Loading
International Journal of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Diseases
ISSN: 2768-5640
All Articles
Omecamtiv mecarbil for heart failure: Unpacking the latest systematic review and meta-analysis
Ramzi Ibrahim
In February 2023, a systematic review and meta-analysis of six randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with a total of 9,596 patients assessed the effectiveness and safety of omecamtiv mecarbil (OM) versus placebo in patients with heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (HFrEF) [1].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-2 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.4.028
Coronary artery fistulae in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Luke Miller, Matthew Shelly, Katelyn Graver, Nicholas Roma, Brett Cohen, Jamshid Shirani
Myocardial ischemia with multifactorial pathogenesis is frequently noted in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Coronary artery fistulas (CAF) may be found in HCM but their contribution to myocardial ischemia has not been studied. From 1984 to 2022, 43 patients with HCM and CAF (age 6–82 years, mean 58; 58% male; 77% apical variant; 12% obstructive) were reported in medical literature. Single and multiple CAF were reported in 24 (56%) and 19 (44%), respectively. Overall, a total of 70 major epicardial coronary arteries were affected.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2026, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.6.032
Mechanisms of cardiovascular injuries in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Ghanshyam Patel, Mario Affinati, Jeffrey Smith, Luqman Baloch, Ammar Aqeel
COVID-19 mainly affects the respiratory system; however, cardiovascular complication is not uncommon. Given the high mortality of COVID-19, it is mandatory to understand the pathogenesis and the mechanism of how it attacks the cardiovascular system. Pre-existing cardiovascular diseases have shown higher morbidity and mortality among COVID-19 patients.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.2.017
Investigation of cardiac pacemaker channel HCN4 leads to new therapeutic approaches in the treatment of viral diseases associated with bradycardia/ cardiac arrest
Lena Mücher, Nathalie Strutz-Seebohm, Stefan Peischard, Guiscard Seebohm
Since the end of 2019, we have been in the midst of a global pandemic caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which has caused immense costs for the global health system and has led to the death of many people. Since then, the number of publications dealing with viral diseases has risen sharply and the field of virology has become visible, partly because research into therapies and vaccinations against viral infections is now in the public spotlight.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.3.023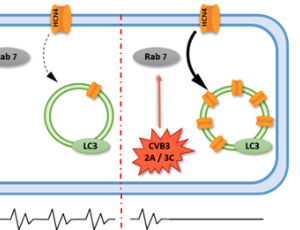
Studies of NT-proBNP testing in the emergency department and evaluation of point of care testing for NT-proBNP using the LumiraDx instrument
Morgan Lundgren, David Smekal, Mats Eriksson, Anders Larsson
Presently, more than 10% of patients >70 years of age suffer from heart failure (HF). As the older population increases in numbers and also as a share of the total population, the prevalence of HF will increase [1,2]. Untreated, approximately 60-70% of these patients will die within 5 years [3,4].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.5.029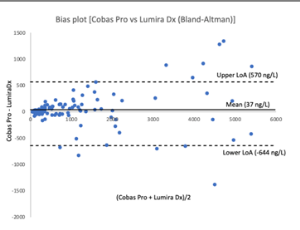
High-resolution 3D fluorescent imaging of intact tissues
Danny El-Nachef, Amy M. Martinson, Xiulan Yang, Charles E. Murry, W. Robb MacLellan
Histological analysis of fluorescently labeled tissues has been a critical tool to understand molecular organization in situ. However, assessing molecular structures within large cells and in the context of human organ anatomy has been challenging because it requires penetration of staining reagents and light deep into opaque tissues, while also conforming to the spatial constraints of high-resolution objective lenses.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-14 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.001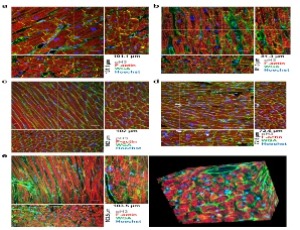
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Shared care left ventricular assist device site to implant center: the next step in advanced heart failure treatment and an essential part of healthcare worldwide
Michael Sobieraj, Pamela Fazio DO, Ricardo Chia MD, Kulpreet Barn MD
Heart failure is a growing pandemic affecting approximately 6.2 million people in the US and 15 million people worldwide. Given its prevalence, high morbidity and mortality, and financial burden on our healthcare system, establishing strategies focused on improving therapeutic outcomes and prognosis has become a major priority.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p6-8 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.2.018
Revealing the link: Cardiac complications in infectious diseases
Chaitenya Verma, Anuradha Tyagi, Vinay Kumar
Cardiovascular disease, also known as heart disease, encompasses a class of medical conditions that affect the heart or blood vessels [1,2]. Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, and it encompasses various disorders and conditions [3-5]. The recognition of the involvement of the heart in many diseases has been established for several decades.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p6-8 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.3.024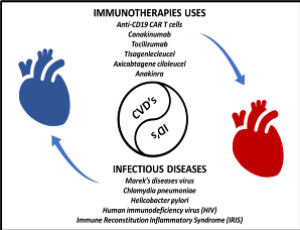
Should the cardiac heart valve prosthesis type choice also consider the valve size at the intraoperatively? Commentary on recent researches about sequential valve-in-valve
Caio Cesar Cardoso
Nowadays, there are two heart valve prosthesis types available: mechanical or biological. Apart from the long-term durability of mechanical heart valves, there are considerable advantages of bioprothesis, specifically regarding biocompatibility and the abdication of oral anticoagulation by warfarin, with the respective drawbacks and risks. A practical proof of this is that is estimated in the United States, between 2007 and 2011, 63.6% of prosthetic valve devices were made of bovine pericardium (an increase of 100% compared to the period from 1998 to 2001) [1,2].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p6-8 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.5.29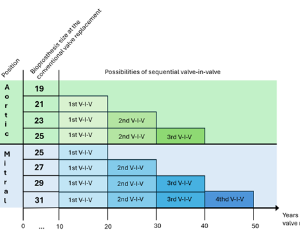
Calcium modification in coronary arteries
Vinoda Sharma
Coronary artery calcification is an independent cardiovascular risk factor, influenced by patient demographics and older age [1-3]. Optimal stent expansion is limited by poorly modified calcified coronary lesions resulting in increased risk of in-stent restenosis and stent thrombosis [4].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p9-13 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.2.019
SGLT2 inhibitors: A review article
Biswajit Majumder
In the beginning, SGLT2 inhibitors were regarded as anti-diabetic agents. But after demonstration of the cardiovascular benefit of SGLT2 inhibitors in EMPAREG-OUTCOME trial, a whole new era of heart failure therapy opened up. It became an integral part of heart failure treatment protocol.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p9-14 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.3.025
Prophylactic use of ACEIs, ARBs and BBs in anthracycline and trastuzumab induced cardiotoxicity in adult cancer patients: A systematic review
Sumana Kundu, Maryam Farhan Baloch, Josephine Ria Pitasari, Bijay Mukesh Jeswani, Yashvi Pethani, Sukhmandeep Singh Benipal, Abhishek Prasad
Cancer therapy related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD) poses a significant challenge to the treatment of cancer patients receiving cardiotoxic chemotherapeutic regimen like anthracyclines and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) inhibitors like trastuzumab. This systematic review evaluated the efficacy and safety of conventional heart failure medications—angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), and beta-blockers (BBs)—in preventing CTRCD in adults undergoing such therapies.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p9-19 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.5.030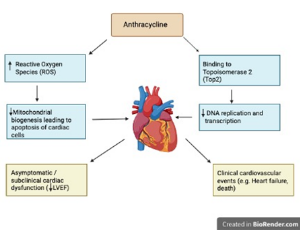
Bridging the cardiac care gap in sub-Saharan Africa: from short-term medical missions to sustainable solutions
Vibhu R. Kshettry MD, Muralidhar Kanchi MD, Dawn R. Witt PhD, MPH, Devi P. Shetty MD
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are one of the leading causes of mortality in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA); however, access to sustainable cardiac care remains limited. The reliance on short-term medical mission-based interventions has not addressed the critical workforce and infrastructure gaps in the region.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2026, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p11-16 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.6.034
Fumarate hydratase as a potential target to ameliorate salt sensitive hypertension
Xuewei Zheng, Zhongmin Tian
Salt sensitive hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke, heart failure, and end-stage renal disease [1]. The development of salt sensitive hypertension is involved in genetic and environmental factors. Excessive dietary salt intake is known as a main risk factor and one of the most important environmental determinants, exacerbates the salt sensitive hypertension by a renal redox metabolism [2,3].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p14-16 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.2.020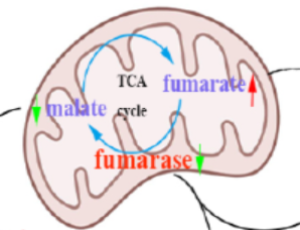
Therapeutic antibody approach for pulmonary arterial hypertension
Cheng Zhang, Shuqian Jing
GMA301 is a novel antagonistic antibody in clinical development. GMA301 targets human endothelin receptor A (ETA), a proven therapeutic target for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p15-19 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.002
Diagnosis of hyperprolactinemia by single serum prolactin determination: Challenges and recommendations
Madhumita Das
Secretion of prolactin follows a circadian rhythm of secretion, and several factors play an important role in the regulation of its secretion. An accurate diagnostic evaluation is essential for the proper management of the patient, which can be accomplished through a narrow observation and critical analysis of all the prolactin results which are above the standard upper limit of normal.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p15-22 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.3.026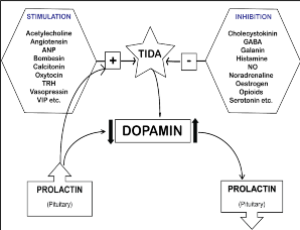
Level of adherence to lifestyle modifications and associated factors among hypertensive patients attending outpatient department at Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia Region, Ethiopia, 2022
Girma Mideksa, Samrawit Solomon, Temesgen Geleta
Hypertension is one of the major important risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. It is the largest cause of death worldwide, accounting for 10.8 million deaths per year [1,2]. Globally, 1.39 billion people had hypertension, and one-third of adults have the condition.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p17-27 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.2.021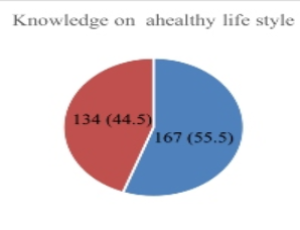
A commentary on "A grand plan for health equity: Philosophy of health equity"
Wei-Ching Chang
In his renowned song "Imagine," John Lennon famously sang about a world where all people live in peace and harmony. As a researcher focused on health outcomes, particularly cardiovascular health, I have a similar dream for "health equity"—the idea that everyone should have access to good health.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2025, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p20-22 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.5.031
Risk of aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in cardiovascular care
G. Aernout Somsen, Daniel Bonn
The ongoing global Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID19) pandemic has enormous social and economic impact. COVID19 is caused by the Coronavirus Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and is characterized by a high transmission rate and increased mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome compared to other viruses.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p20-23 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.003
Myocardial work by 2 echocardiogram in different pathologies
María E Sánchez, Mercedes Panno, Silvia Urrutia, Cecilia Villa Etchegoyen, Juliana Iglesias, Anabel Gafni
Left ventricular performance has traditionally been evaluated by calculating ejection fraction (LVEF), however, the estimation of this by two-dimensional echocardiogram is subject to several limitations. On the other hand, speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE) with global longitudinal deformation (GLS) is increasingly used to assess even subtle myocardial dysfunction, although it is a well-validated method for clinical utility in the assessment of cardiac diseases, it remains limited by its load dependency [1,2].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2023, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p23-28 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.3.027
A twin herbal formula has gained sufficient clinical and laboratory evidences to be accepted as an effective cardio-vascular protective supplement
Woo KS, KWOK Chi-Yui Timothy, Yan Ping Yen Bryan, Leung Ping-Chung
A two herbs formula has been successfully used as a cardiovascular supplement (tonic) to maintain a healthy vascular endothelial state in four groups of patients presenting with different symptom manifestations: coronary obstruction; hypertension; menopausal cardiovascular instability; and peripheral arterial disease.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p24-30 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.004
Commentary on implantation of the Micra transcatheter pacing system: A single center North India experience
Rajendra Kumar Agarwal MD
Transvenous pacemakers (TVPs) using pectoral pulse generators and transvenous leads are a well-established treatment for bradyarrhythmias and have served us well for 6 decades [1]. However, implantation of these pacemaker devices are not devoid of substantial complications.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2022, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p28-30 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.2.022
Retrospective evaluation of heart failure verification and relation to readmission and all-cause mortality in a community-based cohort
Steven J. Lavine, Ghulam Murtaza, Danielle Kelvas, Timir K Paul, Zia Ur Rahman
The use of administrative databases to determine predictors for heart failure (HF) readmission, cardiovascular, or all-cause mortality (ACM) requires HF coding that is verifiable. It is assumed that administrative databases have HF verified via coders based on physician documentation and additional criteria.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p31-40 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.005
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Mechanisms of troponin release into serum in cardiac injury associated with COVID-19 patients
R. John Solaro, Paola C. Rosas, Paulina Langa, Chad M. Warren, Beata M. Wolska, Paul H. Goldspink
In the early phases of the pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) the emphasis of diagnosis and treatment was on acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p41-47 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.006
An incarcerated diaphragmatic hernia presenting as acute chest pain and transient left bundle branch block: A case report
Usama AL-Khalasi, Masoud S. Kashoub, Hatim Al Lawati
Hiatal hernia is not an uncommon condition. Due to inconsistent definition in the literature, the reported prevalence varies widely between 15- 50%. The condition is symptomatic in only 9% of the cases, especially with advancing age [1].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p41-47 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.007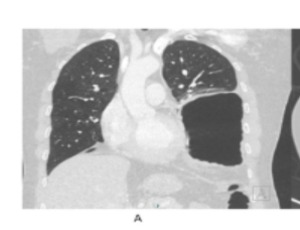
Review of delayed sternal closure after congenital heart surgery
Prashant Jha, Mukul Sehgal, Sandeep Arya, Cathy S. Woodward
Since introduced for the first time in 1975 by Riahi et al, delayed sternal closure (DSC) remains a commonly utilized strategy in congenital heart surgery (CHS) for patients with anticipated hemodynamic instability based upon complexity of the performed procedure or in patients who exhibit instability during surgery [1].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p52-53 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.008
Predicting functional outcomes among CAD who complete cardiac rehabilitation
Stephanie Gerlach, Christine Mermier, Len Kravitz, Lance Dalleck, Micah Zuhl
With over 17 million deaths per year, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of mortality worldwide [1]. For heart disease survivors, rehabilitation is recommended to reduce cardiac mortality risk. Phase two cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is a comprehensive outpatient therapy focused heavily on aerobic exercise.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p57-62 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.009
Arrhythmias in pregnancy: Commentary
Dominique Williams
Cardiovascular disease is a significant contributor to maternal morbidity and mortality worldwide and is the leading cause of adverse pregnancy outcomes in the United States of America, accounting for approximately 25% of maternal deaths from 2008-2017.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p63-65 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.010
The functional importance of the left atrium in patients with coronary slow flow phenomenon
Li Liu, Zhiyuan Shui, Yunzhi Wang
The coronary slow flow phenomenon (CSFP), also known as cardiac syndrome Y, is relatively common in patients scheduled for coronary angiography. The incidence varies from 1% to 5.5% [1-4]. Since its original description by Tambe in 1972 [5], it has garnered intensive attention among interventional cardiologists.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p66-77 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.011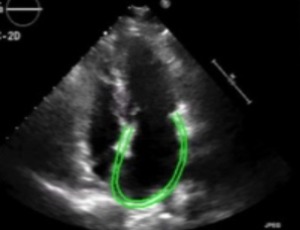
Older women and cardiac rehabilitation: Next steps on the journey
Nanette K. Wenger
Cardiovascular disease, which includes coronary heart disease, hypertension and stroke, is the predominant cause of morbidity and mortality in older women.Cardiac rehabilitation is pivotal in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease, in that it lowers cardiovascular risk and mortality.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p71-75 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.012
Commentary on: Angiographic scoring system for predicting successful percutaneous coronary intervention of uneasy in-stent chronic total occlusion
Yi Mao
As the Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) is prevalent in the recent decades, In-Stent Coronary chronic Total Occlusion (IS-CTO) has become a frequently met lesion in daily PCI procedure. It is estimated IS-CTO PCI accounts for 5-25% of all CTO [1].
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p76-78 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.013
Implications of ATPCI study on trimetazidine use in clinical practice
Jamshed Dalal, Aditya Kapoor
The ATPCI (efficAcy and safety of Trimetazidine in patients with angina pectoris treated by Percutaneous Coronary Intervention) study reported similar primary outcomes between trimetazidine and placebo groups in patients with angina who recently had a percutaneous coronary intervention, but the results of this study reconfirmed the safety of trimetazidine.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p79-82 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.014
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and reperfusion therapy in the COVID-19 pandemic
Daniel A. Gomes, Jorge Ferreira
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has been placing enormous pressure on global healthcare systems. Considerable resource allocation to the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, although fully inevitable, originated remarkable constraints in the access of patients with other diseases – in fact, elective admissions and nonurgent procedures or interventions were mostly canceled or deferred worldwide.
Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p83-85 | DOI: 10.46439/cardiology.1.015