Breast Cancer Res, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p17-18 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.4.023
Progress and perspectives of organoid cultures of primary human breast cancer
Nadine Goldhammer, Ole William Petersen
The prospect of precision or personalized medicine has revived the entire field of predictive drug testing originally pursued in clonogenic assays and soft agar colony forming assays some four decades ago. In particular, the human breast and its derived tumors, while relatively trivial in composition, have proven enormously difficult to establish and interpret ex vivo.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p17-19 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.005
Advances in shared decision-making for breast cancer screening in Spain
María José Hernández-Leal, María José Pérez-Lacasta, Misericordia Carles-Lavila
One of the most recent goals of health programmes in many countries is developing a person-centred healthcare model; however, strategies to implement it are still scarce, especially in health contexts such as preventive medicine. In the context of screening programmes, Shared Decision Making (SDM) can be a good alternative.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p19-22 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.2.013
Overview of lysosome-mediated chemoresistance mechanisms in breast cancer: A mini review
Nhat Nguyen, Manh Tien Tran
Breast Cancer (BCa), a complicated heterogeneous disease, is the most frequent malignancy in females, and it is the leading cancer-related mortality worldwide [1]. Generally, BCa is categorized into three different types based on the presence or absence of molecular biomarkers for (1) estrogen or (2) progesterone receptors and (3) human epidermal growth factor 2 (ERBB2; formerly HER2) [2].
J Breast Cancer Res, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p19-22 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.4.024
Receptor discordances between primary and recurrent breast cancer
Tsung-Yen Hsieh, Chun-Yu Liu, Chih-Yi Hsu, Chin-Jung Feng, Jiun-I Lai, Ta-Chung Chao, Yen-Shu Lin, Pei-Ju Lien, Chi-Cheng Huang, Jen-Hwey Chiu, Yi-Fang Tsai, Ling-Ming Tseng
Background: Modern treatment of breast cancer depends mainly on the expression of biomarkers such as estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). However, a change of receptors was not uncommon during the disease progression. Here we aim to evaluate the impact on clinical outcome from the conversion of receptors in primary tumor and recurrent or metastatic lesions.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p20-28 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.028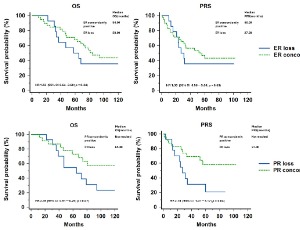
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Kindlins as modulators of breast cancer progression
Edward F. Plow, Elzbieta Pluskota, Katarzyna Bialkowska
Kindlin-1 (K1, FERMT1), Kindlin-2 (K2, FERMT2), and Kindlin-3 (K3, FERMT3) are the three members of the kindlin family of adapter proteins found in mammals. One or more kindlins are found in most cell types, K1 primarily in epithelial cells, K3 in primarily hematopoietic cells and also endothelial cells, and K2 is very broadly distributed.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p20-29 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.006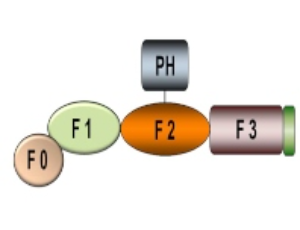
Sentinel lymph node biopsy in early breast cancer: A brief review
Sachin S Kadam, Tejaswini Kadam
In breast cancer, the status of the axillary lymph node decides the prognosis of the disease. Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) was the traditional method to address the lymph node. Final histopathological examination is the confirmatory method to detect metastasis in axillary lymph node. As the tumor stage advances, the rate of metastasis in axillary lymph nodes increases, simultaneously.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p23-27 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.2.014
Neoangiogenesis and immune-regulation: Two armour of VEGF in the tumor microenvironment
Subhanki Dhar, Tania Sarkar, Gaurisankar Sa
The formation of new blood vessels, or angiogenesis, is a hallmark of cancer and one of the most important conditions for tumor growth. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of the most important factors in angiogenesis. Increased VEGF expression has been associated to rapid cancer progression and poor prognosis.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p28-39 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.2.015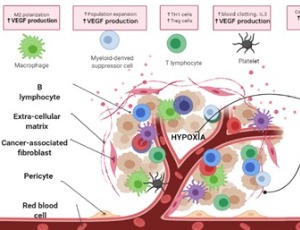
Knowledge, attitude and practice of breast cancer treatment among health care providers and traditional healers in Tanzania: A crosssectional study
Elizabeth F. Msoka, Kim Madundo, Frank B. Bright, Modesta Mitao, Angela Pallangyo, Bob C. Mulder, Linda Minja, Victor Katiti, Clotilda S. Tarimo, Godfrey Mariki, Baraka Moshi, Innocent Peter Uggh, Yotham Gwanika, Charmaine Blanchard, Maureen Joffe, Eva J. Kantelhardt, Gileard G. Masenga, Brandon A. Knettel, Blandina T. Mmbaga
Introduction: Healthcare providers (HCPs) and traditional healers (THs) play a pivotal role in the breast cancer treatment pathway and can impact access to timely and effective healthcare. This study aimed to assess the knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding breast cancer treatment among HCPs and THs in Northern Tanzania.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p29-42 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.29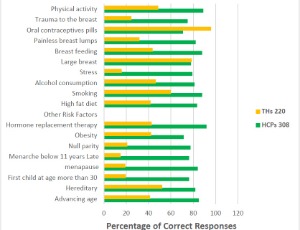
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
How to inhibit breast cancer and breast cancer metastasis with Akt inhibitors: Lessons learned from studies in mice
Nissim Hay
The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is frequently hyperactivated in different types of breast cancer. In the past two decades, major efforts have been made to develop inhibitors of this pathway to treat cancer patients.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p30-33 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.007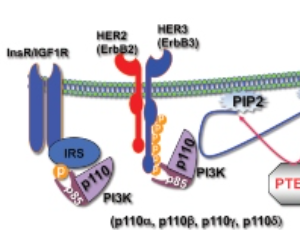
Analysis of treatment and outcomes in patients with locally advanced breast cancer
Kimiyasu Yoneyama, Motohito Nakagawa, Asuka Hara
Background: Locally advanced (stage III) breast cancer has high local recurrence and distant metastasis rates and its prognosis is poor. Multimodal local treatment consisting of surgery/radiotherapy after chemotherapy is generally recommended.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p34-39 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.008
Weaknesses with research models and disparities: how PDX models strengthen both
Khoa Nguyen, Maryl K Wright, Madlin Alzoubi, Thomas Cheng, Margarite D Matossian, Bridgette M Collins-Burow, Matthew E Burow
In the manuscript titled Drug resistance profiling of a new triple negative breast cancer patient-derived xenograft model, our research group generated a novel PDX model TU-BcX-2K1 (2K1 for short) by implanting a piece of primary patient tumor derived from a pre-neoadjuvant 59-year-old Black woman with invasive ductal carcinoma, triple negative subtype, into SCID/Beige mice.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p40-42 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.1.009
Unraveling metabolic signatures in breast cancer: Machine learning for improved therapeutic targeting
Fatemeh Mehdikhani, Parnian Habibi, Sajad Alavimanesh
Background: Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality among women worldwide. Despite advancements in treatment, therapeutic resistance remains a major challenge, necessitating novel approaches for more effective interventions.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p43-50 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.029
ER negative PR positive breast cancer: Revisiting a rare and controversial molecular subtype
Smita Chandra
Estrogen receptor-negative/progesterone receptor-positive (ER-/PR+) breast carcinoma is a rare and controversial subtype that challenges conventional understanding of hormone receptor biology in breast cancer. Traditionally, the expression of progesterone receptors is considered a downstream effect of estrogen receptor activity, making the presence of PR in the absence of ER biologically puzzling.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p51-53 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.030
A rare BRCA1 alternative missense mutation identified in African American women with breast cancer
Desta Beyene, Luisel J. Ricks-Santi, Delisha A. Stewart, Muneer Abbas, Andrea Hayes-Dixon, Ahmed Ali, Olakunle O. Kassim, Robin Williams, Steven Nagel, Babak Shokrani, Robert L. Copeland, Yasmine M. Kanaan
Introduction: Hereditary breast cancer is most commonly caused by inherited mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, which significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p54-62 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.032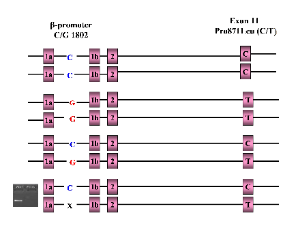
Emerging insights into DNA polymerase epsilon subunit 2 (POLE2) in cancer prognosis and tumour microenvironmental interplay: A comprehensive overview
Kaushik Ahammad, Abu Jihan
DNA polymerase epsilon subunit 2 (POLE2) is a vital component of the DNA polymerase epsilon complex, essential for leading-strand DNA synthesis and maintaining genomic stability. Recent cancer studies have highlighted POLE2's oncogenic importance, as it is overexpressed in breast, lung, liver, and kidney cancers. Elevated POLE2 levels often correlate with poor overall and relapse-free survival, though some cancer types show contradictory associations, suggesting context-dependent roles.
J Breast Cancer Res, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p63-68 | DOI: 10.46439/breastcancer.5.033
