Loading
Cell Signaling
ISSN: 2837-8253
All Articles
Unlocking the significance of CD226 in cancer
Weili Sun
CD226 is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a well-defined structural organization, which is primarily expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, cytotoxic T cells, and some subsets of B cells [1,2]. Its primary structure consists of an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail [1]. Each of these domains contributes to the protein's overall function.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.021
EGCG modulates nuclear formaldehyde-induced Tau phosphorylation in neuronal cells
Shweta Kishor Sonawane, Anshu Raina, Amitabha Majumdar, Madhura Chandrashekar, Subashchandrabose Chinnathambi
Tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease is known to hamper several cellular functions including microtubule dynamics, proteostasis etc. Tau is a microtubule-stabilizing protein, playing an important role in maintaining the integrity of the axonal microtubules [1,2].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.001
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
PDE4 inhibition and enhancement of human memory and cognition
Graeme B. Bolger
Two distinct, but intertwining, threads of inquiry have demonstrated that the PDE4, or cAMP-selective, phosphodiesterases, have an essential role in human cognition, learning and memory. Study of genetically-modified preclinical models, and of humans with mutations in the PDE4D gene, has provided some of the most rigorous proof of the importance of PDE4 signaling in the CNS. More recently, clinical trials of PDE4-selective inhibitors have shown promising clinical activity in disorders of cognition and memory.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-9 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.048
Friend or foe? The elusive role of ANGPTL4 in inflammation
Yueqi Zhang, MD, Yueqi Zhang, MD, Lei Dai, MD
Angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) is a multifaceted secreted protein discovered by three different institutions in 2000 simultaneously [1]. It is expressed in adipose tissues, liver, muscle, heart, kidney, skin, and other tissues. The nutritional, metabolic, and inflammatory status of the organism regulate the expression of ANGPTL4 [2-4].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p5-9 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.022
Review of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Challenges, diagnostics, management, and pathophysiology
Michael Goutnik, Ramya Reddy, Sandra Yan, Brandon Lucke-Wold
Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae (sdAVFs) are rare (5-10 per million per year), often misdiagnosed vascular lesions most commonly found in the thoracolumbar spine [1-7]. These lesions commonly present with progressive myelopathy in male (approximately 80%) patients who are usually in their 7th decade of life [3-6,8].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p9-13 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.002
Commentary: Interferons in Influenza and Streptococcus Pneumoniae co-pathogenesis
Sunil Palani, Keer Sun
Influenza A virus (IAV) and Streptococcus pneumoniae (SPn) are two major respiratory pathogens in humans. IAV infection alone is often self-limited, and SPn colonization can be found in 5-90% of healthy individuals, as normal flora [1,2].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p10-13 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.023
Cellular conversations at the crossroads of health and disease
Anne-Sophie Armand, Patrice X. Petit
The first issue of Cell Signaling in 2025 provides an interdisciplinary overview of cellular communication, covering topics ranging from neuronal and metabolic regulation to immune evolution and regenerative processes. The studies featured in this volume collectively demonstrate how signaling pathways govern the delicate, finely tuned balance between adaptation and dysfunction, and how their manipulation continues to inspire biotechnological and therapeutic innovation.
Cell Signal, 2026, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p10-13 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.4.088
The extract of Nicotiana glauca induces apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells
Lucía Pronsato, Lorena Milanesi, Andrea Vasconsuelo, Natalia Frattini, Nicolás Blanco
Cancer is a leading cause of childhood mortality, with rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) being the most prevalent type diagnosed in approximately two-thirds of pediatric cancer cases, particularly the embryonal subtype. RMS represents the most common soft tissue sarcoma in children and adolescents, accounting for around 2-3.5% of all pediatric malignancies [1].
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p10-18 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.049
Effects of salt on A2A adenosine receptors expression and function: in vitro approach and pathophysiological perspectives
Farid El Oufir, Aboubacar Sow, Claire Guiol, Marion Marlinge, Aissatou Pethwol Bah, Nathalie Kipson, Christine Criado, Marie-Charlotte Chaptal, Simon Lledo, Julia Dodivers, Julien Fromonot, Jean Ruf, Régis Guieu, Giovanna Mottola
Salt (sodium chloride) and A2A adenosine receptors (A2AR) have both been implicated in blood pressure regulation. While high salt consumption raises blood pressure, A2AR is a key mediator of coronary vasodilation. Although a sodium ion binding pocket has been identified in A2AR, the physiological link between salt and A2AR remains poorly investigated. Hereby, we explored how salt modulates its expression and function in vitro.
Cell Signal, 2026, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p14-20 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.4.089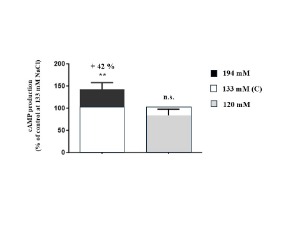
Perspective study of UPR signaling molecules as potential biomarkers in bone metabolism
Yiming Pan, Kaiwen Liu, Yuanlan Ye, Mengtian Fan, Xiaoli Li, Fengjin Guo
The skeletal system consists mostly of extracellular matrix and mineral salts. Osteoblasts and chondrocytes create enormous amounts of extracellular matrix proteins for skeletal systems to grow and sustain. Many skeletal metabolism related proteins are produced by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and secrete outside cell membrane then form to extracellular oligometric matrix proteins and collagens.
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p14-21 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.003
Biomarkers for monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR in NSCLC: Challenges, current status, and future perspectives
May-Lucie Meyer, Fred R. Hirsch
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths [1]. However, significant improvements in the past decades have been achieved with improved outcomes [2-4]. Several mutations have been described as promoters of oncogenesis, and specific treatments are available, including those for Epidermal Growth Factor (EGFR) mutations [4].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p14-22 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.024
Cognitive impairment in hemodialysis needs sufficient attention
Jun Liu, Yani He, Kehong Chen
Hemodialysis is the most common form of kidney replacement worldwide. It is expected that the acceptance rate of hemodialysis will continue to increase in the coming decades [1]. About 89% of dialysis patients worldwide receive hemodialysis. The majority of these patients are living in high-income countries or middle to high-income countries such as Brazil and South Africa.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p19-22 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.050
Emerging hallmarks of GEMIN5 in neurodevelopmental disease
Encarnacion Martinez-Salas, PhD, Salvador Abellan, Rosario Francisco-Velilla
GEMIN5 is a modular RNA-binding protein responsible for the recognition of snRNAs through its WD40 domain placed at the N-terminus. A dimerization module at the central region of the protein acts as a hub for protein-protein interaction, and a non-canonical RNA-binding domain is placed towards the C-terminus. Recent studies reported loss of function Gemin5 biallelic variants which develop cerebellar ataxia, hypotonia and neurodevelopmental delay, indicating that GEMIN5 deficiency is detrimental for survival.
Cell Signal, 2026, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p21-24 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.4.090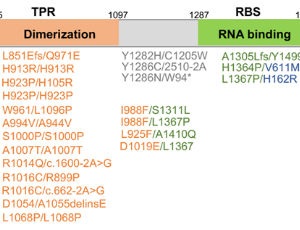
Selecting ideal combined immunotherapy for treating HCC
Rui Han, Lingeng Lu
The discovery of proper sensitizers for immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment represents a significant breakthrough in the field of cancer therapy, but it is still in initial stage [1,2].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p22-24 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.004
Recombinant protein synthesis and isolation of human interferon alpha-2 in cyanobacteria
Anastasios Melis, Bharat Kumar Majhi
Interferons (IFNs) are a class of small immunological proteins that are secreted by infected cells during viral or bacterial infections to combat and prevent infection propagation [1]. They play important roles in triggering signal cascade processes inside the cell that activate other immune cells and limit viral multiplication.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p23-26 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.051
Molecular docking combined with in vitro validation study to explore the effect of lupenone on alleviating renal fibrosis based on TGF-?/Smad/CTGF signaling pathway
Xiangpei Wang, Hongyun Liu, Xiaofen Li, Mei Zhang, Feng Xu, Mei Liu, Hongmei Wu
According to the global epidemiological report on chronic kidney disease (CKD) published by The Lancet, CKD is recognized as a global public health problem with high morbidity and mortality [1]. Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the most main microvascular complication of diabetes and is one of the leading causes of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and CKD [2].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p23-34 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.025
Current advances and future directions in cell signaling: redox communication and emerging therapeutic paradigms
Andrea Albieri-Borges
Cell signaling represents a highly coordinated molecular dialogue that governs cellular behavior and tissue homeostasis. Among its many facets, redox signaling has emerged as a pivotal mechanism, transforming our understanding of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from mere metabolic byproducts to essential messengers [1]. Historically associated with oxidative stress and cellular damage, ROS are now recognized as regulators of physiological processes through reversible oxidation of cysteine residues in proteins.
Cell Signal, 2026, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p25-27 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.4.091
Radiation induced molecular signalling in the cells: A real struggle between death or breathe
Raj Kumar
Radiation is omnipresent in the universe. Since the primitive period, chemical evolution led to a biological evolution somehow driven by the ionizing and non-ionizing radiation on the Earth’s atmosphere [1,2].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p25-28 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.005
NUB1 protein localization as a prognostic modifier in ER-negative breast cancer
Ka-Liong Tan, Francesco Pezzella
Breast cancer remains a heterogeneous disease in which prognostic stratification, particularly within estrogen receptor (ER)-negative subtypes, remains clinically challenging. While genomic and transcriptomic profiling have advanced risk classification, protein-level regulation and subcellular localization are rarely incorporated into prognostic frameworks. NEDD8 ultimate buster 1 (NUB1) is a proteostasis-associated protein involved in degradation of ubiquitin-like modifiers and regulation of cell-cycle progression.
Cell Signal, 2026, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p28-30 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.4.092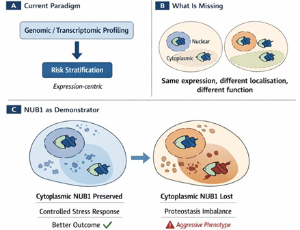
Approach to testicular adrenal rest tumors in children and adolescents with congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Sirmen Kizilcan Cetin, Zehra Aycan
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a disorder affecting cortisol biosynthesis in the adrenal cortex [1]. 21-hydroxylase deficiency is the most frequent reason for CAH, with an incidence between 1:10.000 and 1:20.000 [2]. Due to the lack of enzyme function, patients with any enzyme deficiency cannot synthesize cortisol effectively.
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p29-34 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.006
Development of an error-corrected next-generation sequencing method for the quantification of hotspot cancer driver mutations
Kelly L. Harris
Low-frequency somatic mutations accumulate in normal tissues throughout life and contribute to cancer initiation, yet their detection is limited by the sensitivity of conventional sequencing methods. We describe CarcSeq, an error-corrected, targeted next-generation sequencing platform developed to quantify rare cancer driver mutations (CDMs) at variant allele frequencies as low as ~10-4. CarcSeq integrates high-fidelity amplification, unique molecular identifiers, and single-strand consensus sequencing to accurately measure mutant frequency (MF) across a curated panel of sequences encompassing recurrent oncogene and tumor suppressor hotspots.
Cell Signal, 2026, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p31-36 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.4.093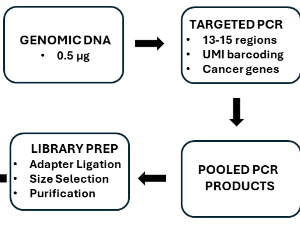
Insights into early acne pathogenesis: Exploring intercellular dynamics and key dysregulated genes
Min Deng, Kiana Farahani, George W. Agak
Acne vulgaris, the most common skin condition worldwide, affects over 85% of adolescents, with nearly half continuing to experience it into adulthood. The Scarring and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation associated with acne can profoundly impact mental health and self-esteem, underscoring the importance of early and effective treatment [1].
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p32-39 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.053
Aiming for the brain: a new thermogel-based drug delivery platform
Mario Chiariello, Lisa Gherardini
The design of safe drug delivery systems that locally allow efficacious concentration of curative molecules has become the latest frontier in nanomedicine. It usually relies on the entrapment of drugs into micro/nano carriers guaranteeing for the controlled release of the drugs while protecting them from degradation and fast clearance.
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p35-37 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.007
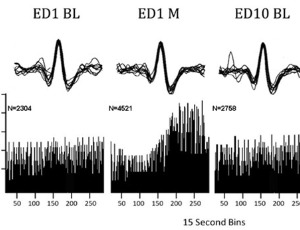
Methylphenidate (Ritalin) affects serotoninsignaling differently in young compared to adults. Concomitant behavioral and neuronal recording from dorsal raphe in freely behaving rats
Elizondo GM, Raymond A, Perez-Vasquez C, Dafny N
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a complex behavioral disorder characterized by hyperactivity, increased impulsivity, and inattention [1-3]. Methylphenidate (MPD) is the most
commonly prescribed psychostimulant for management and treatment of ADHD [3-7].
Comment on “Hsa_Circ_0105596/FTO inhibits progression of Parkinson’s disease by sponging miR-187-3p and regulating eEF2”
Taoli Liu, Shumin Cheng, Qingqing Zhu
Parkinson’s disease (PD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by clinical features such as bradykinesia and resting tremor. It is characterized by specific neuropathological changes. These changes include the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) pars compacta.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p40-41 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.054
Do arrestin oligomers have specific functions?
Vsevolod V. Gurevich
Arrestins were discovered as key players in the conserved two-step homologous desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): they specifically bind active phosphorylated GPCRs, precluding their coupling to cognate G proteins, thereby stopping (“arresting”) G protein-mediated receptor signaling [1].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p42-46 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.009
The role of stress granules in heavy metal-induced carcinogenesis
Rukayat Aromokeye, Megan Carver, Haining Zhu, Lei Wang
Stress granules (SGs) are dynamic, membraneless organelles that assemble in response to cellular stress, such as oxidative stress, hypoxia, or nutrient deprivation [1,2]. Protein translation typically is halted under stress conditions, leading to assembly of SGs containing mRNAs, RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), and other proteins.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p43-46 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.055
Immune-enhanced nanocomposites provide hope for drug-resistant infection treatment
Tao Zhang, Mo Chen, Sagit Makhanov, XianZuo Zhang, Yao Luo, Chen Zhu
Antibiotic misuse contributes to the emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms, resulting in infections that cause over one million deaths annually [1-3]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop new antimicrobial methods. Traditional antibiotic therapy is often incomplete due to the emergence of drug-resistant strains, leading to relapse.
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p47-50 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.010
Deciphering Notch signaling notch by notch
Lidia Borkiewicz, Adolfo Rivero-Müller
The NOTCH receptors are mechanosensing proteins that require cell-cell contact and physical force for activation. While most receptors have evolved to respond to one or a few unique ligands, the four NOTCH receptors can respond to any of the five Delta/Serrate/Lag-2 (DSL) ligands - Jagged (JAG) 1, 2, and Delta-like (DLL) 1, 3, 4 [1].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p51-56 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.011
Camping in the backyard: Identifying extracellular matrix targeting ligands using yeast surface display
Benjamin J Umlauf
Camping trips are often a lot of work, especially with children. Purchasing supplies, finding a location, and dealing with scary animals are often just too much. Inspired by so many films, my family instead set up a tent to camp in the backyard.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p54-57 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.027
The role of circulating anti-aging αKlotho in cardiac aging
Dong I Lee, Dao-Fu Dai
Aging is an inevitable biological process that significantly affects various organs, including the heart. Cardiac aging, with its associated structural and functional changes, can lead to left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, increased arterial stiffness, and reduced overall cardiac functional reserve [1,2].
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p54-58 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.057
A vicious cycle happened in the progress of hyperhomocysteinemia, the same may exist in the development of cancer
Chenghua Luo, Dengyu Ji, Wen Wang
Homocysteine (Hcy) metabolism is at the intersection of two metabolic pathways: remethylation and trans-sulfuration, which abnormality can result in hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy). In the past few years our team has been working on the molecular mechanism of HHcy development.
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p57-60 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.012
An essential role for hepatocyte adenosine kinase in regulating fat metabolism and inflammation
Jiayu Yu, Juan Zheng, Chaodong Wu
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is comprised of a spectrum of conditions, which is a progressive form of liver disease ranging from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis. The liver regulates fat metabolic homeostasis through de novo lipogenesis, fatty acid uptake and oxidation, low-density lipoprotein secretion in hepatocytes.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p58-60 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.029
The combination of TSPO ligands and CDK1 inhibitors may be a novel approach for the treatment of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
Xingnan Zhang, Song Liu
MPNSTs are aggressive Schwann cell-derived sarcomas, frequently associated with NF1 mutations. Traditional treatments, including surgery and chemotherapy, are largely ineffective, highlighting the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies. NF1 loss leads to RAS pathway activation, which in turn activates multiple signaling cascades, including RAF-MEK-ERK1/2, PI3K-AKT, and RalGDS pathways. Inhibition of these pathways has been explored, with MEK inhibitors, such as selumetinib, showing some promise in clinical trials (NCT03433183).
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p59-63 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.058
Commentary to: Anti–miR-93-5p therapy prolongs sepsis survival by restoring the peripheral immune response
Gabriel Lopez-Berestein, M.D
The major message of this manuscript is that miR-93-5p is a potential therapeutic target in sepsis through the regulation of both innate and adaptive immunity, with possibly a greater benefit for elderly patients than for young patients.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p61-61 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.030
The value of EGFR in individualized treatment for brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer
Li Tan, Juan Ren
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a member of the ErbB family. It is involved in biological processes such as cell proliferation, angiogenesis, inhibition of apoptosis, adhesion, metastasis, and is associated with the progression of lung cancer [1-3].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p69-71 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.014
Sirt1-mediated deacetylation in MAFLD: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
Libang Chen, Qian Lu, Tingting Yang
Apart from alcohol and other definitive factors, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), formerly known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a clinicalpathological syndrome characterized by hepatic steatosis and lipid accumulation.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p69-75 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.060
HK2 fuels anoikis resistance to accelerate ICC metastasis
Xiaojing Du, Sunkuan Hu
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), the second most frequent primary liver tumor, is a highly metastatic malignancy and often leads to disaster outcome in majority of patients, bringing significant challenges in the medical field [1].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p71-73 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.032
Development of an authentic light-activated calcium channel
Wenyu Li, Liuqing Wang, Youjun Wang, Lian He
Optogenetics utilizes the fusion of naturally occurring light-sensing proteins with target proteins to induce conformational changes, oligomerization, or dissociation in response to illumination of light with specific wavelengths.
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p72-75 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.015
Are the N-terminal derivatives of IGF-I neuropeptides agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease?
Laura M. Frago, Sandra Canelles, Vicente Barrios
Alzheimer´s disease (AD) is a devastating disease caused by the accumulation and interaction of tau-containing neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid beta peptide (Aβ) plaques in the brain [1,2].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p74-79 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.033
A new role of dopamine receptor D2 agonist ropinirole: Targeting NAT10 for treating periodontitis
Jiahui Tan, Jialei Wu, Lufei Wang
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects more than 40% of the adult population aged over 30 years in the United States, indicating a high prevalence [1]. It impairs the integrity of the tooth-supporting tissue with clinical manifestations featured of gingiva bleeding, periodontal ligament degradation, and alveolar bone resorption. Periodontitis is a multifactorial disease, involving interactions of bacterial pathogens, host immune responses and environmental factors such as smoking [2].
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p76-79 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.061
GABA fluctuations driven by astrocytic Glu-GABA exchange explain synaptic acuity
László Héja, Julianna Kardos
Gliocentric paradigms showcase functional association of neurons with astrocytes, as in tripartite glutamatergic synapses. Astrocytes, activated by Glu:3Na(+) symport apply GABAergic inhibitory feedback on synaptic excitation via GABA efflux by GAT-3 reversal and subsequent GABAA activation (astrocytic Glu/GABA exchange [1-3]).
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p76-80 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.016
Complex actions of amyloid beta on hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis
Jaehoon Song, Inhee Mook-Jung
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive cognitive decline and memory impairment. One of the key pathological hallmarks of AD is the accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ), a peptide derived from the sequential cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β- and γ-secretases .
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p80-84 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.062
Modulation of mitochondrial gene expression by testosterone in skeletal muscle
Lucía Pronsato, Lorena Milanesi, Andrea Vasconsuelo
Testosterone plays a crucial role in determining the body composition of male mammals, including humans, due to its effects on muscle and fat mass. Age-related declines in serum testosterone levels in men have been linked to loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, and physical performance [1-4].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p80-85 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.034
Commentary: Role of estrogen receptor β in kidney disease
Wen Su, Rong Cao, Qijun Wan, Hui-yao Lan
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has become a growing global health challenge, impacting over 800 million individuals worldwide [1]. Numerous evidences have shown that women are more resistant to CKD than men before menopause, however this beneficial effect is diminished in those with post-menopause, highlighting the pivotal role of estrogen in kidney disease [2-5].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p81-84 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.017
In search for molecular mechanisms of Post COVID-19 vascular damage
Sarah Halawa, Yasmine Aguib, Magdi H Yacoub
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the world has changed significantly with newchallenges constantly arising (Figure 1) [1]. One of the main challenges is the increased prevalence of a prolonged post-COVID-19 syndrome, widely known as "Post COVID", which is currently regarded as a public health issue worldwide [2].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p85-89 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.018
Engineered Ag135Cu60 nanoclusters with buckminsterfullerene topology: Structure and optical dynamics
QiKai Han, Li Tang, Shuxin Wang
Metal nanoclusters, serving as a mesoscopic bridge between discrete atoms and bulk materials, have emerged as a frontier in the convergence of coordination chemistry and material science.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p85-89 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.063
Intracellular signaling mechanism of sweat secretion by PACAP
Michio Yamashita, Junko Shibato, Randeep Rakwal, Naoko Nonaka, Fumiko Takenoya, Seiji Shioda
Sweat, an exocrine fluid secreted (sweat gland tissue of the eccrine and apocrine glands) by skin has an indispensable function for regulating body temperature and skin hydration [1]. The eccrine gland performs 90% of sweat secretion and secretory fluid of eccrine glands consists of 99% water and 1% inorganic substances.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p86-89 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.035
Pathogenic contribute of unaffected cardiac cells in female Fabry cardiomyopathy
Andrea Frustaci, MD, Romina Verardo, PhD, Cristina Chimenti, MD
Cardiac hypertrophy is one of the most common manifestations of Fabry disease (FD) [1] and it can be the only clinical expression, in the so called cardiac variant, as result of specific mutation of
alpha-galactosidase-A gene (GLA), as the N215S one [2].

Regulating ferroptosis by glutathione s-transferases: From mechanistic to potential therapeutic targets
Yanyun Shi, Qi Yao
Ferroptosis is a type of cell death caused by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. In recent years, certain isoforms of glutathione-S-transferases (GSTs) have been identified that may play a key role in regulating ferroptosis. Previous study demonstrated that the NRF2/GSH/GST/RLIP76 and MRP1 axis acts as an independent anti-ferroptosis pathway. Furthermore, this study evaluated the therapeutic potential of mifepristone (RU486) for mitigating acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury in vivo.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p90-94 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.064
Del(5q) MDS and erythroid maturation
Alfredo Fallorina, Tuoen Liu
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are acquired neoplastic myeloid proliferations in the bone marrow, where hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are impacted. MDS are characterized by clonal proliferation of HSCs, recurrent genetic abnormalities, progressive cytopenia, increased risk of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and myelodysplasia [1].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p90-95 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.036
Probes for cancer metastasis imaging and therapeutic targeting
Suridh Adhikari, Ali Azhdarinia, Mikhail G. Kolonin
Metastasis of cancer is the process by which the primary tumor spreads from the original site to other parts of the body. Palliative care is the most common treatment option available for patients with metastatic cancer, but most patients eventually succumb to the disease due to the lack of therapeutics that can specifically target disseminated tumors [1].
Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p92-94 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.1.020
Beyond single targets: Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress, ferroptosis, and vitamin D signaling in stroke treatment
Yifeng Zhang, Xiaolu Wang, Zimeng Chen, Yanqiang Wang
Stroke remains a leading cause of death and long-term disability worldwide, with ischemic stroke representing approximately 85% of all stroke cases. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury significantly exacerbates neuronal damage through mechanisms such as oxidative stress, ferroptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS).
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p95-102 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.065
Inhibitory potential of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn extract on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
Rakesh Sahu, Bhaskar Sahu
The lotus or Indian lotus has a rich history of traditional use in various cultures for its medicinal properties [1,2], with the increasing prevalence of diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and inflammatory conditions, there is a growing interest in exploring natural products for their therapeutic potential [3-6].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p96-101 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.037
Can a mouth wash prevent atherosclerosis and ischemic stroke?
Lizymol P.P
Poor oral health, particularly gum disease, has been linked to an increased risk of atherosclerosis and ischemic stroke. The theory behind this connection is that the bacteria involved in gum disease can enter the bloodstream and contribute to inflammation in the arteries, potentially promoting the development of atherosclerosis.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p102-103 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.038
Revisiting the effects of curcumin on postmenopausal women’s health—insights from a systematic review and meta-analysis
Dachuan Jin, Shunqin Jin
The myriad health issues triggered by hormonal changes in postmenopausal women have garnered increasing attention in recent years. Among various nutraceuticals and phytoestrogens, curcumin—a bioactive compound derived from Curcuma longa—has emerged as a promising candidate due to its favorable safety profile, multi-targeted biological activities, and growing evidence supporting its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic benefits.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p103-105 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.066
Coloring outside the lines: Exploring the dysbiotic impact of azo dyes on gut health and inflammation
Hanan Salah El-Abhar, Marwa Ali-Tammam, Sara Ahmed Zahran, Amal Emad Ali, Suzan Mohamed Mansour
Beyond mere aesthetics, the vibrant hues of fruits, vegetables, and culinary creations evoke sensory experiences that influence perceptions of flavor, freshness, and even nutritional value. This concept highlighted the pivotal role that color can play in the realm of food, serving as a powerful tool to captivate consumers and entice their taste buds.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p104-107 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.039
Gut microbiota-immunity interaction and personalized immune response
Chien Dinh Huynh
As presented in our previous article, the human immune system is built upon a genetic framework passed down through countless generations. Traditional dietary habits rooted in specific ethnicities have fostered profound immune diversity, enabling adaptation to harsh environmental conditions and ultimately ensuring survival. Consequently, it’s evident that each individual’s immune characteristics are uniquely shaped by a combination of racial background, environmental exposure, and dietary practices.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p106-110 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.067
Accelerating metal nanocluster synthesis: A high-throughput approach with machine learning assistance
Li Tang, Shuxin Wang
Metal nanoclusters, consisting of a few to a few hundreds of metal atoms, have been of great scientific interest due to their potential applications in areas like bio-labeling and catalysis [1-9].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p108-112 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.040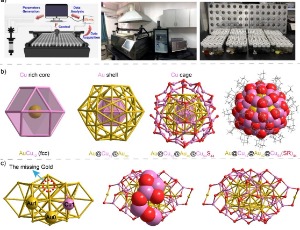
NCAM1: A newly discovered immune checkpoint in molluscs and its functions in immune regulation
Muchun He, Renle Chang, Jiejie Sun, Linsheng Song
Natural killer cells (NK cells), a unique subset of cytotoxic lymphocytes, play pivotal roles in immune defense through directly recognizing and eliminating pathogen-infected cells or cancer cells. Currently, NK cells have been identified in humans, mice, and teleost fishes. However, the existence, identification and functional characterization of NK-like cells in invertebrates remain poorly understood. Studies in Drosophila [6] and shrimp [7] had revealed that their undefined type of hemocytes analogous to vertebrate NK cells had direct cytotoxic activity against invading pathogens or abnormal cells.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p111-114 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.068
Sample multiplexing in CyTOF: Path to optimize single-cell proteomic profiling
Muharrem Muftuoglu, Michael Andreeff
In biomedical research, achieving single-cell resolution in investigation of cellular systems is of paramount importance. Ongoing research efforts to explore and decode the heterogeneity in cellular phenotype, functionality, genomics, epigenetics, and transcriptomics in biological systems have propelled significant technological advancements through innovative breakthroughs [1-3].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p113-119 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.041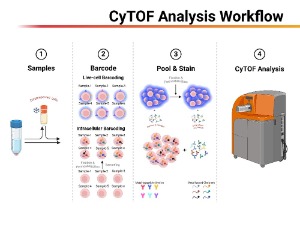
Hepatic stellate cells as RSPO3-Wnt/β- catenin hubs governing liver zonation and regenerative capacity
Qiang Yang, Chunsheng Lin, Ying Cai, Chao Wang, Zhibo Wang, Sifan Guo, Shi Qiu, Aihua Zhang
The liver emerges as an ultimate metabolic nexus—a polyfunctional organ that simultaneously performs biochemical detoxification, macromolecular processing, and systemic nutrient governance. While hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) were historically confined to their fibrogenic identity, their broader homeostatic orchestration remained enigmatic. RSPO3 as a linchpin in hepatocyte dynamics, with targeted pharmacological modulation enhancing hepatic lobular repatterning, regenerative capacity, and metabolic optimization.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p119-122 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.070
The interplay of regulatory T cells, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and unfolded protein response activation in post-transplant alloimmune hepatitis and autoimmune hepatitis
Kumar Subramanian, Udeme D. Ekong
The incidence and prevalence of autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) globally is 1.28 per 100,000 population-years (95% CI, 1.01-1.63) and 15.65 per 100,000 population (95% CI, 13.42-18.24), respectively [1]. The incidence and prevalence in children is 0.4 and 3.0 cases per 100,000 children [2], and in adults 17 per 100,000 [3,4].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p120-125 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.042
From mitosis to mutagenesis: Chromosomal passenger proteins at the crossroads of replication stress and cancer resilience
Shirley K. Knauer, Roland H. Stauber
The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC), comprising Survivin, Aurora B kinase, INCENP, and Borealin, is classically known for its essential functions during mitosis. However, recent findings expand the CPC's role beyond cell division, uncovering novel functions in replication stress response and genome stability maintenance.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p123-129 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.071
Chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and antiangiogenesis: Emerging trends in the comprehensive treatment of advanced gastric cancer
Yuting Ding, Hao Qian, Yitong Tian, Jiaguang Zhang, Xinyi Zhang, Ling Ma, Taisong Li, Ke Jin, Fengyuan Li, Yongqian Shu, Xiaofeng Chen
Gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma remains a fatal condition worldwide, ranking fifth in prevalence and fourth in mortality globally [1]. The treatment of advanced gastric cancer is currently stratified based on MSI (Microsatellite Instability) status and HER2 status.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p126-133 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.043
FBXOing down V-ATPase: Implications for combating cancer metastasis
Zhenyi Wang, Weiyi Zhou, Xiaodong Chen, Zhe Zhao, Dongping Wei
FBXO9, an evolutionarily conserved member of the F-box protein family, functions as a substrate receptor within the Cullin 1-RING ubiquitin ligase complex (CRL1), also known as the SKP1-Cullin 1-F-box (SCF) complex [1].
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p134-136 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.044
Chemokine-like Orion presentation as a potential switch in phagocytic signaling pathway activation during neuronal remodeling
Charline Gal, Clarisse Perron, Jean-Maurice Dura, Ana Boulanger
Immature nervous systems are initially overpopulated with neurons. A crucial step of remodeling that removes inappropriate connections is required and performed predominantly by phagocytic glial cells. The Drosophila chemokine-like Orion tags axons to be eliminated. Could the way Orion is presented by neurons be the critical factor in modulating subsequent intracellular glial responses?
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p135-140 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.074
Integrating “fast” and “slow” systems therapeutics for physiological renormalization in neurodegenerative disorders
Greg Maguire, George Ayoub
In Goodman and Gilman's, “The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics,” we were all taught to search for the one molecule that targets a single pathway, and specifically targets only that one pathway, underlying a disease or condition to optimally develop a therapeutic.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p137-143 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.045
Targeting inflammation in progeria – insights from combined baricitinib and lonafarnib treatment in a mouse model of progeria
Moritz Schroll, Karima Djabali
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS) is a rare and fatal premature aging disorder caused by progerin accumulation, leading to nuclear abnormalities, systemic inflammation, and early cardiovascular decline. Lonafarnib, a farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI), improves nuclear shape and extends lifespan, but its efficacy is limited and accompanied by pro-inflammatory effects. Here, we discuss preclinical findings from a combination therapy using the JAK1/2 inhibitor baricitinib (BAR) with FTI in a progeria mouse model.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p141-146 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.075
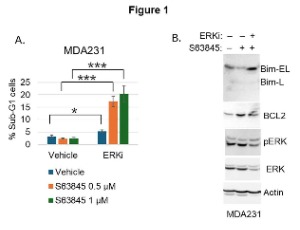
Potential biomarkers for MCL1 inhibitor sensitivity
Lei Duan, Carl G. Maki
Myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL1) is an anti-apoptotic member of the B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL- 2) family and plays a key role in cancer cell survival and resistance to therapy [1,2]. MCL1 is often
overexpressed in cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and solid tumors, allowing cancer cells to evade apoptosis and resist conventional treatments.
Angiotensin-(1-7) steers macrophages to inflammation resolution
Simone de Araújo, Erick Bryan de Sousa Lima, Lirlândia P. Sousa, Mauro Martins Teixeira
Angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] is a biologically active peptide of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) that counterbalances the actions of angiotensin II (Ang II), primarily through binding to the Mas receptor (MasR). This axis exerts significant immunomodulatory effects by influencing several features of leukocytes, including macrophage function, a central component in the resolution of inflammation. Macrophages contribute to tissue homeostasis by clearing apoptotic cells, releasing anti-inflammatory mediators and supporting tissue repair.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p147-152 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.076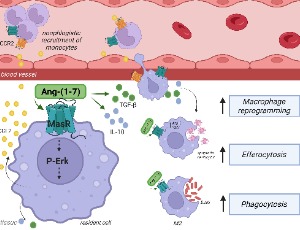
Carbon nanostructure: Cutting-edge platforms for advanced genetic transport
Sara Yazdani, Mehrdad Mozaffarian, Gholamreza Pazuki, Naghmeh Hadidi
Gene therapy represents a revolutionary approach to treating a wide range of genetic disorders, cancers, and infectious diseases by directly modifying or correcting defective genes within a patient’s cells. Unlike conventional treatments that focus on managing symptoms, gene therapy targets the underlying molecular causes of diseases, offering the potential for long-lasting or permanent cures.
Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p148-154 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.2.047
Neuroimmune interplay in peripheral neuropathies
Xiangyun Yao, Cunyi Fan, Song Guo Zheng
The interplay between neural cells and immune cells is a determinant factor for microenvironment restoration following nerve injury. Nerve-resident immune cells respond microenvironment signals and switch to pro-inflammatory or pro-regenerative phenotype. These phenotypes have different effects on axon regeneration. Early-phase neuroinflammation clears debris and remodels a permissive microenvironment for nerve repair. However, persistent and overactive inflammation is destructive and detrimental to regeneration. Despite all this information, our understanding of neuroimmune interplay in traumatic and diabetic neuropathies remains poor.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p153-157 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.077
Confine to create: ER-endosome contacts foster autophagy initiation
Juliane Da Graça, Etienne Morel
Autophagy is a conserved cellular process in which eukaryotic cells degrade and recycle intracellular material via a dedicated trafficking toward lysosomes. Under starvation, autophagy is initiated by the formation of a double-membrane organelle called the autophagosome, which originates from the closure and maturation of a transient membrane structure known as the phagophore. The precise membrane source of the phagophore and the mechanisms underlying its biogenesis remain incompletely understood.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p158-162 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.078
Dual roles, targeting dilemmas, and future priorities: Rethinking METTL-mediated m6A modification in head and neck cancer
Ming Yang, Han Zhu, Zile Zhang, Xuexia Liu, Hua Zhang, Gang Qin
With the recently published review in Cellular Signaling, we highlight the importance of Methyltransferase-like (METTL) family-mediated N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in head and neck cancer (HNC) progression, providing a theoretical foundation for their potential use as therapeutic targets.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p163-167 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.079
Insights into the methyltransferase activity and methylation status of PRDM16 in malignant tumors
Yu Wang, Yuting Wang, Anjia Han
The PRDM16 (PRDI-BF1-interacting and RIZ1-homologous domain 16) participates in a range of biological processes including tumorigenesis. The protein regulates gene transcription through intrinsic chromatin-modifying enzymatic activity or by forming complexes with histone modifications or other nuclear proteins. Accumulating evidence indicates that the methyltransferase activity and its methylation status of PRDM16 had been further studied.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p168-172 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.080
Insulin or islet: That’s the question
Byung-Joon Kim, Hee-Kyeong Park, Jun-Seop Shin, Jin Kuk Kim, Kwang-Won Kim
This commentary discusses our recent findings that, contrary to the β-cell rest hypothesis, early short-term insulin administration in a mouse model of marginal β-cell deficiency paradoxically worsened glycemic control and induced adverse α-cell-mediated islet remodeling. Early insulin intervention is hypothesized to preserve β-cell function; however, its utility in marginal β-cell deficiency is not well-established.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p173-175 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.081
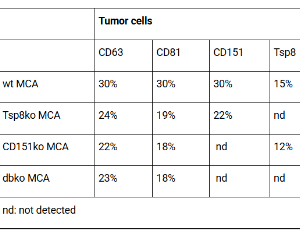
A review on molecular mechanisms underlying the contribution of Tspan8 and CD151 tumor and host exosomes to tumor progression, hematopoiesis and angiogenesis
Kun Zhao, Zhe Wang, Margot Zöller
Tetraspanins associate with many proteins and are involved in numerous activities like the crosstalk between cells and matrix, tumor progression, angiogenesis, and hematopoiesis.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p176-207 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.082