Loading
Archive
2025
2024
2022
2021
2020
Recommended Articles
Osteoarthritis in older adults: Disability associations and the corona virus
Background: Osteoarthritis, a widespread highly painful oftentimes incapacitating joint disease continues to impose immense personal and societal challenges among adults of all ages, especially older adults.
Objective: This review aimed to describe the extent to which older adults with osteoarthritis may suffer excess disability, compared to healthy age-matched older adults, and why this is important to note and prevent in the context of the novel COVID-19 corona virus pandemic.
Effect of senescence on behavior of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells
During lifespan the homeostasis and repair of organs and tissues are guaranteed by the adult stem cell population. Among them, mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), which contain a subpopulation of multipotent stem cells, are emerging as promising candidates for cell therapy of numerous diseases. MSCs are non-hematopoietic cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into osteocytes, adipocytes, and chondrocytes.
Provincial situation of elderly population in Nepal
The world is witnessing a rapid demographic shift towards an aging population. People are living longer due to advances in education, technology, medicine, food distribution, and sanitary conditions. According to the 2011 census data, Nepal had a total of 2,154,003 elderly 60 years and above which accounts for 8.1 percent of the total population of Nepal.
Association between physical function and perceived stress among U.S. Chinese older adults
Objectives: Physical function impairment can cause great stress to older adults. The purpose of the study is to investigate the association between self-reported and directly-observed physical function on perceived stress among U.S. Chinese older adults.
Cultural context and social engagement of Third Age adults
Third Age adults are able to engage in society in ways inaccessible to previous generations of older adults, ways facilitated by today’s unique cultural context of late modernity. The combination of myriad personal strengths and specific cultural context raises the challenge of whether and how these adults want to and can play a role in their societies.
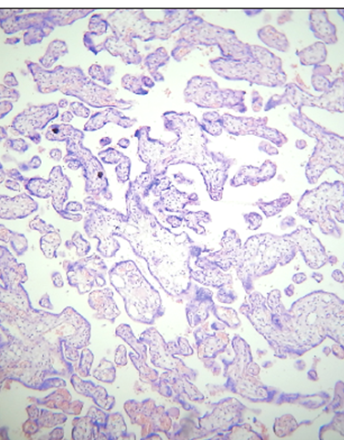
Age-associated hepatic steatosis and liver proliferation in NAFLD
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the growing epidemic which is rapidly increasing in USA. Elderly people are the most affected population which suffers from NAFLD. The earliest stage of NAFLD, hepatic steatosis has no evidence of liver injury, but is characterized by an accumulation of triglycerides in hepatocytes. Hepatic steatosis progresses in age-dependent manner to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis. Mechanisms of development of age associated NAFLD are not well understood and approaches to treat this disease are not developed. Recent studies within last three years; however, provided several lines of evidence showing that although hepatic steatosis strongly correlates with development of NAFLD, it might be not a cause of next steps of NAFLD: fibrosis and NASH. Moreover, some reports suggest that hepatic steatosis might play a protective role in development of fibrosis and NASH. Recent studies of NAFLD in animal models showed that the increase of liver proliferation is the first event in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD.
COVID 19 in Nursing homes
COVID-19 pandemic is a global threat that is having devastating consequences in congregate settings such as nursing homes and assisted facilities around the world. Several measures have been adapted by the nursing home through the guidance of CMS for protecting the most vulnerable population.
Astrogliosis after ischemic stroke: Neuroprotection or neuroinflammation?
Ischemic stroke is the main cause of disability worldwide affecting around 6 million deaths per year. A cascade of events following the ischemic insult induce energy failure, excitotoxicity and release of inflammatory mediators that provoke cell death and brain injury. In this process, astrocytes undergo a change on gene expression that leads to reactive astrocytes.
The ambiguous effects of population aging on macroeconomic stability: A cross-country analysis
While a vast literature has shown that population aging reduces productivity and slows down economic growth, the evidence on the impact of aging on business cycles’ volatility is scarce. Population aging compromises the effectiveness of fiscal and monetary policy and affects the labor market’s dynamics, which may lead to increased macroeconomic volatility.
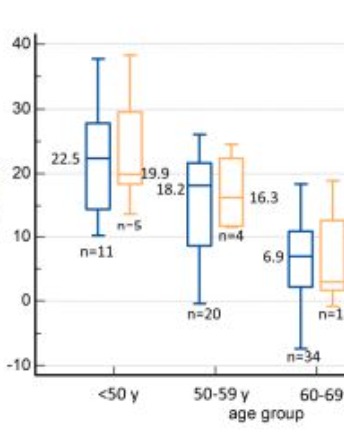
Transcription factor motif activity as a biomarker of muscle aging
In prior work, we analyzed gene expression profiles of mouse, rat and human gastrocnemius muscles to identify conserved regulators of muscle aging processes. By further comparing data obtained from different muscles we found stronger conservation of aging-related factors at the level of molecular pathways than at the level of individual genes.
COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in nursing: Home staff and the need for ongoing education and vaccine access
Objective: To study vaccine hesitancy among health care workers who provide direct care in nursing homes and long-term care facilities which cater to the most vulnerable population of the community.
Modelling a web app to facilitate Family Doctors and General Practitioners screen dementia in general and multicultural population
Background: Though dementia has become a world-wide priority, there is a low recognition rate in primary care settings, mostly due to time constraints and luck of suitable, brief and validated measures. In the case of multicultural population, primary care health systems face a variety of challenges during the diagnostic process. However, thanks to technological advantages, dementia early screening is becoming a key element factor of regular health check-ups.
Implementation study of a Web-App, which facilitates dementia screening for general and multicultural population in primary care settings
Background: Primary care professionals are well positioned to help identify patients at risk of developing dementia, support them and proceed to referral to a specialist. Individuals from multicultural backgrounds belong to a vulnerable group, as they often face underdiagnosis of dementia, for various reasons.
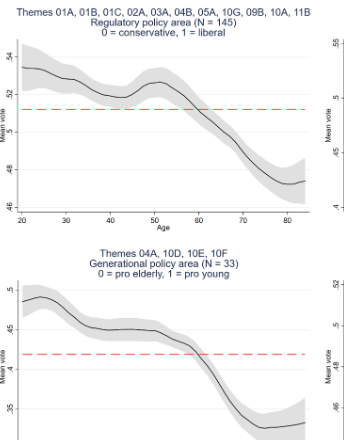
Population ageing and intergenerational conflicts in direct democracy: Separating age from cohort effects
A strong intergenerational divide in voting behaviour has become a frequently reported stylized fact in post-referendum analyses, raising the question of whether myopia of elderly voters is a cause for concern in ageing societies. However, identifying the origins of a generation gap is empirically challenging because age and birth cohort are collinear at any given point in time. Building on a previous study, we summarize how this problem can be overcome. We discuss an unconstrained rank regression approach that allows estimating the causal ageing effect on political attitudes conditional on arbitrary cohort effects in a flexible manner.
A commentary regarding the link between two of today’s biggest global challenges: a rapidly ageing population and energy consumption
Let us talk about a demographic shift that is affecting the modern world. Not only do we observe a rapid population expansion, but also a considerable change in its structure. In the last few decades, the prevalence of low birth rates and higher life expectancy have altered the demographic structure of the population to one that is much older, a phenomenon dramatically changing the shape of the EU age pyramid and making it top-heavy.
The fight against loneliness in old age: A summary of articles and studies – An integrative national plan
“An old man – what does he have in his life? He wakes up in the morning, and the morning does not get up in him. He shuffles to the kitchen and there, the lukewarm water will remind him that at his age … at his age...” [1]. These words by poet David Avidan illustrate the fear that accompanies aging – a fear of loneliness, which is the most prominent foe with which elderly people worldwide must contend.
Can a study that’s not statistically significant be meaningful?
In ongoing efforts to bring innovation to healthcare, technology and patient self-management are at an important intersection. Our study, "A Mobile App for Chronic Disease Self-Management for Individuals with Low Health Literacy: A Multisite Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial” [1], serves as a potentially useful contribution to this intersection by addressing the challenges faced by older adults with chronic conditions and low health literacy in managing chronic health conditions.
Environmental determinants for protein structuring and amyloid transformation
Amyloid transformation under laboratory conditions is achieved by shaking an aqueous solution of any protein. The shaking time varies significantly, demonstrating the variable degree of ease of structural transformation in a given protein. The structural specificity that distinguishes amyloid forms from biologically active proteins is the flatness (two-dimensionality) of the form of each chain in the amyloid fibril.
The role of psychoeducation and yoga in reducing the burden of family caregivers of people with Alzheimer’s disease
The continuous increase in the elderly population and chronic health conditions present significant challenges to healthcare systems, particularly in developing countries. Among these conditions, dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease (AD), is one of the most concerning, causing cognitive decline, behavioral changes, and progressive dependence on family caregivers.
P38 molecular targeting for next-generation kidney damage therapy
p38 MAPK is a multifunctional signaling kinase. It is a responder to stress stimuli performing various pleiotropic functions ranging from maintenance of cellular homeostasis to contributing to cellular dysfunction, depending on the tissue environment. The p38 MAPK family consists of four isoforms: p38α, p38β, p38γ, and p38δ, each with distinct roles in cellular signaling. Among these, p38α is the most extensively studied and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various diseases due to its expression in almost all cellular types [1].