Loading
Cell Signaling
ISSN: 2837-8253
Featured Articles
PDE4 inhibition and enhancement of human memory and cognition
Graeme B. Bolger
Two distinct, but intertwining, threads of inquiry have demonstrated that the PDE4, or cAMP-selective, phosphodiesterases, have an essential role in human cognition, learning and memory. Study of genetically-modified preclinical models, and of humans with mutations in the PDE4D gene, has provided some of the most rigorous proof of the importance of PDE4 signaling in the CNS. More recently, clinical trials of PDE4-selective inhibitors have shown promising clinical activity in disorders of cognition and memory.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-9 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.048
Biomarkers for monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR in NSCLC: Challenges, current status, and future perspectives
May-Lucie Meyer, Fred R. Hirsch
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths [1]. However, significant improvements in the past decades have been achieved with improved outcomes [2-4]. Several mutations have been described as promoters of oncogenesis, and specific treatments are available, including those for Epidermal Growth Factor (EGFR) mutations [4].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 2, Issue 1, p14-22 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.024
Recombinant protein synthesis and isolation of human interferon alpha-2 in cyanobacteria
Anastasios Melis, Bharat Kumar Majhi
Interferons (IFNs) are a class of small immunological proteins that are secreted by infected cells during viral or bacterial infections to combat and prevent infection propagation [1]. They play important roles in triggering signal cascade processes inside the cell that activate other immune cells and limit viral multiplication.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p23-26 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.051
Do arrestin oligomers have specific functions?
Vsevolod V. Gurevich
Arrestins were discovered as key players in the conserved two-step homologous desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): they specifically bind active phosphorylated GPCRs, precluding their coupling to cognate G proteins, thereby stopping (“arresting”) G protein-mediated receptor signaling [1].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 1, Issue 1, p42-46 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.009
Intracellular signaling mechanism of sweat secretion by PACAP
Michio Yamashita, Junko Shibato, Randeep Rakwal, Naoko Nonaka, Fumiko Takenoya, Seiji Shioda
Sweat, an exocrine fluid secreted (sweat gland tissue of the eccrine and apocrine glands) by skin has an indispensable function for regulating body temperature and skin hydration [1]. The eccrine gland performs 90% of sweat secretion and secretory fluid of eccrine glands consists of 99% water and 1% inorganic substances.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 2, Issue 1, p86-89 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.035
Del(5q) MDS and erythroid maturation
Alfredo Fallorina, Tuoen Liu
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are acquired neoplastic myeloid proliferations in the bone marrow, where hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are impacted. MDS are characterized by clonal proliferation of HSCs, recurrent genetic abnormalities, progressive cytopenia, increased risk of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and myelodysplasia [1].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 2, Issue 1, p90-95 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.036
Accelerating metal nanocluster synthesis: A high-throughput approach with machine learning assistance
Li Tang, Shuxin Wang
Metal nanoclusters, consisting of a few to a few hundreds of metal atoms, have been of great scientific interest due to their potential applications in areas like bio-labeling and catalysis [1-9].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 2, Issue 1, p108-112 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.040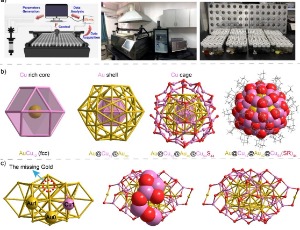
The interplay of regulatory T cells, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and unfolded protein response activation in post-transplant alloimmune hepatitis and autoimmune hepatitis
Kumar Subramanian, Udeme D. Ekong
The incidence and prevalence of autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) globally is 1.28 per 100,000 population-years (95% CI, 1.01-1.63) and 15.65 per 100,000 population (95% CI, 13.42-18.24), respectively [1]. The incidence and prevalence in children is 0.4 and 3.0 cases per 100,000 children [2], and in adults 17 per 100,000 [3,4].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 2, Issue 1, p120-125 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.042
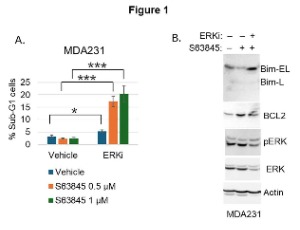
Potential biomarkers for MCL1 inhibitor sensitivity
Lei Duan, Carl G. Maki
Myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL1) is an anti-apoptotic member of the B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL- 2) family and plays a key role in cancer cell survival and resistance to therapy [1,2]. MCL1 is often
overexpressed in cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and solid tumors, allowing cancer cells to evade apoptosis and resist conventional treatments.