Loading
Journal of Clinical Pediatrics and Neonatology
ISSN: 2767-3995
All Articles
Partnering for success- A prototype for integrating evidence-based practices between referring professionals and mental health professionals
Richard P Barth, Jessie Watrous
Children who experience abuse and neglect often have behavioral health sequalae which are poorly addressed because services are not evidence-based and partnerships with behavioral health providers lack precise coordination. Partnering for Success provides interprofessional training on EBPs, communication, and data sharing and has now been expanded to address the unique needs of children in treatment foster care.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.001
Pediatric telemedicine and abdominal pain in children
Stefan Bittmann
Telemedicine is a sub-area of telematics in healthcare and refers to diagnostics and therapy bridging a spatial or temporal distance between doctor, therapist, pharmacist, and patient or between two doctors consulting each other by means of telecommunications.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.3.020
Incidence and outcomes of peripherally inserted central catheter associated thrombosis in a tertiary neonatal intensive care unit
Kamela Loo, Vidhi Shah, Naisha Chokshi, Indira Chandrasekar
Neonatal PICC and umbilical lines are common vascular access lines in the NICU. Venous thrombosis, phlebitis, local or systemic infections, and mechanical problems such as catheter leakage or breakage, occlusions, and incidental dislodgement are well documented complications of PICC lines.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.5.031
Trends among a population of neonatal abstinence syndrome patients in Huntington, West Virginia
Taylor Boggess, Mitzi Payne
Neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) represents a serious emotional toll for the families of affected children and represents a significant financial burden for healthcare providers. Historically, patients living in rural regions, such as Appalachia, have limited access to healthcare facilities.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-6 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.2.016
A community-based cross-sectional study of neonatal hypothermia and its associated factors among neonates in Shebadino woreda, Sidama region, South Ethiopia
Gizu Tola Feyisa, Andargachew Kassa, Belay Amare, Shambel Negese, Shimelis Tadese, Melkamu Getu Wondimu, Derebe Chekol, Beshatu Berkessa Tola
The necessity of a warm environment for the care of low-birth-weight newborns was first recognized in the early 1900s [1]. In 1992, the World Health Organization (WHO) developed the guideline for the prevention and management of hypothermia. It is defined as a drop in a newborn's body temperature below 36.5°C (97.7°F) before the age of 28 days.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-13 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.4.023
Dynamics of the ‘free’ maternal healthcare policy intervention in Ghana; Facility delivery utilization and neonatal mortality indices from a developing country setting
John Azaare
The one conceptual key to improving newborn healthcare outcomes is thought to be bridging the access gap to care, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. However, recent studies have reported conflicting results relative to establishing a link between outcomes and access to care intervention programs.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p4-8 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.002
Investigation of urinary β2 microglobulin; substitute for interferon-γ as a suppressor of pulmonary fibrosis in a preterm with chronic lung disease following intrauterine infection
Toshihiko Nakamura, Michiko Kusakari, Kana Ito, Shota Inoue, Eisuke Fukama, Tomoaki Nomura, Daisuke Hatanaka, Hidehiro Takahashi
In the respiratory management of preterm infants of less than 33 weeks gestational age and very low birth weight infants, it is essential to understand changes in chest X-ray and blood gas findings in addition to observing their clinical symptoms.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p7-12 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.2.017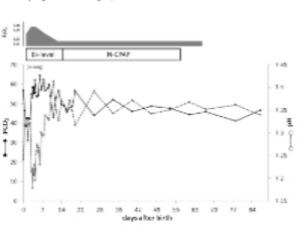
Unique genotypic features of HIV-1 C gp41 membrane proximal external region variants during pregnancy relate to mother-to-child transmission via breastfeeding
Li Yin, Kai-Fen Chang, Kyle J. Nakamura, Louise Kuhn, Grace M. Aldrovandi, Maureen M. Goodenow
Mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) through breastfeeding remains a major source of pediatric HIV-1 infection worldwide. To characterize plasma HIV-1 subtype C populations from infected mothers during pregnancy that related to subsequent breast milk transmission, an exploratory study was designed to apply next generation sequencing and a custom bioinformatics pipeline for HIV-1 gp41 extending from heptad repeat region 2 (HR2) through the membrane proximal external region (MPER) and the membrane spanning domain (MSD).
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p9-20 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.003
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Frequency and risk factors of retinopathy of prematurity among preterm neonates in a tertiary care hospital of Bangladesh
Md. Abdul Mannan
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is one of the major emerging but preventable causes of childhood blindness. ROP is a disease of premature babies. Over the past decade, perception of pathogenesis of ROP has improved tremendously. The condition was initially introduced by Terry in 1942 as retrolental fibroplasia [1].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p11-17 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.3.021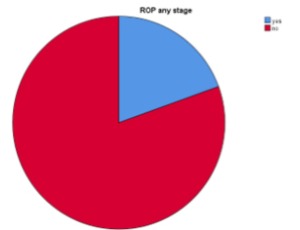
Commentary on “A global provision of preventive oral health measures for children with special needs: A scoping review”
Yahya S Alholimie, Diaa Almutairi, Hussain Ali Alhasan, Ali Abdalwhab Alkhamis, Hussain IbnAhmad, Esraa Nassir Almarzooq
The scoping review titled "A Global Provision of Preventive Oral Health Measures for Children with Special Needs" provides a comprehensive exploration of the preventive oral health measures available for children with special health care needs (CSHCN) and the barriers to their implementation.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, Volume 5, Issue 1, p12-15
Quality of stillbirth and neonatal death audit in Malawi: A descriptive observational study
Mtisunge Joshua Gondwe , Nicola Desmond, Mamuda Aminu, Stephen Allen
In 2019, an estimated 2 million babies were stillborn [1] and 2.4 million died within 28 days of life (neonatal deaths) [2]. About 80% of these stillbirth and neonatal deaths occurred in low- and lower-middle- income countries (LMICs) with sub-Saharan Africa region contributing to more than 50% of these deaths [1-3].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p13-25 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.2.018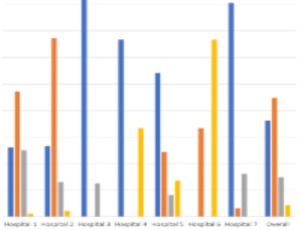
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Compassion fatigue: The trojan horse in nursing
Jodi Collier
Nurses are leaving the profession at an alarming rate [1]. Like soldiers on the battlefield, many nurses post pandemic are left alive but injured, with a catalogue of emotional experiences to wrestle with. Using Stamm’s [2] breakdown, Compassion fatigue (CF) can be understood as the combination burnout and secondary trauma.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p14-15 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.4.025
Recent therapeutic progress to treat achondroplasia in children
Stefan Bittmann
Achondroplasia is the most common form of genetically inherited dwarfism. Affected individuals are mainly characterized by severely shortened arms and legs and a large head. In 1878, the term achondrodysplasia was coined by the French physician Joseph Marie Jules Parrot. The term achondroplasia is purely historical and does not explain the cause or manifestations of this disorder.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, Volume 5, Issue 1, p16-18
Withstanding the COVID19 pandemic - A tertiary children’s hospital’s commitment to equitable care
Alicia D. Menchaca, MD, Candace C. Style, MD, MS, Mehak Chawla, MBA, BS, Allie Kouche, Maria Burdjalov, Tyler A. Kyhl, MS, BS, Benedict C. Nwomeh MD, MPH, Oluyinka O. Olutoye, M.D, Ph. D
Acute appendicitis is one of the most common surgical procedures performed among pediatric patients in the United States [1]. The pathophysiology of the disease begins with luminal obstruction of the appendix, leading to venous congestion, with eventual arterial inflow obstruction, and finally luminal rupture, resulting in spillage of enteric contents into the abdominal cavity.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p16-21 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.4.026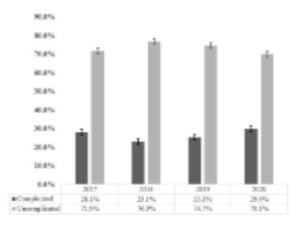
Cholestasis in Neonates with Fetal Growth Restriction
Bhavishya Devireddy, DO, Archana Lingannan MD, Indira Chandrasekar
Neonatal cholestasis (NC) is usually a result of hepatobiliary dysfunction and can lead to extensive workup and prolonged stay in the NICU. NC is never physiological but rather a sign of hepatobiliary and/or metabolic disorders, some of which can become fatal if it is not identified and treated in time.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p18-20 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.3.022
Commentary on "Empirical profile Bayesian estimation for extrapolation of historical adult data to pediatric drug development"
Yaoshi Wu, Jianan Hui, Qiqi Deng
We are writing to promote a novel Bayesian dynamic borrowing approach, the empirical profile Bayesian estimation, in the published article "Yaoshi Wu, Jianan Hui, Qiqi Deng. Empirical profile Bayesian estimation for extrapolation of historical adult data to pediatric drug development. Pharmaceutical statistics 2020; 19; 787-802. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pst.2031."
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p21-22 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.004
Evaluation of chronic pediatric diarrhea: use of newer imaging tools – a more practical approach
Atul Kapoor
Diarrhea in children has a worldwide prevalence and it is estimated that more than 5 million children succumb to the disease worldwide and is the fifth largest cause of mortality in third-world countries [1]. An operative definition of diarrhea as proposed by the World Health Organization refers to the passage of three or more loose or liquid stools per day or more frequently than is normal for the individual based on the duration of symptoms it can be classified as acute –i.e. less than 14 days duration and chronic if more than three weeks duration [2].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p22-24 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.4.027
Is vitamin D the missing link between childhood obesity and adenovirus-36 infection?
Tirang R. Neyestani, Bahareh Nikooyeh
It may seem irony that nutrition science historically pertained mostly to undernutrition and deficiency syndromes [1] but nowadays prevention, control and treatment of overnutrition, manifested as overweight and obesity, has become the main task of most nutritionists and related professionals [2].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p23-25
Plastic compounds and liver diseases in pediatrics: Navigating the hazards
Sonal Sangwan, Rajasri Bhattacharyya, Dibyajyoti Banerjee
Recent research underscores the risk posed by plastic compounds to pediatric liver health. These compounds can permeate the maternal-fetal-child barrier through the placenta and breastfeeding, exposing fetus/child to potential harm during crucial developmental stages [1,2].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p25-27 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.4.028
Congenital Cytomegalovirus screening in newborns: Current status in the United States
Suhas M Nafday, MD, MRCP (Ire), FAAP
Congenital Cytomegalovirus (cCMV) infection is the leading cause of non-hereditary sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) and developmental delay in children with an approximate prevalence rate of 0.7% [1].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p26-27 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.2.019
Case of traumatic tongue defect: A commentary
Ajaipal S. Kang, Kevin Kang
The tongue is a complex muscular organ essential for speech, taste, chewing and swallowing [1]. Tongue injuries range in severity from minor lacerations to complete amputation. The most common location is anterior dorsum as a result of falls, seizures, self-mutilation, electroconvulsive therapy or child abuse [1,2].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p26-29 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.006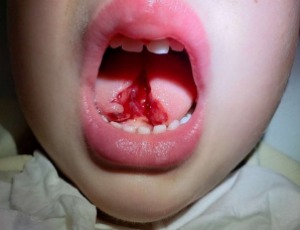
Prenatal phenotype-genotype discordance allows for earlier identification of disorders of sexual development
Maya Muhanna, Brandon Godinich, Stephanie Stokes, Lee D. Moore, Natalia Schlabritz-Lutsevich M.D., PhD, James Maher III, M.D., Lawrence Devoe M.D
Disorders of sexual development (DSD) are a spectrum of conditions characterized by abnormal chromosomal, gonadal or phenotypic sex, leading to atypical development of the urogenital tract [1]. Recently, Snipes et al. presented a case of a 46 XY DSD patient whose condition was caused by a rare genetic mutation, identified by a workup initiated after discovering a discrepancy between the genetic sex on the Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) and the phenotypic sex on the 20-week ultrasound (US) [2].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p28-31 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.4.029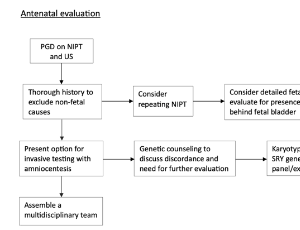
A late and unusual diagnosis of intrathoracic stomach
Jennifer Lorén Martín, Sara Jimeno Ruiz, María Miralles Molina, Alejandro López Escobar
A 2-month-old girl came to our Radiology Department to perform an abdominal ultrasound. At 38 weeks she was born and she was hospitalized for 3 weeks due to intrauterine growth retardation and hypotonia and the results of the medical study were normal, included cerebral and abdominal ultrasound exception karyotype (47 XX with chromosome marker of unknown origin).
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p30-34 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.007
Our experience in providing anesthesia during surgical interventions for necrotizing enterocolitis
Nasibova E.M, Rahimova K.H.S
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is one of the most common serious acquired diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, both in full-term and premature infants. Studies show that the incidence of NEC among newborns is 2.4 per 1000 children. It was found that NEC in premature newborns occurs 12 times more often than in full-term patients [1].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p32-40 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.4.030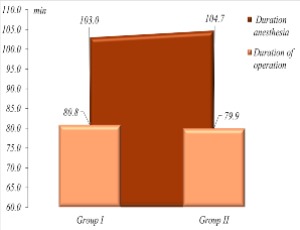
Extension: Beliefs about causes of autism and vaccine hesitancy
Robin P. Goin-Kochel
There are many reasons why people may feel hesitant to accept vaccines for their children, with fears about a link between vaccines and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) being one of the most common. In fact, parents of children with ASD are among those most likely to become vaccine hesitant. Vaccine-hesitant parents may delay and/or refuse one or more vaccines for their children, which subsequently places them at increased risk for contracting and spreading vaccine-preventable diseases.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p35-36 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.008
Differences among racial and ethnic groups in vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with autism spectrum disorder
Ashley M. Butler
Achieving and maintaining recommended vaccination coverage is a major public health goal [1]. Indeed, rates of childhood vaccine coverage in the U.S. among young children have remained high and stable in recent years [2]. While racial/ethnic disparities in recommended childhood vaccine coverage in the general population have been absent or reduced over time, income disparities have changed at different rates within racial/ethnic groups and in some cases have increased [3].
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p37-38 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.009
Parents’ perception and satisfaction assessment: a potential extension of EAR-Q
Yiyuan Li, Ruhong Zhang
We are profoundly glad to be engaged in Dr. Klassen’s work of “An international study to develop the EAR-Q patient-reported outcome measure for children and young adults with ear conditions [1]”, our center provided over 40% data for this EAR-Q study. Dr. Klassen [1,2] has already proved the acceptability, reliability and validity of EAR-Q, it can be widespread used for varied ear conditions.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p39-40 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.010
Antenatal SARS-COV-2 exposure leading to multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-N) presenting with neonatal encephalopathy
Varnit Shanker, Madhu Chaudhary, Pooja Shanker
A 22-day-old male neonate was admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) with complaints of abnormal movements, fever, breath holding spells, refusal and bluish discoloration of skin. He was born at term with a birthweight of 2·72 kg to a mother with a history of positive polymerase chain reaction for SARS-Coronavirus-2 (SARS-COV-2) virus (RT-PCR-positive), asymptomatic 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) at 32-33 weeks gestation, which did not require any supportive measures.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p41-44 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.011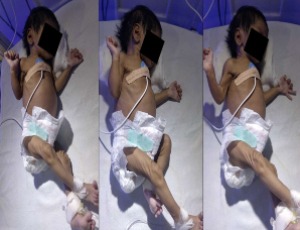
Commentary: Utilization of a modified ecomap as a practice approach for identifying and enhancing support networks for LGBTQ youth
June C. Paul
In a recent issue of the Children and Youth Services Review, I published an article examining systems of support for LGBTQ youth transitioning from foster care to emerging adulthood [1]. The methodology I used to gather this data included in-depth interviewing combined with ecomapping techniques that I modified to identify the strength and structure of LGBTQ youths’ support networks.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p45-48 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.012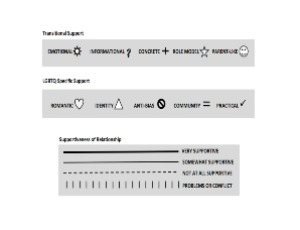
Iron status: an update on learning, memory, and implications for addiction
Eliana Sherman, Christopher B Jenney
In a follow-up to the 2016 paper “Preweaning iron deficiency increases non-contingent responding during cocaine self-administration in rats”, we briefly discuss relevant new data regarding iron deficiency published through August, 2021. The original work investigated if early iron deficiency would increase later vulnerability for substance use disorder.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p49-52 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.013
Hypothermic neuroprotection following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: medico-legal implications
Steven M. Donn, Jonathan M. Fanaroff
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) continues to be an important cause of long-term neurologic disability among newborn infants. The estimated incidence ranges from 2-3/1000 live births in developed countries, to as high as 10-20/1000 in developing countries [1]. Affected infants who survive are at a 25% risk for cerebral palsy, epilepsy, and cognitive deficits and may require lifelong medical care.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p53-54 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.014
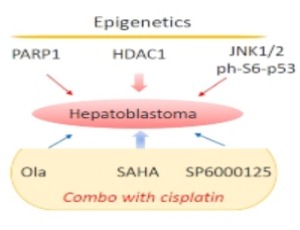
Epigenetics of pediatric liver cancer and potential therapy
Nikolai Timchenko
The pediatric liver cancer hepatoblastoma (HBL) has a complex etiology which is not yet determined. In contrast to adult liver cancer hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), pediatric HBL has a low rate of genetic mutations suggesting that other mechanisms play a critical role in development of this disease.
J Clin Pediatr Neonatol, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p55-58 | DOI: 10.46439/pediatrics.1.015