Loading
2026
Volume 7, Issue 1, p1-4
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Brucellosis as a cause of acute-on-chronic liver failure in a person with advanced HIV disease and HBV reactivation: a case report
Antonella Gallicchio, Alessandro Bianchi, Alessandro Marocco, Viviana Rizzo, Massimo Sardo, Elio Manzillo
Brucellosis is a zoonosis in which hepatic involvement is common but usually mild. Acute liver failure and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) are rarely attributed to brucellosis, and even more rarely to people living with HIV (PLWH).
J Allergy Infect Dis, 2026, Volume 7, Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.46439/allergy.7.056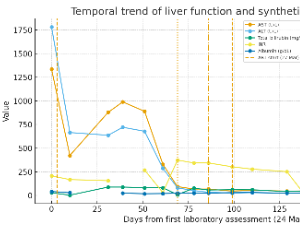
Recommended Articles
Applications of impulse oscillometry in the diagnosis and monitoring of preschool asthma
Impulse oscillometry is a lung function test that has become more widely used over the past 30 years. It is particularly useful in patients who have difficulty performing forced respiratory maneuvers, such as preschool children, who have shorter expiration times, less strength to inhale, less coordination and shorter attention spans than older children or adults.
Targeting Caspase-4 and pyroptosis as a new therapeutic approach for asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the lung caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Although symptoms of mild asthma are treated with current medications, such as bronchodilators and steroids, severe asthma remains very difficult to manage. Asthma rates are constantly on the rise and there is a clear need for novel asthma therapies especially in severe asthma.
Dynamics of the coronavirus pandemic in Italy and some global predictions
The pandemic caused by coronavirus COVID-19 are of great concern. A detailed scientific analysis of this phenomenon is still to come, but now it is urgently needed to evaluate the parameters of the disease dynamics in order to make some preliminary estimations of the number of cases and possible duration of the pandemic. The corresponding mathematical models must be simple enough, since their parameters are unknown and have to be estimated using limited statistical data sets.
Influenza infection and aortic dissection: A commentary on the association between a viral syndrome and major cardiac events in the context of the current COVID-19 pandemic
Acute type A aortic dissection (ATAAD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality for patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms, despite significant advances in the surgical treatment. An aortic dissection is a life-threatening condition which occurs when blood enters through a tear in the wall of the aorta causing the aortic layers to separate or “dissect”.
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease should not be mistaken for drug allergy
A 36-year-old Hispanic male, with a history of ulcerative colitis (UC) presented to the inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) clinic for initial evaluation. Over the past six years, the patient had been treated for his UC with various therapies including prednisone, multiple mesalamine formulations, and budesonide but always discontinued therapy due to what he perceived were adverse drug reactions. He described onset of pruritic blisters, affecting his chest, abdomen, back, and arms.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C): The role of viral superantigens in COVID-19 disease
Superantigens are viral or bacterial virus proteins that can specifically activate a large ratio of T cells. In contrast to classic peptide antigen recognition, superantigens do not require processing in small peptides, but act as fully or partially processed proteins. They can bind to class II molecules of the main histocompatibility complex and stimulate T cells that express certain beta chains of the T cell recipient V.
Ticks positive for Lyme disease causing bacteria present on white-tailed deer in Northeast Iowa
n Iowa there has been an upward trend in the number of cases of Lyme disease. Due to this increase, it is important to understand the transmission pattern and the factors that play a role in the spread of this disease. Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi, and is transmitted by Ixodes scapularis, within the United States. I. scapularis has a two-year life cycle that includes three life stages: larva, nymph, and adult, and requires a blood meal between each stage.
Basic reproduction number, effective reproduction number and herd Immunity: Relevance to opening up of economies hampered by COVID-19
Several countries are in different phases of safely lifting the lockdowns necessitated by the Covid-19 pandemic and re-opening their economies. As they do so, it is important for authorities to recommend or impose some public health measures like social distancing and wearing face masks. Scientific articles are appearing in peer reviewed medical journals and even in the lay press on this topic. Some of the scientific definitions used in these articles might be erroneous.
The unit-based stress and anxiety correlation of healthcare workers during the COVID 19 outbreak
Stress is defined as ''a state of mental or emotional strain or tension resulting from adverse or very demanding circumstances''. In today’s world, we are hearing the word “stress” quite frequently in our daily lives and conversations. Stress comes out in different forms that can change from one person/society to another. The physiological results of stress are regulated by the central nervous system (CNS) through the stimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
A newly discovered dendritic cell subtype responsible for viral and dust mite inflammation
Ralph Steinman discovered and defined dendritic cells (DCs) in the 1970s [1] and at the time, no one would have expected the diversity of DC lineages to be discovered as well as their contribution to playing out the orchestra that is the adaptive immune response. In the late 20th century, researchers identified and characterized various DC subtypes, such as conventional DC (cDC), plasmacytoid DC (pDC), and Langerhans cell (LC).
Possible protective role of 17β-estradiol against COVID-19
Severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); a worldwide pandemic as declared by the World Health Organization (WHO). SARS-CoV-2 appears to infect cells by first binding and priming its viral-spike proteins with membrane-associated angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2).
Policy and law changes to address healthcare inequities for minority populations during COVID-19
While other countries have begun to see a flattening of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome – Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) curve, the United States continues to see a rise in cases, with approximately 7.4 million confirmed cases to date. Even more worrisome, various news articles have begun to shed light on the healthcare inequities that have become increasingly more transparent during this crisis.
Feeding cats egg product with Polyclonal-Anti-Fel d1 antibodies decreases environmental Fel d1 and allergic response: A proof of concept study
Background: Cat allergens are a major contributor to environmental allergens' overall burden, but efforts to reduce cat allergens are often unsuccessful.
Objective: To determine whether feeding cats a diet containing an egg product with anti-Fel d1 IgY would produce clinically relevant reductions in allergy symptoms of human subjects.
Hyponatremia in COVID-19 infection: possible causal factors and management
SARS-CoV-2 disease (COVID-19) has dramatically increased since March 2020. There is no sufficient data to establish the risk of acquiring the hyponatremia in patient with COVID-19 infection. The prevalence, causal factors, clinical characteristics, severity, treatment and prognosis of hyponatremia in patients with pneumonia due to COVID-19 is not yet known, although several articles on kidney injury and electrolyte abnormalities have recently been described.
The impact of HIV and HAART in the pathogenesis of COPD
The advent of highly active antiretroviral therapy has significantly increased the longevity of people living with HIV infection. Consequently, the HIV patient population is maturing, and age-related diseases now have a much greater impact on their health and well-being than do HIV associated infections. Cigarette smoke exposure is highly prevalent in the HIV community and chronic smoke inhalation triggers the onset and progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
COVID-19 vaccination in children in India: A way forward
India has an estimated population of 1.39199 billion and current vaccination approach plans to cover adult population (>18 y, about 67.53%) very soon. As on 24 December 2021, the country completed about 1.41 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines, in about eleven months since the drive began.
Period-varying confirmed case-fatality risk still being depicted
Kathy Leung and colleagues assessed the transmissibility and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during the first wave in mainland China outside Hubei. Their research will contribute to resist the potential second wave. The confirmed case-fatality risk (cCFR) adjusting for the time between onset and death was used as a better measure of the severity of COVID-19. However, the cCFR and its correlation with the number of hospital beds per 10,000 population may be inaccurate and misleading.
Intranasal therapy and COVID-19: A comprehensive literature review
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19, is highly virulent and can be transmitted via respiratory droplets and close contact. Recent studies suggest that although viral load could be a poor predictor of disease, the concentration of the virus in the respiratory tract may be linked to contagiousness when coupled with significant co-variables factors such as nasal discharge and cough, hence impacting transmission.
SARS-CoV-2: Omicron changed my perspective
As a boosted, vaccinated infectious diseases physician I remained careful outside of work. I always wore a mask outside of my home. I even wore a mask while I am driving alone in my car because I needed it for my next encounter and it kept me warm.
So how did I get SARS-CoV-2 infection? The same way most people do, from household exposure [1].
Impact of COVID-19 vaccination drive in adults on vaccine-induced immunity in India: A Markov cohort model
Objective: Need to control the COVID-19 pandemic resurgence is a priority in India which has an estimated population of 1.39199 billion. Immunity whether acquired by recovery or vaccine, controls an infectious disease epidemic. In case of COIVD-19, the latter is more desirable. The objective of this study is to answer a research question “What is the impact of current vaccination drive in adults in generating vaccine-induced immunity in India?”
