Loading
Archives of Autoimmune Diseases
ISSN: 2767-3340
All Articles
Theory on the involvement of retroviruses and EBV in autoimmunity
Bjørn A. Nexø
There is a striking likeness between an old model for the action of mobile genetic elements in Maize and recent observations on endogenous retroviruses in human Multiple Sclerosis. Nexø discussed this and other developments in his recent theory on autoimmunity. Specifically, in analogy to the onc genes Nexø suggest that insertion of a retrovirus activates a so-called aut gene. This aut gene may well be an EBV genome.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-2 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.001
A unified viral theory of autoimmunity
Bjørn A. Nexø
Retroviruses and EBV have been championed by different schools of thought as inducers of autoimmunity. The present theory suggests ending this competition between schools: They are both right. The viruses synergize! Probably, they even form a hybrid genome.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.2.011
Stromal cells set the myeloma bone marrow on fire
Yubao Wang
Multiple myeloma is a blood-borne cancer with its cell-of-origin in plasma cells or progenitors of plasma cells. In contrast to the extensively studied biology of myeloma cells, the bone marrow microenvironment for myeloma cells remains an uncharted field and poorly understood.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.3.013
COVID-19 and the Liver: Uncovering the Hidden Culprit behind Liver Injury
Zeppieri Marco, Grando Martina
The effects of COVID-19 have been of increasing interest in all fields of medicine after the pandemic, especially considering the important impact and incidence of patients infected with coronavirus. Numerous studies have reported the vast clinical implications related to permanent organ and tissue damage after infection and long COVID.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.4.014
"I see the light": The role of seasonal photo period in the development of immune regulation, a potential explanation for the latitude gradient of autoimmunity and allergy
Margaret S. Clark
Prevalence of common autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease and allergies such as food allergies or eczema affect approximately 20% of the human population.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-6 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.5.016
Adiponectin receptor fragmentation in mouse models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Dylan Frabutt, Natalie Stull, Annie R. Pineros, Sarah A. Tersey, Donalyn Scheuner, Teresa L. Mastracci, Michael J. Pugia
The protein hormone adiponectin regulates glucose and fatty acid metabolism by binding to two PAQR-family receptors (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2). Both receptors feature a C-terminal segment which is released by proteolysis to form a freely circulating C-terminal fragment (CTF) found in the plasma of normal individuals but not in some undefined diabetes patients.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p3-13 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.002
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Rheumatic fever: A classical model of a postinfection autoimmune disease and vaccine perspectives
Luiza Guilherme, Lea Demarchi, Jorge Kalil
Streptococcus pyogenes infection continues to be a worldwide public health problem causing various diseases in humans, including impetigo and oropharyngeal infections that are responsible for the development of rheumatic fever (RF), a multi-organ inflammatory disorder, Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is its major sequel that leads to heart valves lesions, clinically classified as regurgitation and/or stenosis.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p4-6 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.2.012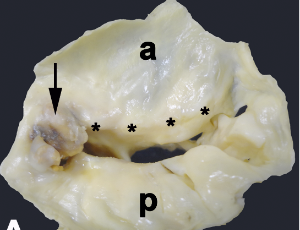
Positive-DAT and autoimmune manifestations in patients with JAK2V617F mutation
Riad Akoum, Rita Chidiac, Joseph Yammine, Michel Saade, Emile Brihi
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) are occasionally associated with autoimmune manifestations. The prevalence of positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) in patients with JAK2V617F mutation is not yet known.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p4-9 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.4.015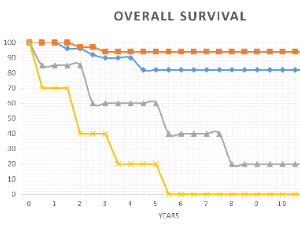
IgG4-related hepatopathy
Pankaj Bansal, Sri Krishna Chaitanya Arudra, Bhavin Sonani, Dhiraj Gulati
IgG4-related disease is a phenotypically heterogeneous systemic autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The described phenotypes of this rare disease include (a) Pancreato-hepatobiliary disease, (b) head-and-neck limited disease, (c) retroperitoneal fibrosis and/or aortitis and (d) Mikulicz’s syndrome with systemic involvement. However, IgG4-related hepatopathy has not been well described in the literature with very few cases reported so far.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p14-16 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.003
Utilization of electronic health records for the assessment of adiponectin receptor autoantibodies during the progression of cardio-metabolic comorbidities
Michael J. Pugia, Meeta Pradhan, Rong Qi, Doreen L. Eastes, Anna Vorsilak, Bradley J. Mills, Zane Baird, Aruna Wijeratne, Scott M. McAhren, Amber Mosley, Anantha Shekhar, Daniel H. Robertson
Diabetes is a complex, multi-symptomatic disease whose complications drives increases in healthcare costs as the diabetes prevalence grows rapidly world-wide. Real-world electronic health records (EHRs) coupled with patient biospecimens, biological understanding, and technologies can characterize emerging diagnostic autoimmune markers resulting from proteomic discoveries.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p17-27 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.004
Cxcl17 and its association with T cells
Marcela Hernández-Ruiz, Albert Zlotnik
We recently published an article describing the importance of CXCL17 in T cell responses [1]. In summary, we observed the following:
1) Cxcl17 is necessary to maintain normal ratios of T cell subpopulations in lymph nodes (LN).
2) Cxcl17-/- mice develop more intense inflammatory responses than wild type mice.

iBALT and nodular lymphoid hyperplasia in TNF-overexpressing mice
Elise Clayer, Philippe Bouillet
In response to any danger signal, cytokines are promptly secreted to help fight back the attackers. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is one of the most potent inflammatory cytokines and its expression is tightly regulated to prevent uncontrolled inflammation. We have shown that three regulatory elements located in Tnf 3’untranslated region (3’UTR) cooperate post-transcriptionally to maintain low levels of Tnf expression during homeostasis.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p32-36 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.006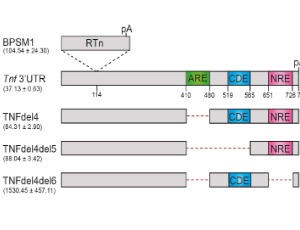
Role of estrogen in neuroimmunomodulation in the periphery and onset of autoimmune dysfunction
Rahul S. Nair, Hannah P. Priyanka
Maintenance of neuroendocrine-immune homeostasis is tightly regulated by the active involvement of neural, endocrine and immune mediators. As age progresses, this bidirectional regulation losses its robustness due to the influence of several factors especially, gonadal hormones. Among the hormones, estrogen has gained significant attention due to its diverse effects as a potent modulator on the cellular and systemic level which influences both physiological and psychological functions.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p37-43 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.007
The Role Of IL-16 As a lymphocyte attractant appears to be conserved through phylogeny: preliminary evidence that recombinant human IL-16 preferentially attracts regulatory lymphocytes in the amphibian, Xenopus Laevis
Acadia L. Kopec, Zak E. Michaud, Gregory D. Maniero
IL-16 is a pleiotropic, pro-inflammatory cytokine that induces regulatory CD4+ T cells to migrate to a site of inflammation or tissue damage. IL-16 is a ligand for CD4 and binds at the proximal, D4 region well outside of the binding site for MHC class II.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p44-48 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.008
Occurrence of cervical spine arthritis highly responsive to adalimumab in a patient with psoriatic peripheral arthritis and longstanding remission while on etanercept therapy
Giuseppe Provenzano, Maria Concetta Miceli, Livia Bruno, Chiara Arcuri
Cervical spine involvement frequently occurs in patients with Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) even in absence of sacroiliitis. Long disease duration, high disease activity in the first five years and presence of peripheral involvement are all predictors of this peculiar articular involvement.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p49-53 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.009
Opsoclonus myoclonus syndrome and hyper IgM syndrome in the pediatric patient: A nonimmunosuppressive approach
Cynthia M. Wong, Irim Salik
Opsoclonus myoclonus syndrome (OMS), also known as Kinsbourne Syndrome, is a rare disorder affecting the central nervous system. It presents clinically with ataxia, diffuse or focal muscle spasms, and rapid, irregular eye movements.
Arch Autoimmune Dis, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p54-57 | DOI: 10.46439/autoimmune.1.010
