Loading
Archives of Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology
ISSN: 2692-4331
All Articles
Neodymium:YAG laser posterior capsulotomy in the lateral decubitus position
J. Virdee, P. Mandal, A. Brown, I. Khan
Here we report a novel method of performing a Neodyminium:YAG (Nd:YAG) laser posterior capsulotomy in an adult patient, unable to tolerate the procedure awake with topical anaesthesia in the outpatient clinic setting. The procedure was performed by altering the chin rest and arms of the Nd:YAG laser machine so that the procedure could be undertaken in an anaesthetized patient in the operating theatre, in the lateral decubitus position, with the laser machine upright in its normal position.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.1.001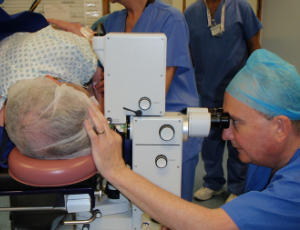
Evaluating refractive outcomes after pars plana vitrectomy and scleral fixated intraocular lens with Gore-Tex suture
Matthew P. Ohr
It has been nearly 20 years since Girard first described the technique of placing a lens in the absence of capsular support [1]. Since that first report, numerous procedures have been described [2-9]. While the techniques have continued to evolve, little has been reported on refractive outcomes.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.020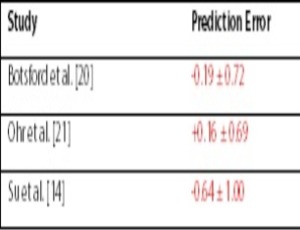
“Poppers Maculopathy” is an Electrochemical Overload
Fabrizio Magonio, MD
Poppers maculopaty is a rare retinal disease which is poorly understood. It is characterized by disruption of inner segment/outer segment junction of central cones and yellow foveal lesions causing photophobia, central scotoma and impaired visual acuity. ”Poppers” is a slang term referring to recreational substances of abuse belonging to the alkyl nitrite family of compounds. Inhalation of the fumes from these volatile nitric oxide donors provides a brief sense of euphoria, sexual arousal and myorelaxation. High concentrations of nitric oxide are suspected to represent the underlying cause of retinal damage linked to poppers intake.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.4.029
Surgical removal of intravitreal glass foreign bodies using nephrolith and sialolith baskets
Nishay V. Bhatnagar BA, Sydney B. Langer, Orlando G. Gonzalez-Martinez MD, Simran Ohri MD, Neelakshi Bhagat MD, MPH
Intraocular foreign bodies (IOFBs) are a major cause of visual impairment in adolescents and young adults and are associated with 18–41% of open globe injuries. Motor vehicle accidents resulting in penetrating ocular trauma are commonly associated with windshield glass IOFBs, in up to 70% of cases.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, Volume 8, Issue 1, p1-4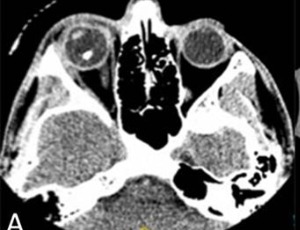
New Frontiers in the Rehabilitation of Neurological Damage
Emilia Gallo, Chanda Cavallini, Emanuele Lo Curto
Epidemiologic data show a high incidence of central nervous system (CNS) disease, which therefore is a prominent healthcare issue. Adults and the elderly are most commonly affected, with heavy repercussions on society and caregivers. The outcome of CNS disease, whether the etiology is vascular, degenerative or traumatic, is often significant disability or death. Motor, language and cognitive deficits are most prevalent, but vision is also frequently affected, in the form of visual field defects or oculomotor and binocular disorders. In the present paper, we discuss peripheral and central visual field defects.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.006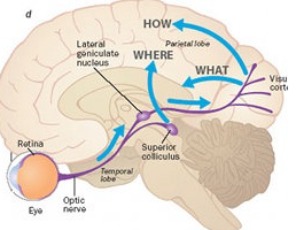
From observation to diagnosis: Implications of calcified sclero-choroidal choristomas in mosaic RASopathies
Brian M Grodecki, Saipriya C Potluri, Karl Olsen, Amgad Eldib, Hannah L Scanga, Matthew S Pihlblad, Ken K Nischal
The identification of calcified sclero-choroidal choristomas (CaSCCs) in patients with mosaic RASopathies introduces a new dimension to understanding ocular manifestations in these genetic disorders.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.5.033
Bevacizumab (Avastin) in treatment of maculopathy secondary to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) in Afghanistan
Mohammad Delsoz, MD, Sayed Hamid Mousavi, P. Hollands, Phd
This is a clinical study which assessed the safety and efficacy of Bevacizumab (Avastin), manufactured by Genentech, in the treatment of maculopathy secondary to Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR). All of the patients suffered from Type II Diabetes Mellitus.
A total of 174 (97 male, 77 female) patients (308 study eyes in total) took part in the clinical study with an average age of 57 years (range 27-80 years). 56 patients (32%) in the study were insulin dependent diabetics. Bevacizumab was given to patients by monthly intra-vitreal injections at a dose of 50 µL per treatment. The Visual Acuity (VA) was assessed using the Snellen technique before and after the Bevacizumab injection and with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT).
Ocular surface disease management in cataract surgery
Alessandro Mularoni, Antonio Di Zazzo, Daniele Gaudenzi, Francesco Cutrupi, Francesco Gaudenzi, Giovanna Linda Possati
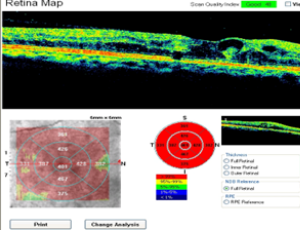
According to the literature, 80% of patients undergoing cataract surgery suffer from ocular surface disease (OSD). Along with postoperative refractive surprise, the onset of OSD is the main cause of dissatisfaction in cataract surgery patients, accounting for 35% of cases. These patients are characterized by persistent dysregulation of ocular surface para-inflammation, leading to chronic low- grade inflammation with significant consequences on daily activities and work productivity. This study aims to investigate the effects of topical desonide sodium phosphate 0.025% eye drops on the signs and symptoms of OSD in patients undergoing cataract surgery.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.7.035
Presbyopia correcting IOLs and the ocular surface disease… The good, the bad and the ugly
Slavomir Kirilov
The last two decades were especially fruitful for the refractive surgeons and for the industry who have been showing tremendous development in both understanding and meeting patients’ desire for spectacle independence. Ever since the first trials from Dr. Kenneth Hoffer with his early 1980’s effort in producing a multifocal IOL to the latest achievements from different companies in putting trifocals and EDOF optics to the market.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p4-5 | DOI: DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.1.002
A case of trigeminal neuralgia after COVID-19
Jeanie C. Lucy, OD, MPH, MS, PhD, FAAO
The trigeminal nerve is one of twelve pairs of cranial nerves that attach to the brain. The name “trigeminal” literally means three twins and refers to the fact that the fifth cranial nerve has three major divisions: the ophthalmic (V1), the maxillary (V2), and the mandibular (V3) [1]. The trigeminal nerve is the major sensory nerve of the face and is the nerve of the first branchial arch.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p4-6 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.5.30
Visual field defect as an idiosyncratic reaction to topiramate
Neelakshi Bhagat, Lekha Mukkamala, Paul D. Langer
Topiramate is an increasingly popular medication used in the treatment of migraines, seizures, and other neurologic disorders. Its several mechanisms of action include enhancement of postsynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor activity (an inhibitory neurotransmitter) and mild inhibition of carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p4-7 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.021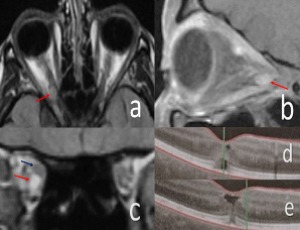
How many mutations does it take to make a uveal melanoma?
Francesca Piaggio, Veronica Tozzo, Cinzia Bernardi, Michela Croce, Claudia Lo Sicco, Rosaria Gangemi, Roberto Puzone, Silvia Viaggi, Serena Patrone, Annalisa Barla, Domenico Coviello, Martine J. Jager, Pieter A. van der Velden, Davide Cangelosi, Alessandra Eva, Silvano Ferrini, Ulrich Pfeffer, Adriana Amaro
Uveal melanoma (UM) is a rare cancer that affects the choroid and, less frequently, the ciliary body or the iris (for recent reviews see [1-3]). Despite a profound knowledge of the oncogenic mechanisms behind UM tumorigenesis and despite an accurate cytogenetic and molecular prognosis, only limited advances have been made in UM therapy.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p6-11 | DOI: DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.1.003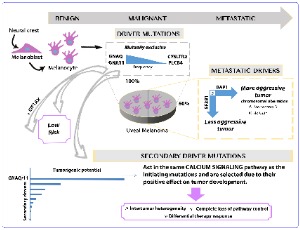
Ocular cystinosis – A review of disease, diagnosis, and future treatment options
Lauren Devitt
Cystinosis is a rare autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder, characterised by the intra-lysosomal accumulation of cystine. Cystinosis results from a defect in the CTNS protein, a lysosomal transport protein for cystine. There are three subtypes of cystinosis: infantile nephropathic cystinosis, juvenile nephropathic cystinosis and ocular non-nephropathic cystinosis.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p6-12 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.6.034
Switching from ranibizumab (0.5 mg) to brolucizumab (6 mg) in the management of wet age-related macular degeneration, real-life one year data
Libor Hejsek, Martina Rubesova, Lenka Havlickova
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common and potentially devastating eye disease affecting millions of people worldwide. Among the two major subtypes of AMD, the wet form poses a significant threat to vision due to the development of choroidal neovascularization and subsequent retinal damage. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) therapy has revolutionized the treatment landscape for wet AMD, particularly with the advent of ranibizumab, a widely used monoclonal antibody targeting VEGF-A. The incidence of wet AMD has been steadily increasing with the ageing population, leading to a growing public health concern. Early diagnosis and prompt initiation of effective treatment are critical to preserving vision and preventing disease progression. The introduction of anti-VEGF agents, particularly ranibizumab, has significantly improved visual outcomes for many patients, leading to a reduction in severe visual loss and stabilizing or even improvement in visual acuity.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p7-9 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.5.032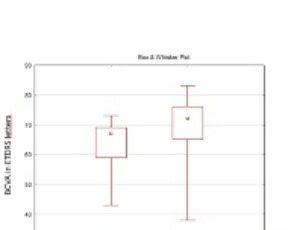
Ocular surface squamous neoplasia treated with topical chemotherapy
Elaine Han, Carol L. Karp
A man in his 90s presented to clinic with a conjunctival lesion on the right eye noticed two months prior. The patient denied pain but endorsed worsening blurry vision. The patient’s past medical history was significant for skin cancer on the right ear removed 3 years ago, and a history of ocular surface lesion removal on one eye approximately 20 years ago that was negative for any neoplasia. Slit lamp photograph revealed a gelatinous and opalescent lesion suspicious for ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) and the high-resolution optical coherence tomography (HROCT) cut (arrow)
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p8-9 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.008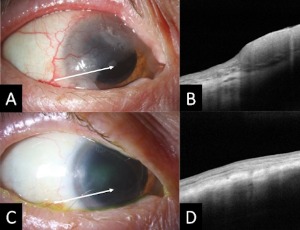
Comment on “Use of refractive aids among adults in a general population”
Ivan Nisted, Bodil Hammer Bech, Toke Bek
This commentary is a further discussion of results from the FORSYN study recently published in Scientific Reports [1]. In the FORSYN study 10,350 people selected by Statistics Denmark to represent the adult Danish population with respect to age, sex, and socio-economical parameters were invited for a non-cycloplegic examination at the Department of Ophthalmology, Aarhus University Hospital.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p8-9 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.7.036
An atypical case of compressive optic neuropathy and cranial nerve 6th palsy caused by a cholesterol granuloma
Sahar Pearson, Amanda Ie, Stephen Ong
In this case report we present an unusual case of orbital cholesterol granuloma associated with compressive optic neuropathy and cranial nerve 6th palsy. Cholesterol granuloma results from a foreign body response to the presence of crystallized cholesterol. Cholesterol granuloma affecting the orbit are a rare presentation as they typically occur in the petrous apex of the temporal bone.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p8-10 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.022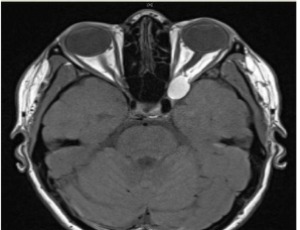
Considerations regarding the visual and social limitations of children with congenital Zika syndrome
Marcia Beatriz Tartarella, MD, PhD, João Borges Fortes Filho, MD, PhD, Islane Maria de Castro Verçosa, MD
Congenital Zika syndrome (CZS) results from maternal exposure to the Zika virus during pregnancy. A large number of newborns were affected during the Zika virus outbreak occurred insome Northeast regions of Brazil during the years 2015 and 2016 .
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p10-11 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.7.037
The GSK3β pathway in optic nerve regeneration
Zubair Ahmed
Adult neurons in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS) fail to regenerate after injury due to a number of factors including the reduced intrinsic growth capacity together with the hostile environment of the injured CNS microenvironment [1-4]. However recent studies have shown that modifying the intrinsic growth capacity through a number of cell signalling pathways can promote regeneration of adult CNS neurons. For example, intrinsic factors such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and the repressors phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 (SOCS3) promote CNS axon regeneration [5-7].
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p10-16 | DOI: https://doi.org/10.46439/ophthalmology.2.009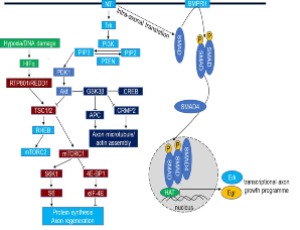
Ocular Manifestation of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Parth S Patel, Aditya Uppuluri, Neelakshi Bhagat
Gardner Syndrome is a phenotypic variant of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) characterized by extracolonic manifestations including pigmented ocular fundus lesions with malignant polyps in the large intestine. We present the case of a 41-year-old female with FAP, who presented with numerous congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium ocular lesions.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p11-15 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.023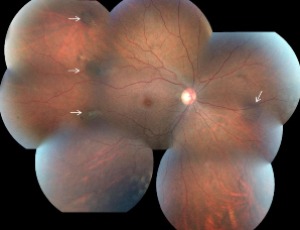
MSICS is a Simple Solution for a Big Problem
Mohamed. A. Almousa
Manual small-incision cataract surgery (MSICS) is a sutureless cataract surgery that has multiple advantages over traditional phacoemulsification and extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE) procedures. SICS became the procedure of choice for international ophthalmology, where the microscopes and operating room can be more challenging, in addition to the more advanced pathology often seen.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p12-12 | DOI: DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.1.004
Commentary on analysis of contrastsensitivity in patients implanted with AcunexVario and LuxSmart extended depth of focus (E-DOF) intraocular lenses (IOLs)
Boryana Irinkova
The significance of contrast sensitivity (CS) in impacting real visual ability cannot be emphasized enough. In recent years, cataract surgeons and ophthalmologists globally have been focusing more on it. Visual acuity is no longer the sole measure of vision quality, especially in low-light conditions.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p12-16 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.7.038
Pegaptanib sodium influences capillary nonperfusion secondary to diabetic retinopathy
Asad F. Durrani, Thomas R. Friberg
Retinal capillary nonperfusion is a hallmark of numerous retinal disease processes including diabetic retinopathy, retinal vascular occlusions, sickle cell retinopathy, as well as infectious and inflammatory diseases of the retina. Capillary nonperfusion in the macula, or ischemic maculopathy, typically leads to photoreceptor death and irreversible visual impairment [1,2].
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p16-22 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.024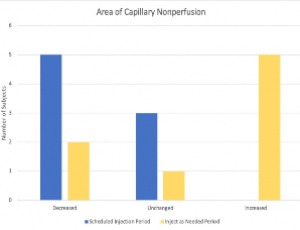
Long-term success in phacoemulsification surgery: what can we learn?
Orezime Mayor Atima, Emeka John Dingwoke
Phacoemulsification has become the gold standard in cataract surgery due to its effectiveness and rapid visual recovery. Understanding the long-term factors influencing surgical success is critical, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p17-20 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.7.039
Acanthamoeba keratitis - is there another perspective: Extrapolations from the Acanthamoeba – fungal keratitis study
Anita Raghavan, Nidhi Bhosale, Shaffie Baidwal, Prathyusha Bellamkonda, Kavitha N, Prabhu Vijayaraghavan, Narendran Venkatapathy, Ram Rammohan
Identified only in 1974 as an etiological agent of keratitis [1] and occurring primarily in contact lens wearers, Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK) occupies a unique niche in microbial keratitis because of its propensity to be misdiagnosed, the paucity of therapeutic options, as well as its recalcitrance to standard medical therapy. Moreover, the tendency of the organism to form cysts under adverse circumstances (that are resistant to amebicides and extremes of temperature) makes eradication of the infection very challenging.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p17-21 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.010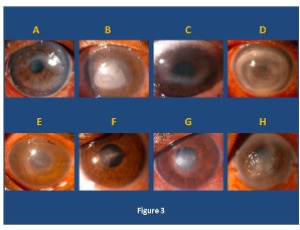
Non-human primate models and multimodal technologies synergistically drive translational breakthroughs in gene therapy for optic nerve diseases
Jian Wu
This commentary systematically examines the pivotal role of non-human primate (NHP) models in advancing gene therapy for optic nerve diseases, alongside the ethical and practical challenges they face. It highlights how synergistic innovations in artificial intelligence (AI), organoid technology, CRISPR-based gene editing, and novel delivery systems are reshaping translational paradigms.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p21-24 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.7.040
Involvement of TGFβ signaling pathway in oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy
Reanna Rodriguez, Kristine Lowe, Megan Keniry, Andrew Tsin
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of blindness in the U.S. However, not much is known of underlying molecular mechanism and how oxidative stress contributes to its development. In the present study, we investigated the involvement of TGFβ signaling pathway on the effect of oxidative stress on VEGF secretion and viability of retinal cells. VEGF is the hallmark that exacerbates DR progression in prolonged diabetes. Some major concerns that have arisen are the underlying effects of antioxidants in elevating VEGF secretion in diabetes.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p23-28 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.025
Complement C5 inhibition in acute AQP4-IgG NMOSD attacks: A review of the rationale and clinical evidence
José M. Valdés, Juan P. Mansilla, Tamara Santibañez, Lorna Galleguillos
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) with aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G positivity (AQP4-IgG) is a severe autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS) characterized by inflammatory attacks targeting the optic nerves and spinal cord. Pathologically, these attacks are driven by the binding of pathogenic AQP4-IgG to astrocytes, which triggers a potent, complement-dependent cytotoxicity.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p25-29 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.7.041
The effect of brimonidine tartrate 0.025% on palpebral fissure height: A randomized controlled trial
Sasha Hubschman, Jackie Laplant, Yuval Peleg, Alexandra Levitt, Oded Ohana, Apostolos Anagnostopoulos, Elizabeth Vanner, Wendy Lee
Upper eyelid height is primarily determined by the actions of the levator palpebrae superioris and Muller’s muscle. Muller’s muscle, a smooth muscle with a predominance of α-1D adrenergic receptors, contracts in response to sympathetic stimulation or adrenergic agonists. Compounds such as apraclonidine, a medication with mixed α and α-1 receptor agonist properties, have been shown to reverse ptosis caused by Horner’s syndrome and botulinum toxin-induced ptosis, and to help assess blepharoptosis preoperatively.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p29-34 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.026
Epidemiology of United States ocular injuries at home in preschool age children from 2000-2019
Parth S Patel, Aditya Uppuluri, Marco A. Zarbin, Neelakshi Bhagat
Injuries to the eye are a common cause of emergency department (ED) visits in the pediatric age group. There were nearly 14 million ED visits for traumatic injuries in children under age 5 in 2017 in the US, and most of these occurred at a private residence [1]. The highest number of pediatric ED visits for ocular injury were reported in children ages 1-5.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p35-38 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.027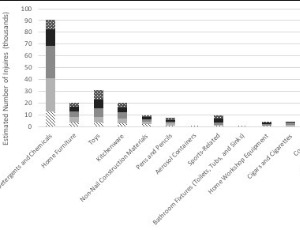
Long Term Follow-Up of Tocilizumab in Refractory and Non-Infectious Uveitic Cystoid Macular Edema
Nuria Vegas-Revenga, José Luis Martín-Varillas, Vanesa Calvo-Río, Marina Mesquida, Alfredo Adán, David Díaz-Valle, Luis F Linares, Rosalía Pablo- Demetrio, Elena Aurrecoechea, José L. Hernández, Miguel A. González-Gay, Ricardo Blanco
Uveitis includes a large spectrum of inflammatory disorders characterized by intraocular inflammation. Most uveitis may complicate with cystoid macular edema (CME) and permanent blindness. CME is a swelling of the macula with fluid accumulation within the intracellular spaces of the retina, leading to the formation of cystic spaces [1]. According to anatomical location, panuveitis (36%-66%) and intermediate uveitis (40%- 60%) are the patterns most commonly associated with CME [2]. The immune mediated systemic diseases most related to CME are sarcoidosis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), Birdshot chorioretinopathy and Behçet disease [3-9].
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p35-43 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.011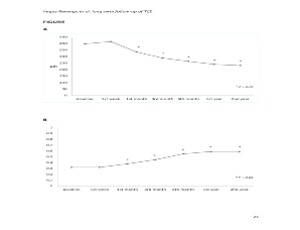
Artisan and artiflex phakic intraocular lenses for high ametropia: long-term results
Sergio Kwitko, Gabriela Maria Zambon, Samara Barbara Marafon
Phakic intraocular lenses have been available as an option for the treatment of refractive errors in eyes whose corneal surgical procedures such as photorefractive keratectomy (PRK), laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) or small incision lenticule extraction (Smile) are formally contraindicated or unacceptable [1-3].
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p39-46 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.3.028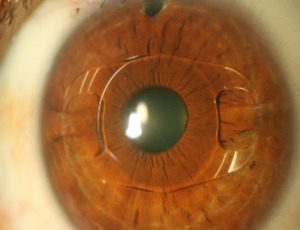
Long-term outcome of open globe injuries: a 3-year follow-up
Tian Xia, Tony Y. Chen, Aditya Uppuluri, Neelakshi Bhagat
Ocular trauma is one of the leading causes of visual impairment in adults [1]. The incidence of open globe injury (OGI) worldwide is between 2 to 6 cases per 100,000 people per year [2,3]. Visual outcomes range from 20/20 to no light perception.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p44-51 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.012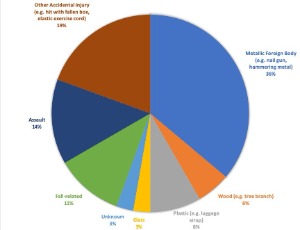
Pterygium excision with conjunctival autograft using Tisseel glue; 6-year outcomes from a UK tertiary referral corneal unit
Shokufeh Tavassoli, Rhys Harrison, Kieren Darcy, Derek Tole
Pterygia are a fibrovascular growth of the bulbar conjunctiva, with the potential to extend onto the cornea [1]. The prevalence can vary from 1-15% depending on patient geographic location, with risk factors including ageing and exposure to UV light [1]. Surgical excision is typically indicated if there is irritation, inflammation, reduced vision, encroachment of the visual axis, increasing astigmatism or due to cosmesis [2].
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p60-66 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.013
Observations on nascent matrix structures in embryonic cornea: Important in cell interactions, or merely vestiges of the lens surface?
Robert D. Young, Carlo Knupp, Elena Koudouna, James R. Ralphs, Yanhui Ma, Peter Y. Lwigale, James V. Jester, Andrew J. Quantock
Here we present some new observations on early stages in chick corneal development obtained by re-mining of datasets obtained via serial block face scanning electron microscopy. We focus on matrix cords, proteoglycan-rich structures of apparent ectodermal origin, emerging from the epithelial basal lamina, which extend proximally into the growing collagenous matrix destined to become the corneal stroma.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p67-72 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.014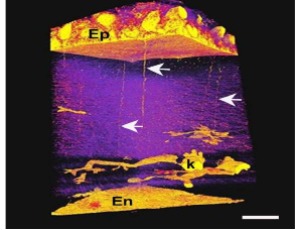
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Recent advances on visual cycle protein research and progress on clinical translation
Xin Yee Ooi, Rujman Khan, Anjalee Choudhury, Francisco Xavier Elisarraras, Jeff Grigsby, Brandi Obregon, Andrew Tsin
Since the publication of our previous paper, Visual cycle proteins: Structure, function, and roles in human retinal disease (Tsin, et.al, JBC 293:13016, 2018) there has been significant progress on multiple topics discussed in this paper. In the present communication, we further explore research advances on two visual cycle proteins: DES1 and IRBP.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p73-76 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.017
Conjunctival lymphangiectasia in the setting of cavernous sinus thrombosis
Gina Shetty, Praneetha Thulasi
We present a unique case of cavernous sinus thrombosis as a likely etiology of conjunctival lymphangiectasia, with resolution of symptoms with anticoagulation. A 58-year-old male presented with 6-months of chemosis and conjunctival lymphangiectasia. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a right cavernous sinus and superior ophthalmic vein filling defect, consistent with thrombosis.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p77-79 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.018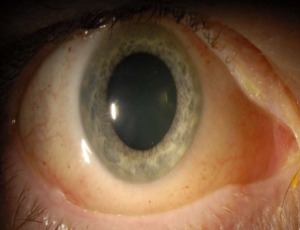
Congenital cavitary optic disc anomaly in Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome
Elliot S. Crane, Neelakshi Bhagat
Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome (WHS, OMIM 194190) is a rare congenital malformation syndrome caused by a partial deletion of the short arm (p) of chromosome 4. It is characterized by “Greek warrior helmet” facies, central nervous system disorders including seizures and structural defects, and intrauterine growth restriction, among numerous other systemic anomalies.
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p80-82 | DOI: 10.46439/ophthalmology.2.019
